By clicking the “I Accept” button, or by accessing, participating, or submitting any information, or using the Jabil Global Intelligence Portal or any of its associated software, you warrant that you are duly authorized to accept the Global Intelligence Portal Terms and Conditions on behalf of your Company, intending to be legally bound hereby, and your company shall be bound by the terms and provisions of the Global Intelligence Portal Terms and Conditions, accessible under the following link Portal T&Cs.
Jabil's Global Category Intelligence Archive
Global Category Intelligence
Q3 2023
Jabil's Global Category Intelligence Archive
Global Category Intelligence
Q3 2023
CAPEX, MRO, INFRASTRUCTURE
AUTOMATION
Market Overview
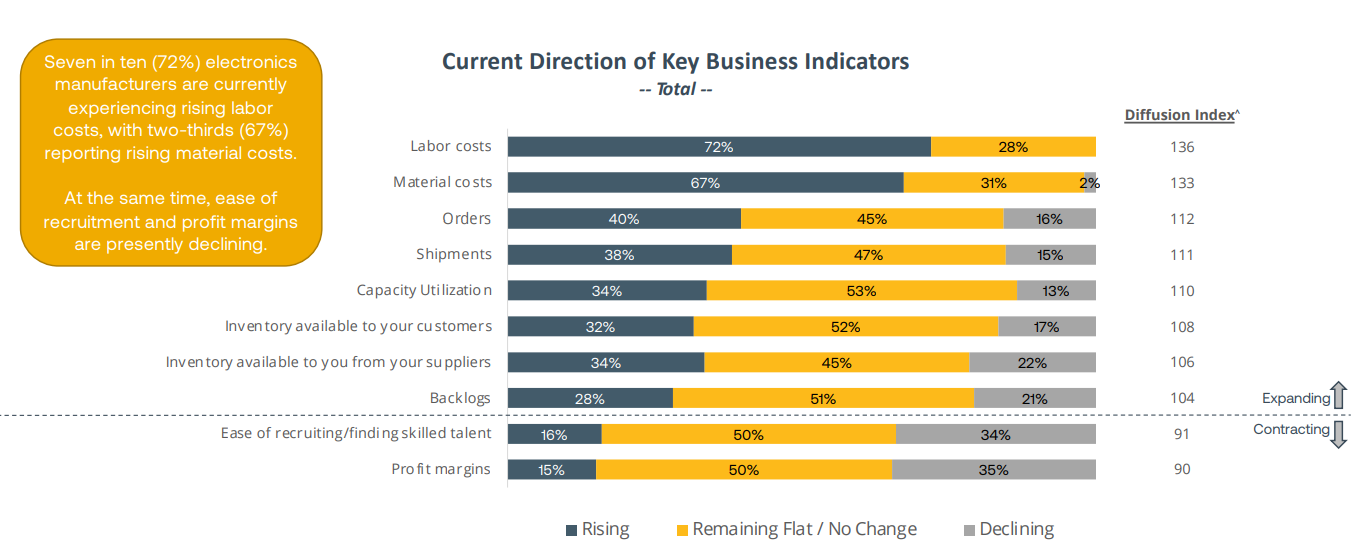
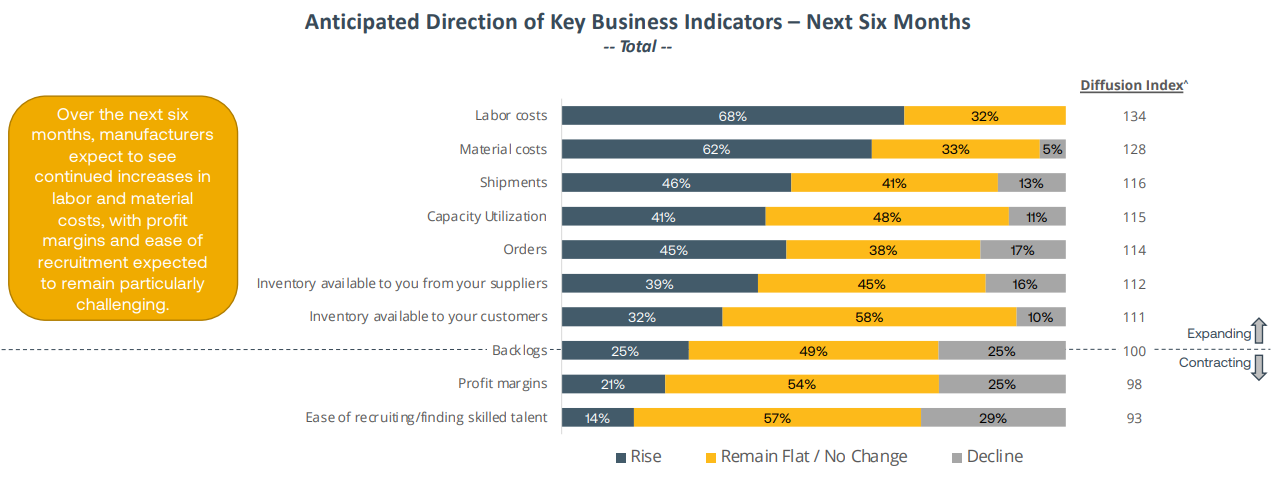
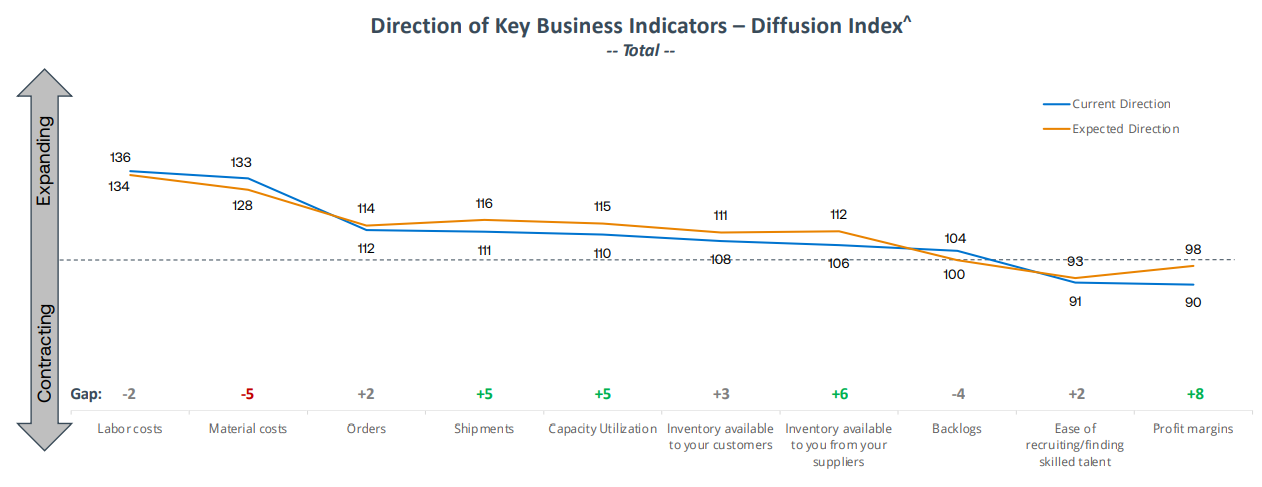
- The automotive industry is a front-runner in automation with operational robot stock reaching a new record of around one million units.
- India entered the world´s top ten in annual robot installations with installations growing rapidly.
- Global commodity prices were reduced due to restrictive monetary policy.
- Lead times have improved for most automation parts; however, some remain constrained due to IC component shortages.
Demand Commentary
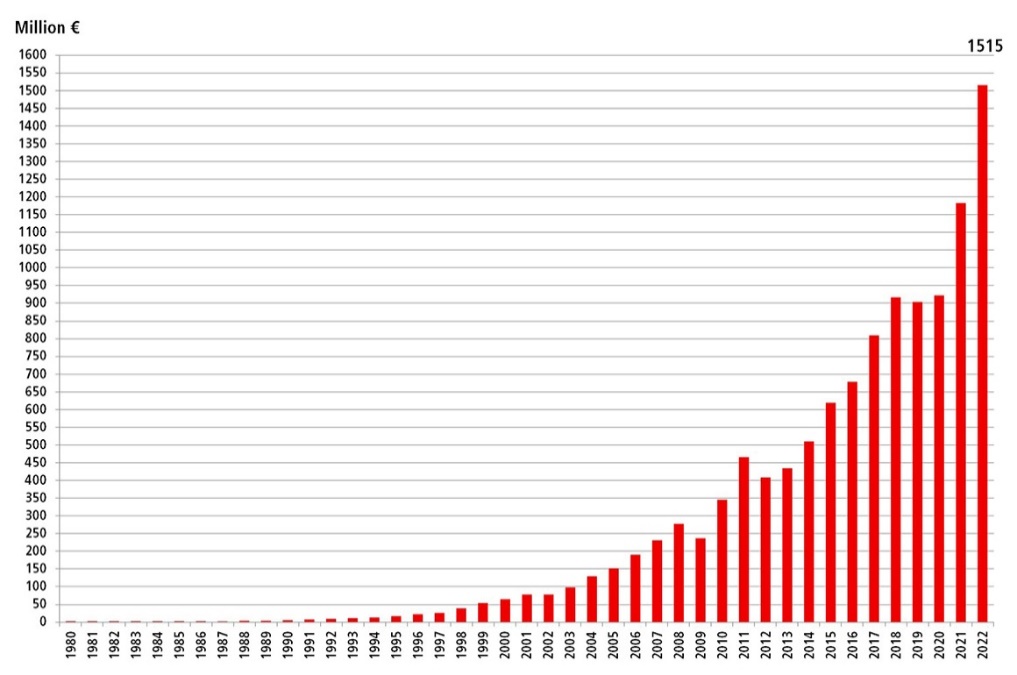
- One Million Robots Work in Car Industry Worldwide – New Record
- 2022 global sales: €1.515 billion (+28%)
- The automotive industry has the largest volume of robots working in factories around the world.
- The operational stock hit a new record of about one million units. This represents about one-third of the total number installed across all industries.
- Robot density is a key indicator that illustrates the current level of automation in the top car-producing economies.
- In the Republic of Korea, 2,867 industrial robots per 10,000 employees were in operation in 2021.
- Germany ranks in second place with 1,500 units followed by the United States counting 1,457 units and Japan with 1,422 units per 10,000 workers.The world´s largest car manufacturer, China, has a robot density of 772 units but is catching up fast.
- Within a year, new robot installations in the Chinese automotive industry almost doubled to 61,598 units in 2021- accounting for 52% of the total 119,405 units installed in factories globally.
- Ambitious political targets for electric vehicles are forcing the car industry to invest.
- The European Union has announced plans to end the sale of air-polluting vehicles by 2035.
- The US government aims to reach a voluntary goal of 50% market share for electric vehicle sales by 2030 and all new vehicles sold in China must be powered by “new energy” by 2035.
- Half of them must be electric, fuel cell, or plug-in hybrid – the remaining 50%, are hybrid vehicles.
- Most automotive manufacturers who have already invested in traditional “caged” industrial robots for basic assembling are now also investing in collaborative applications for final assembly and finishing tasks.
- Tier-two automotive parts suppliers, many of which are SMEs, are slower to automate fully. Yet, as robots become smaller, more adaptable, easier to program, and less capital-intensive this is expected to change.
- India´s Robot Boom Hits All-Time High
- India enters the world´s top ten in annual robot installations: Sales of industrial robots in India reached a new record of 4,945 units installed. This is an increase of 54 percent compared to 2020: 3,215 units.
- In terms of annual installations, India now ranks in the tenth position worldwide. India is one of the world's fastest-growing industrial economies, within five years, the operational stock of industrial robots has more than doubled, to reach 33,220 units in 2021.
- This corresponds to an average annual growth rate of 16% since 2016.” And this trend is expected to continue for 2023 and beyond.
- Today, India is the world’s fifth-largest economy measured by manufacturing output.
- According to World Bank data, India´s manufacturing value added in 2021 was USD 443.9 billion, a 21.6% increase from 2020.
- India’s GPD growth rate was robust and reached 6.9% in 2022 and the forecast number is 6.4% for 2023.
- The automotive industry remains the largest customer for the robotics industry in India with a share of 31% in 2021. Installations more than doubled to 1,547 units (+108%).
- The general industry in India is led by the metal industry with 308 units (-9%), the rubber and plastics industry with 246 units (+27%), and the electrical/electronics industry with 215 units (+98%).
- Impressive potential for India: The long-term potential of robotics in India becomes clearer when compared to China: India´s robot density in the automotive industry, which is the number of industrial robots per 10,000 employees, reached 148 robots in 2021.
- China´s robot density hit 131 units in 2010 and skyrocketed to 772 units in 2021. The Indian government supports growth in the industrial sector as one of the vital figures that affect the Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
- Today, the country´s GDP of about USD 3 trillion ranks in fifth place, head-to-head with the UK and France – behind Germany, Japan, China, and the USA - the International Monetary Fund reports.
- Outlook for India: As a result of the recent supply chain disruption, companies are rethinking their nearshoring strategies in Southeast Asia. India has traditionally been a popular destination for nearshoring in the manufacturing segment.
- The Indian government wants the country to be considered for new diversification options such as friend-shoring, which is partnering with countries that share similar values and interests.
- The manufacturing sector is also expected to benefit from the government's initiatives to boost its competitiveness and attractiveness for investors.
- The Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme, for example, currently set to run until 2025, subsidizes companies that create production capacity in India in robot customer industries like automotive, metal, pharmaceuticals, and food processing.
- Robots help to create new jobs: new manufacturing capacities in India are an important step to providing adequate education and employment opportunities for its people: According to projections of the United Nations, India now has a population of 1,4 billion, surpassing China for the first time.
- This means that India has a large and young workforce that can drive economic growth and innovation. India is expected to have the largest working-age population in the world by 2027.
Supply Commentary
- Global automation supply is back to normal gradually as the backlog clears up and manufacturing capacity resumes.
- Robot Lead time is from 6 weeks to 12 weeks, but IPC/Safety module lead time remains long due to IC chip shortage.
Supplier Spotlight - Beckoff
- Beckhoff Automation at a glance:
- 2022 global sales: €1.515 billion (+28%)
- Headquarters: Verl, Germany
- Managing owner: Hans Beckhoff
- Employees worldwide: 5,680
- Engineers: 2,200
- Subsidiaries/representative offices worldwide: 40
- Sales offices in Germany: 24
- Representatives worldwide: >75
- Beckhoff implements open automation systems using proven PC-based control technology. The main areas that the product range covers are industrial PCs, I/O and Fieldbus components, drive technology, automation software, control cabinet-free automation, and hardware for machine vision.
- Product ranges that can be used as separate components or integrated into a complete and mutually compatible control system are available for all sectors.
- New Automation Technology stands for universal and industry-independent control and automation solutions that are used worldwide in a large variety of different applications, ranging from CNC-controlled machine tools to intelligent building control.
- Since Beckhoff’s foundation in 1980, the development of innovative products and solutions based on PC-based control technology has been the foundation of the company's continued success.
- Beckhoff recognized many standards in automation technology that are taken for granted today at an early stage and successfully introduced to the market as innovations.
- Beckhoff’s philosophy of PC-based control as well as the invention of the Lightbus system and TwinCAT automation software are milestones in automation technology and have proven themselves as powerful alternatives to traditional control technology.
- EtherCAT, the real-time Ethernet solution, provides a powerful and future-oriented technology for a new generation of control concepts.
- Worldwide presence on all continents: The corporate headquarters of Beckhoff Automation GmbH & Co. KG in Verl, Germany, is the site of the central departments such as development, production, administration, sales, marketing, support, and service.
- Beckhoff’s presence in the international market is guaranteed by its subsidiaries. Beckhoff is represented in more than 75 countries by worldwide cooperation partners.
Pricing Situation
- Global commodity prices were reduced due to tightened monetary policy.
- 2022 global sales: €1.515 billion (+28%)
- US Economic activity expanded at a modest pace in the first quarter. Job gains have been robust in recent months, and the unemployment rate has remained low. Inflation remains elevated.
- The U.S. banking system is sound and resilient. Tighter credit conditions for households and businesses are likely to weigh on economic activity, hiring, and inflation. The extent of these effects remains uncertain. FED remains highly attentive to inflation risks.
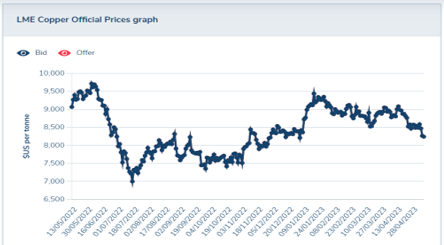
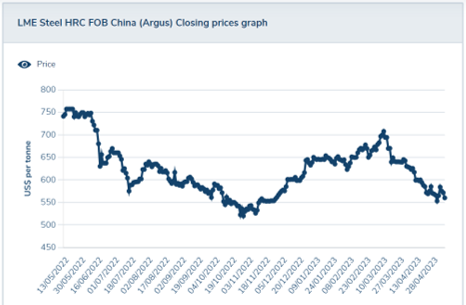
- Steel and copper are primary raw material inputs in many types of automation parts, changes in steel and copper prices can affect prices for automation parts.
- Copper has decreased in price by 10% over the past 12 months
- Copper is estimated to be ~5% of the total robot cost
- Steel has decreased in price by 25% over the past 12 months
- Steel is estimated to be ~10% of the total robot cost
- Automation part price is in a downtrend, because of several reasons:
- The global commodity price is reducing as above analysis.
- Manufacturing capacity is recovering, and the backlog is cleared up.
- Overall demand shrinks due to global economic recession concerns.
Supply Analysis
- The automation industry supply has been gradually improved, the backlog is cleared up and manufacturing capacity increased.
- FANUC/ABB robot lead time improved, from 6 weeks to 12 weeks if out of stock.
- Beckhoff’s lead time improved. But IPC/Safety module lead time is still long mainly due to semiconductor component shortage.
- Geopolitical conflict still posts disruption and increases the uncertainty of the automation supply chain.
Key Takeaways
- The automotive industry is a front-runner in automation, The automotive industry has the largest number of robots working in factories around the world.
- Global commodity prices were reduced due to tightened monetary policy.
- The lead time issue has been improved for most of the automation parts, but some parts are still constrained due to IC component shortage.
- Today, India is the world’s fifth-largest economy measured by manufacturing output.
- According to World Bank data, India´s manufacturing value added in 2021 was USD 443.9 billion, a 21.6% increase from 2020.
- India’s GPD growth rate was robust and reached 6.9% in 2022 and the forecast number is 6.4% for 2023.
- The automotive industry remains the largest customer for the robotics industry in India with a share of 31% in 2021. Installations more than doubled to 1,547 units (+108%).
- The general industry in India is led by the metal industry with 308 units (-9%), the rubber and plastics industry with 246 units (+27%), and the electrical/electronics industry with 215 units (+98%).
- Impressive potential for India: The long-term potential of robotics in India becomes clearer when compared to China: India´s robot density in the automotive industry, which is the number of industrial robots per 10,000 employees, reached 148 robots in 2021.
- China´s robot density hit 131 units in 2010 and skyrocketed to 772 units in 2021. The Indian government supports growth in the industrial sector as one of the vital figures that affect the Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
- Today, the country´s GDP of about USD 3 trillion ranks in fifth place, head-to-head with the UK and France – behind Germany, Japan, China, and the USA - the International Monetary Fund reports.
- Outlook for India: As a result of the recent supply chain disruption, companies are rethinking their nearshoring strategies in Southeast Asia. India has traditionally been a popular destination for nearshoring in the manufacturing segment.
- The Indian government wants the country to be considered for new diversification options such as friend-shoring, which is partnering with countries that share similar values and interests.
- The manufacturing sector is also expected to benefit from the government's initiatives to boost its competitiveness and attractiveness for investors.
- The Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme, for example, currently set to run until 2025, subsidizes companies that create production capacity in India in robot customer industries like automotive, metal, pharmaceuticals, and food processing.
- Robots help to create new jobs: new manufacturing capacities in India are an important step to providing adequate education and employment opportunities for its people: According to projections of the United Nations, India now has a population of 1,4 billion, surpassing China for the first time.
- This means that India has a large and young workforce that can drive economic growth and innovation. India is expected to have the largest working-age population in the world by 2027.
Supply Commentary
- Global automation supply is back to normal gradually as the backlog clears up and manufacturing capacity resumes.
- Robot Lead time is from 6 weeks to 12 weeks, but IPC/Safety module lead time remains long due to IC chip shortage.
Supplier Spotlight - Beckoff
- Beckhoff Automation at a glance:
- 2022 global sales: €1.515 billion (+28%)
- Headquarters: Verl, Germany
- Managing owner: Hans Beckhoff
- Employees worldwide: 5,680
- Engineers: 2,200
- Subsidiaries/representative offices worldwide: 40
- Sales offices in Germany: 24
- Representatives worldwide: >75

- Beckhoff implements open automation systems using proven PC-based control technology. The main areas that the product range covers are industrial PCs, I/O and Fieldbus components, drive technology, automation software, control cabinet-free automation, and hardware for machine vision.
- Product ranges that can be used as separate components or integrated into a complete and mutually compatible control system are available for all sectors.
- New Automation Technology stands for universal and industry-independent control and automation solutions that are used worldwide in a large variety of different applications, ranging from CNC-controlled machine tools to intelligent building control.
- Since Beckhoff’s foundation in 1980, the development of innovative products and solutions based on PC-based control technology has been the foundation of the company's continued success.
- Beckhoff recognized many standards in automation technology that are taken for granted today at an early stage and successfully introduced to the market as innovations.
- Beckhoff’s philosophy of PC-based control as well as the invention of the Lightbus system and TwinCAT automation software are milestones in automation technology and have proven themselves as powerful alternatives to traditional control technology.
- EtherCAT, the real-time Ethernet solution, provides a powerful and future-oriented technology for a new generation of control concepts.
- Worldwide presence on all continents: The corporate headquarters of Beckhoff Automation GmbH & Co. KG in Verl, Germany, is the site of the central departments such as development, production, administration, sales, marketing, support, and service.
- Beckhoff’s presence in the international market is guaranteed by its subsidiaries. Beckhoff is represented in more than 75 countries by worldwide cooperation partners.
Pricing Situation
- Global commodity prices were reduced due to tightened monetary policy.
- 2022 global sales: €1.515 billion (+28%)
- US Economic activity expanded at a modest pace in the first quarter. Job gains have been robust in recent months, and the unemployment rate has remained low. Inflation remains elevated.
- The U.S. banking system is sound and resilient. Tighter credit conditions for households and businesses are likely to weigh on economic activity, hiring, and inflation. The extent of these effects remains uncertain. FED remains highly attentive to inflation risks.
- Steel and copper are primary raw material inputs in many types of automation parts, changes in steel and copper prices can affect prices for automation parts.
- Copper has decreased in price by 10% over the past 12 months
- Copper is estimated to be ~5% of the total robot cost

- Steel has decreased in price by 25% over the past 12 months
- Steel is estimated to be ~10% of the total robot cost

- Automation part price is in a downtrend, because of several reasons:
- The global commodity price is reducing as above analysis.
- Manufacturing capacity is recovering, and the backlog is cleared up.
- Overall demand shrinks due to global economic recession concerns.
Supply Analysis
- The automation industry supply has been gradually improved, the backlog is cleared up and manufacturing capacity increased.
- FANUC/ABB robot lead time improved, from 6 weeks to 12 weeks if out of stock.
- Beckhoff’s lead time improved. But IPC/Safety module lead time is still long mainly due to semiconductor component shortage.
- Geopolitical conflict still posts disruption and increases the uncertainty of the automation supply chain.
Key Takeaways
- The automotive industry is a front-runner in automation, The automotive industry has the largest number of robots working in factories around the world.
- Global commodity prices were reduced due to tightened monetary policy.
- The lead time issue has been improved for most of the automation parts, but some parts are still constrained due to IC component shortage.
WAREHOUSE AUTOMATION
Market Overview
- Regardless of the type of warehouse and type of material being handled (raw material, semi-finished goods, finished goods, etc.) industry warehouses usually are divided as defined below. These are in line with main warehouse activities as well:
- 2022 global sales: €1.515 billion (+28%)
- Receiving
- Storage (racking system, shelves, special storage systems, etc.)
- Order picking (preparation/ piece picking, consolidation areas, etc.)
- Shipping
- Majority of the activities are linked to order picking-related processes, but it is eye-opening that 75% of these activities are non-value add types of activities. This area is the most labor-intensive part of warehousing and therefore, ideal for automation.
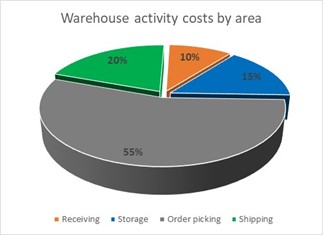
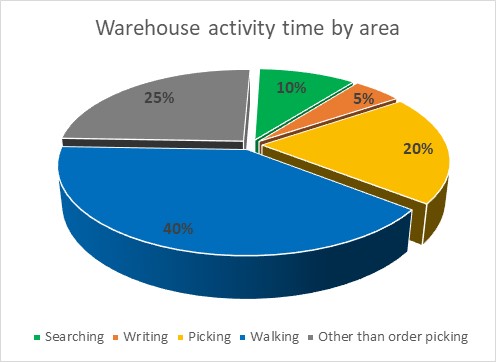
- COVID-19 impacted warehousing activities in several different ways, worldwide:
- Delays in transportation increased the need for more storage space and high-level inventory management,
- Regardless of the type of warehouse and type of material being handled (raw material, semi-finished goods, finished goods, etc.) industry warehouses usually are divided as defined below. These are in line with main warehouse activities as well:
- E-commerce growth created a need for more efficient warehousing and logistics solutions,
- Personnel shortages generated new demand for processes with less human assistance.
- Due to these factors, warehousing became a key asset class in the real estate sector and continues to drive its growth in the market.
- Warehouse stock and operations are largely manual–approximately 80% of warehouses are still operated without automated solutions. In prior years we could see more activity related to automation within this segment.
- Market and service providers are challenged due to different root causes:
- Transforming manual warehouses into automated fulfillment operations, and
- Implementing new, fully, or semi-automated systems when new warehouses are ramped up.
- Both prove vital to meeting customer demand at scale while managing operating costs in the future.
DEMAND COMMENTARY
- Currently available technologies can ensure almost complete end-to-end automation of order fulfillment processes. Improvements in robot technology are rapidly filling in the remaining gaps.
- To deliver efficient warehouse automation, both information technology and equipment/machinery areas should receive equal and simultaneous focus and investment.
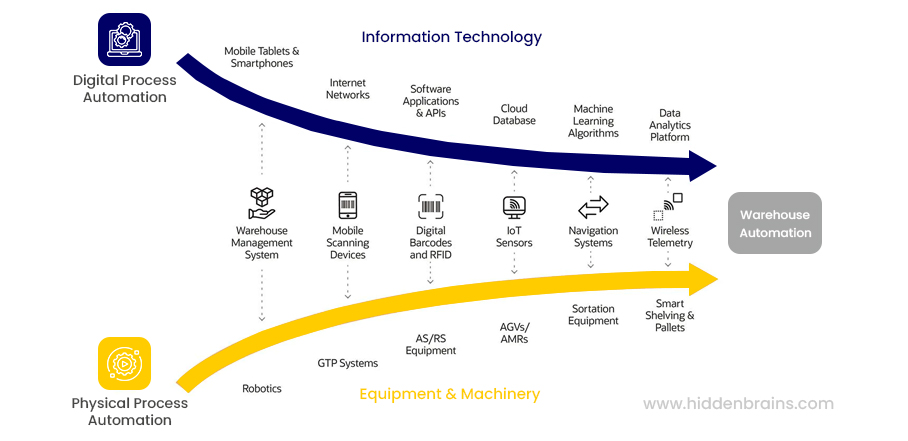
- Main segments of automation:
- Software:
- Warehouse Management System (WMS)
- Hardware:
- Warehouse Management System (WMS)
- Warehouse Management System (WMS)
- Automatic Identification and Data Capture (AIDC)
- Conveyors, Sorting, and Overhead Systems
- Autonomous Guided Vehicles (AGVs, AMRs)
- Piece Picking systems
- Automated Storage and Retrieval System (AS/RS) or Pallet Rack
- Miniload systems
- Palletizing/Depalletizing System
- Demand in this market is driven by increased requirements for efficient material movement (AGV/AMR) as an easy win from an implementation and investment point of view. Core warehouses are motivated by low ROI and the ability to reduce labor costs (repetitive physical work and manual data entry and analysis) as there is constant pressure on costs.
- Another key area for this segment is automated storage and retrieval systems, regardless of whether new or existing warehouses, as this investment improves operational effectiveness and improves order fulfillment accuracy at the same time.
- The global warehouse automation systems market was valued at $14 billion in 2022, and is projected to reach $30 billion by 2028, however, there is various and different increases on different segments of automation:
- ASRS and Packing segments are considered mature segments recording the lowest vendor growth (sub 3% CAGR-Cumulative Average Growth Rate)
- Picking robotics vendors’ growth is higher, moving around 25% CAGR
- AGV/AMR represents a solid market with its 11,6% CAGR
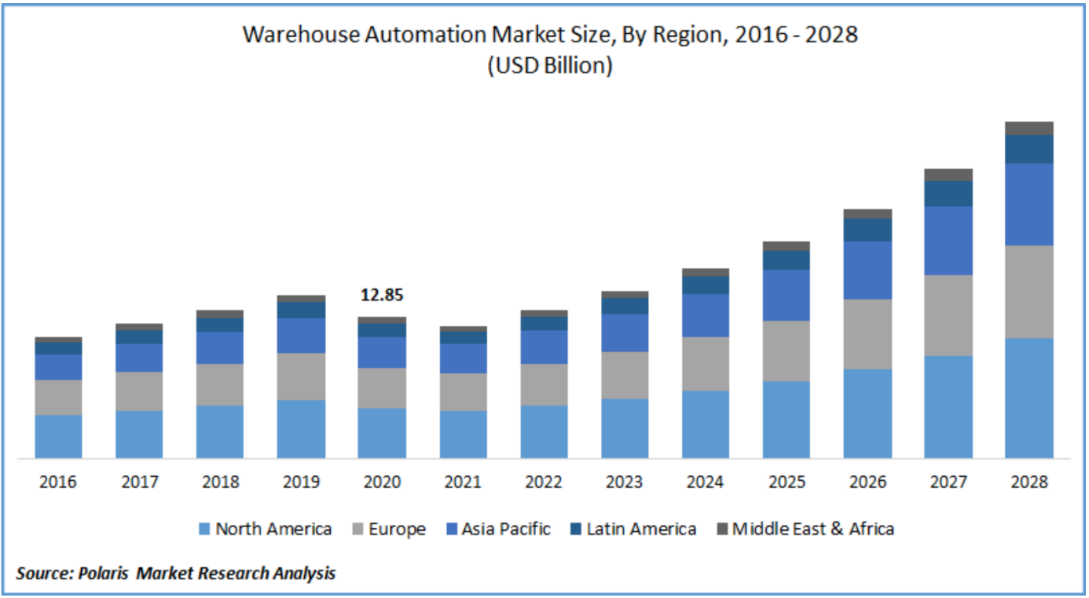
- APAC with China, Vietnam, and Malaysia are experiencing increasing investments. Automation solutions are being offered by regional suppliers, so installation and maintenance are fully covered at low cost.
- This market is expanding significantly due to the increasing number of industries in the region.
- Prices will likely maintain on the lower end due to a special program introduced by the Chinese government which helps the country take a leading position within the warehouse automation sector
- Europe, Mexico, and the USA are experiencing more moderate growth. Globally recognized suppliers specializing in logistics and warehouse systems are active, but pricing is high.
- Canada and South American countries are taking smaller steps on the automation journey.
Supply Commentary
- As of today, over 700 companies are operating in the warehouse automation space worldwide. It is challenging to select the right partners to work with covering more specific areas:
- 200+ on AGV/AMR
- 90+ on Material handling solutions
- 80+ on ASRS
- 50+ on WMS
- 20+ on Micro fulfillment
- 20+ on Piece Picking robots
- 10+ Warehouse drones
- 10+ on Automated truck loading
- The supply base is diversified, but key partners who can cover all hardware-related requirements are limited. Dominant players in the space are offering end-to-end solutions, but we are also observing more regional, and less global coverage.
- Key global players in this market are:
- Dematic Group (Kion Group)
- Daifuku Co. Limited
- Swisslog Holding AG,
- Honeywell Intelligrated,
- Knapp AG,
- Kardex Group
- Mecalux SA
- SSI Schaefer AG
- Vanderlande Industries BV
- Jungheinrich AG
- Beumer Group GmbH
- Daifuku Manufacturing Technology Co., Ltd.
- Global automation supply is back to normal gradually as the backlog clears up and manufacturing capacity resumes.
- Robot Lead time is from 6 weeks to 12 weeks, but IPC/Safety module lead time remains long due to IC chip shortage.
- The market is characterized by fragmentation and consolidation will continue.
- Unpredictable demand and a lack of transparency and collaboration with the supply chain present a significant barrier to fulfilling business goals for many manufacturers.
- Because some of the raw materials required by manufacturers are difficult to source the lead time of different automation solutions is long—for example, AS/RS and Autostore solutions move around 12-15 months.
Pricing situation
- Negotiation power varies by region. In APAC, power resides on the buyer’s side: not only on price but in securing beneficial payment terms as well. In EMEA and the Americas, buyers’ ability to control prices, terms, or payment conditions is weak, but strengthening, slightly, over the past few months.
- Suppliers are more open-minded to combined payment conditions and are accepting long-term closed-end lease (3 or 5 years) solutions, replacing 1-time investments. As a result, cash flow management is improving on the investors’ side.
- ROI for a high-volume operations warehouse is typically between 18-48 months, but it depends on selected solutions and the complexity of the manual warehouse being transformed to automated.
- Investing into an AS/RS can save 60-80% of the utilized shopfloor area (depending on building conditions, height, etc.) and can reduce labor costs by 50%.
- Fluctuation in FX (mainly in the EMEA region) makes market prices unpredictable.
- Interest in automation and commitment to the required changes are high, but as of today, only approximately 20% of warehouses are automated, which suggests there will be a long runway for automation market growth.
Key Takeaways
- Develop an approved vendor list (AVL) with multiple partners to maintain commercial competitiveness, access to supply, and overall leverage.
- Strong, close collaboration with inventory control specialists is key. Due to differences in warehouse space and layout, no one-size-fits-all type of solution is available; warehouse automation requires tailor-fit, customized solutions.
- Data collection, historical information, and analysis are important. Design should be managed with the involvement of suppliers. SOWs should be flexible to optimize outcomes.
- Consistent demand from requesters on the market is keeping suppliers busy, driving slower response times.
- Lead time remains a hurdle for warehouse automation projects, but we expect improvement within the next 9-12 months.
SMT
Market Overview
- Due to ongoing geopolitical concerns, many organizations are shifting their manufacturing facilities out of China
- India is benefiting from that sentiment, with SMT producers investing significantly in the country. However, there remain huge supply chain challenges in establishing SMT manufacturing in the country.
- India is benefiting most in the region due to domestic demand and remains one of the fastest-growing major global economies; driven by resilient domestic demand, strong private sector investment, and the healthy balance sheets of many Indian companies.
- In the years ahead, relatively sustainable economic growth will sustain with large domestic markets capitalizing on the potential for growing productivity, attracting cheap labor, and government policies that have become more supportive of improving the business environment.
- Vietnam has been one of the major nearby Asian countries to benefit from the relocation of Chinese manufacturing. This will result in increased hiring costs, especially in the Northern areas around Hanoi and its surrounding provinces. Impact in HCMC is lesser but not completely unaffected.
- Many are China-owned enterprises. As a result, based on information from China-based equipment suppliers, the impact on China’s domestic business has been considerable.
- Eastern Europe, Mexico, and Thailand have also benefited from the manufacturers shifting production from China. Malaysia has already taken its share of SMT demand.
- Indonesia saw strong investment activities in the electronic vehicles (EV) supply chain. Indonesia is finalizing agreements with car manufacturers BYD in China and Tesla in the US to invest in EV production facilities.
- Indonesia is poised to become a regional powerhouse as an original equipment manufacturer and has signed more than a dozen deals worth billions for battery material production with global companies.
- Along with investment from global multinationals, local companies are also trying to transform their business by adopting cleaner technologies. This is part of the reason why Indonesia’s economic performance is so resilient.
- The SMT CM continues moving business out from China to South Asia and Mexico. The new expectation is that 50% of new lines set up in Mexico this year will be coming from Chinese/Taiwanese CM. This will be a threat to US CM when comes to price offerings.
- It is more important than ever for US CM to differentiate themselves from Chinese CM, competing not on price but on services. For example, providing scratch (design) to box (complete solution) in concert with complete regional supply chain solutions.
- AI in SMT is a multidisciplinary field of science where the goal is to create intelligent machines. Historical applications of this goal include natural language processing and translation, visual perception, pattern recognition, and decision-making, though the complexity of applications has been quickly expanding.
- The SMT market is projected to grow from USD 5.8 billion in 2023 to reach USD 8.4 billion by 2028, at a CAGR of 7.8% during the forecast period.
- The major opportunities for the SMT market include the integration of biometrics and security into consumer electronics devices and medical devices.
- While SMT EMS will slow down in Q4, it is projected to come back in the first half of FY24 for some regions.
- To sell products in the US more easily, many businesses will nearshore production, with some semiconductor vendors moving business back to US or Mexico as a proactive strategy for capturing new business segments.
- China will shift from investment-led growth towards more sustainable consumption growth.
- “Energy Transition” is likely to be the next big thing in Asia. China is vying for a pole position in the electric vehicle (EV) and solar power generation supply chain, but it is also investing heavily in wind power, hydrogen, and energy storage.
- The transformation of its energy mix from fossil-fuel-based technologies to cleaner ones will not happen overnight but remains a substantial engine for growth. Asia is also rich in valuable commodities. Indonesia is a global center for nickel production and elsewhere liquid natural gas is in abundance. Both are key resources in the drive toward clean energy.
- Rules and policies are often subject to interpretation by local customs officials, potentially making the import of goods very costly without certainty of what can be imported duty-free.
- Rules may change very quickly depending on the specific dynamics underpinning State policy development and administration.
- In the upcoming years, SMT is anticipated to experience increasing acceptance. Industries are shifting their preference from through-hole technology to surface mount technology because of its many benefits, including fewer components, better component density, improved mechanical performance, and easier and faster-automated assembly.
- The major key benefits of converting to SMT are speed, cost-effectiveness, and reliability.
- Intelligent Factory of the Future investment development of equipment indicates the next level of SMT assembly.
- Advanced EMS Manufacturing efficiency will become an important standard to mark the performance of SMT equipment in the future.
Demand Commentary
- Q4 outlook suggests some slowing due to the potential of last-minute requests coming from customers at shorter lead times.
- As business moves from China to SEA and elsewhere new investments are necessary, in addition to realigning both resource and talent requirements in these locations. For example, Mexico is experiencing growth in SMT for semiconductors, 5G base stations, and automotive applications.
- Industries such as consumer electronics and healthcare continue to be pushed by innovations defined by smaller form factors. The emergence of SMART (Self-monitoring, analysis, and reporting) technology is driving an increased need for miniaturized products such as PCB, and integrated components. SMT equipment partners play a vital role in mounting and inspecting the compact PCBs required to support these trends.
- Electric car sales and manufacturing are increasing because of the rising demand for their use, offering this market promising growth opportunities.
- Southeast Asia is home to several promising industries across its regional economy that will report quicker than the global average growth in 2023. Despite a concerning macroeconomic backdrop, various factors will continue to pull in investment and businesses to this region.
- South Asia is emerging as a new focus for manufacturers exploring alternatives to the "China Plus One" strategy. Many manufacturers have traditionally adopted the "China Plus One" approach, which involves producing goods outside of China to mitigate risks and diversify their supply chains.
- However, in doing so, they often face the challenge of higher production costs in these alternative locations. As a result, these increased costs are eventually passed on to the end consumer.

Pricing Situation
- The USA expected to adjust its overnight interest rate again in July. SMT equipment’s new pricing will continue requiring review; however, the part shortage issue should be back to normal at 90% due to business softness in the back half of the year.
- Uniquely, to date within 2023, we are seeing some material cost (FX) decreasing, which supports an assumption that BOM cost should be slightly lower this year or inventories increasing (see chart below.)
- Vendors with a global support footprint are experiencing labor cost increases in the US and EU while no reduction in Asia.
- The reduction in BOM cost is to hedge the increase in operational cost, but the result decreases Q1 profits. Operations costs will continue to rise but an increase is expected. It may take another 2 quarters for corrections on the operating cost vs revenue vs BOM cost to realign.
- The strong dollar rate increase with slowing growth abroad are headwinds for the 2H of 2023. Tight financial conditions and an uncertain economic outlook are making both businesses and consumers cautious.
- We have reached the end of the post-lockdown rebound as China is opening to travel but investment remains soft in China.
- Generating cost avoidance requires close partnerships with key suppliers. Customers need to provide better forecasts to mitigate potential cost increases and reduce the ability to drive cost improvements.
- Overall, labor costs are expected to rise more for firms operating in North America and Europe. Four-fifths of manufacturers in North America (79%) and Europe (78%) expect labor costs to increase, which compares to a significantly lower 45% reported by global manufacturers, who instead are expecting labor costs to remain stable (50%). EMS can consider increasing supplier residence engineers for total cost ownership management.
- Many believe a recession is a foregone conclusion in 2H 2023, with some projections that up to a third of the world, economy will fall into a recession before the close of 2023. Global economic growth has already fallen, slipping from six percent in 2021 to about 3.2 percent in 2022. Global growth is expected to slow further in 2023, clocking in at less than two percent.
- The impact of global chip shortages has reduced tremendously. We are seeing most suppliers having a much shorter lead time in getting material and manufacturing the equipment. Inventory management requires frequent review to avoid passing along higher costs.
- SMT equipment investment will likely continue to focus on rebate incentives or value process improvement partnerships. In general, pricing for SMT equipment should focus to drive down vs future investment should be captured.
- While EU-based OEMs are still experiencing significant increases in labor and electricity, causing their pricing to remain high, for most non-EU OEMs, prices should reduce by 5% to 10%.
- Expect a similar price decrease once the labor market stabilizes, the conflict between Ukraine and Russia ends, and the electricity inventory increases back to pre-conflict levels.
Supply Analysis
- Key Supplier LT Analysis.
- India also suffers from a shortage of supporting industries – from components to local manufacturers.
- FUJI 8 weeks
- ASM 12-16 weeks
- ITW 4 weeks
- Vitrox AOI is 6-10 weeks / AXI is 12-16 weeks.
- Koh Young 4-6 weeks
- China has opened its borders, but due to supply chain challenges remains less than completely transparent regarding new Covid outbreaks in April 2023
- Continue to monitor incumbent supplier capability and consolidation. Develop new technology-supporting capabilities.
- Aerospace, and EV sector demand has increased in North America, but talent resources are limited.
- Global and regional supplier optimizations as well as alternative developments should be intentional with aggressive due dates. Nearshoring supply is a strategy that was adopted late during the COVID crisis.
- Most customers looked to adopt this strategy for common parts and consumables but have expanded their focus to also include CAPEX due to the rising labor wages and travel costs incurred for after-sales service and integration support.
- The outlook for the next 6 months:
- Continued challenging conditions globally due to the persistence of geopolitical unrest constraining supply chains and impacting logistics.
- Manufacturing in North America is expected to increase driving both improved inventories and profit margins.
- More than a third (35%) of global manufacturers are anticipating a decline in orders over the next 6 months which compares to a decline of only 8% within North America.
- The second half of the year promises good recoveries in the Americas, Europe, and Southeast Asia, while China, Korea, and Japan will continue to struggle for the remaining part 0f 2023.
Key Takeaways
- China Plus One strategy has come to an end, and this is overwritten by the Chip Sanction. There is more and more product that requires being built outside of China, forcing significant numbers of Chinese and Taiwanese CM to move their business to South Asia, India, and Mexico.
- Many do not have local operations, requiring starting up manufacturing from scratch. CMs with global multi-site facilities and global supply chain operations enjoy a competitive advantage in this regard.
- Automotive remains the strongest segment in the first half of 2023 and will likely lead segment revenue in the second half of the year in some regions.
- Currently, China, Mexico, and the EU have the best automotive manufacturing capabilities, as well as the highest growth, with production sites projected to expand.
- China easing on their COVID restrictions, even as new Covid outbreaks have been reported. Market share and funding quickly reverted to China for EV and Consumers Electronics. 2H of FY23 will be soft in demand.
- It is unlikely investment in SMT will see double-digit growth in China. The key is balancing between regional and global customer demand. Investment decisions will be swift.
- During COVID, many customers moved SMT production out of China, implementing a China Plus One strategy. Most are now accustomed to the higher cost of manufacturing outside of China.
- In the future of AI, lean SMT will continue to be a focus for eliminating the NVA. This is to provide a state of advanced manufacturing.
- Many companies are taking precautionary action to reduce budgets which suggests that the electronics market is now moving into a downturn. Forecasts across the next 2 quarters are not uniformly strong.
- Layoffs at some companies are providing a rebalancing of labor resources as well as cost savings due to earlier hiring being executed at higher rates than the current market conditions.
- Manufacturing is undergoing a transformation both globally and locally. Japan, South Korea, China, and other Asia Pacific countries are investing heavily in R&D leading to two global ecosystems between East and West.
- The utilization of Robots and AI in SMT production will result in faster and smarter machines optimized to solve problems and improve process efficiencies.
SOLDER
Market Overview
- Solder markets continue growing as expected in the last quarter. The EV market continues to grow fast, especially within China and the US.
- Solder paste technologies are taking over the spend of the regular solder bar applications, due to higher volumes of new complex boards requiring smaller but powerful components.
- Solder types 4.5, 5 as well as 6 are becoming more common. These types are primarily used in 5G devices, EVs, and other high-tech industries.
- Solder bar prices continue to be driven by the cost of the metals. Tin and silver have been volatile but continue on a path toward stabilization.
- Demand in China is recovering from COVID lockdowns and other tight measures put in place over the last couple of years. The Chinese market has returned to higher consumption levels, both domestically and internationally. Experts expect impacts to follow in global prices and inflation once the demand recovers completely.
- Tin prices have increased due to the Myanmar militia’s announcement of suspending mining activities. Myanmar is one of the top three tin producers in the world.
- Silver continues in a price increase trend based on the fears of a recession in the US in 2024.
Demand Commentary
- The demand for solder continues with good expectations as stated in past reports. The global market accounted for USD 1,477.2 million in 2019 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 4.0% from 2020 - 2030, to account for USD 2,255.3 million by 2030.
- Rising demand for various smart electronics and the advent of energy-efficient electronics are the major factors expected to drive the growth of the solder materials market. Additionally, the rising production of electronic devices or gadgets in developing countries coupled with the presence of a notable electronics aftermarket industry is expected to boost the demand for solder materials during the forecast period. Conventional micrometer solder materials in the paste exhibit several shortcomings, such as high melting temperatures, which may result in undesired stress during the reflow processing, restricted applications, and defects in the joint. This has further led to the introduction of innovative sub-micron and nonparticipating solder materials.
- Increasing demand is also being catalyzed by the importance of smartphones, tablets, laptops, and the growing trend of Internet of Things (IoT) applications.
- The biggest consumption alloy continues to be SAC305—principally in the new technologies for which the customer relies on the secure solderability offered by silver alloys.
- Automotive and EV markets continue as key contributors to the growth in the demand of the solder industry. Recently announced plans for zero-emission target vehicles by 2050 are having an accelerating impact on all aspects of the supply chain and all the related industries.
- De-carbonization challenges being undertaken by most leading nations, supported by various policies and incentives, are accelerating global EV sales in 2023.
- In just the first quarter of the year. 2.3 million EVs have been sold which is 25% more than the same period in 2022.
- With current predictions of 14 million in sales by the end of 2023, EVs could account for 18% of total car sales this year.
- 5G technology is growing across different regions. This accelerated growth has increased the consumption of the solder paste types 4.5 and 5.
- The silver demand at present would be affected as well by the new technologies such as the 5G. Even as its deployment is still in its early stages, 5G-related silver demand currently constitutes approximately 7.5 million ounces (Moz).
- With the rollout of 5G in the coming years, however, silver’s role in the electronic applications used in 5G is forecast to rise significantly to approximately 16 Moz by 2025 and as much as 23 Moz by 2030, which would represent a 206% increase over today.
- For comparison purposes, in 2010, silver’s use in the once-emerging photovoltaic industry was approximately 40 Moz, and by 2018 it stood at 80.5 Moz.
- The report discusses the differences between 5G and the previous generation of digital cellular networks. It also examines the five significant technologies that make up the core of 5G technology, and the role silver will play in these technologies.
- Finally, it looks at the hardware needs and supply chain requirements, given the massive amount of financial capital required in the development and expansion of 5G networks.
Supply Commentary
- Solder Bar.
- Solder suppliers are focusing their organizations on new technologies as an alternative strategy for increasing profits in a very competitive market.
- Solder bar margins are quite low, and the cost structure of the metal is principally the cost of the metals —a factor out of the control of the suppliers and the buyers.
- This along with the pressure from the markets to continue reducing prices has forced suppliers to offer other alloy alternatives for their applications.
- Solder Paste
- Continues to be one of the most important businesses for solder suppliers. The supply of this chemical is very stable, and the customer can enjoy a wide variety of brands and alloys. However, customers have been very conservative regarding testing new brands or products.
- Traditionally, solder is the powder metal and the flux, which is basically the secret formula for each company. Suppliers are relying on their R&D efforts to help ensure the ongoing success of the solder paste in all the different requirements of the industry.
- Solder types are becoming more specialized. Demand for the new technologies over the past 5 years—specifically, the use of solder types 4 to 6—has increased due to increasing requirements driven by micro components.
- Supply of solder in the market continues to be stable and no major threats are expected in the short term, however, the recovery of demand from post-lockdown China is stressing the supply chain.
- Tin supply remains relatively stable; however, the metal is very sensitive to specific geopolitical factors potentially impacting countries where tin is produced.
- One notable recent example is the threats from the United Wa State Army to suspend Myanmar mining operations from 1st August 2023. The ITA estimates this would represent about 10% of the world's tin concentrate supply.
- The threats have created an inflationary effect on pricing. Even as this development’s initial stresses on the market may subside, it is a reminder of how production of this metal could be affected at any moment—and in turn, greatly impact to the solder supply.
Pricing Situation
- Tin prices rose over the last month due to supply woes. Prices averaged USD 25,644 per metric ton in April, which was up 6.9% from March’s price but was 40.4% lower than in the same month last year.
- On 28 April, tin traded at USD 26,398 per metric ton, which was 1.8% higher than on the same day of the previous month.
- Prices increased in recent weeks chiefly due to supply concerns in Myanmar. In mid-April, the United Wa State Army—Myanmar’s largest ethnic armed organization—stated that from August onwards mining operations in Wa State would be suspended.
- Prices spiked immediately after the announcement, given that Myanmar is the third-largest producer worldwide and accounts for over three-quarters of tin imports in China—the top consumer.
- The need to preemptively stock up likely boosted Chinese demand, despite that country’s manufacturing PMI swinging into contraction in April.
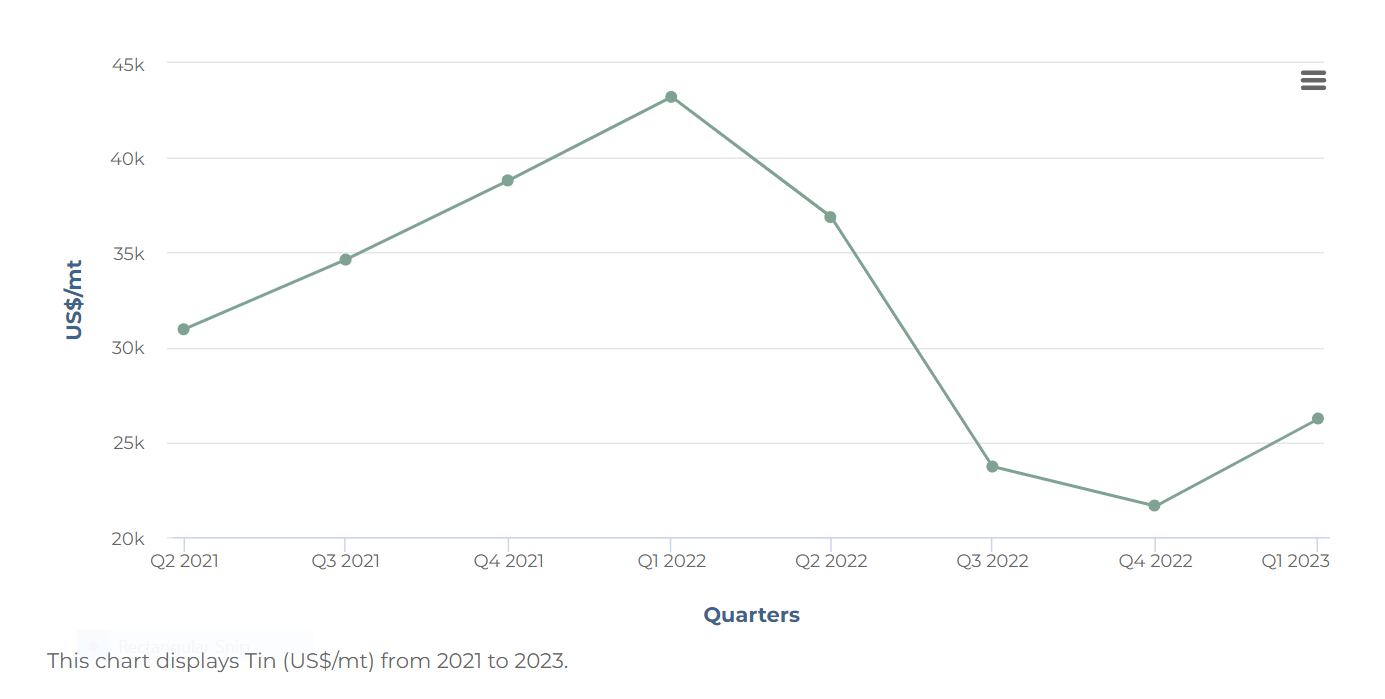
- Silver. While gold price has also dropped significantly in the last two weeks, silver is leading the latest drop in commodity prices.
- In fact, copper and zinc have also shown negative price action during this time. There are multiple factors behind this drop in silver price per ounce, but the biggest impact is due to the slower-than-expected recovery in China.
- Sales of silver coins and bars for investment jumped by 36% to 278.7 million ounces, the highest level since 2015, “as retail investors in North America and Europe, motivated by safe-haven and inflationary concerns, took advantage of periodically lower silver prices to purchase coins and bars,” as reported by the Silver Institute.
- The market saw its first deficit since 2015, with a shortage of 51.8 million ounces, the biggest shortage since 2010.
- In 2022, silver traded up from $22.30 per ounce in late January to USD 26.90 per ounce in early March, (the peak for silver in 2022,) as the market responded to the Russian invasion of Ukraine.
- But while the market traded between USD 24 to 26 until mid-April, it began to sell off sharply later in the month as the dollar strengthened.
- In general, solder is showing a little peak from the past quarter.
- The price of the alloys will continue in a slow but sustained increasing trend as the demand continues its recovery from COVID.
- However, it is important to watch closely the behavior of the metals and the geopolitical factors of the regions where they are produced.
Supply Analysis
- In March 2023, AIM Solder, a leading global manufacturer of solder assembly materials for the electronics industry, announced the release of its newest halogen-free no clean solder paste, H10. H10 offers exceptional fine feature printing, improved electrochemical reliability, and powerful wetting.
- In 2021, electronics manufacturing services provider Foxconn Technology Group and semiconductor company MediaTek announced a collaboration to develop new 5G solutions for smart manufacturing and Industry 4.0 applications.
- This collaboration could lead to new advancements in the soldering electronics industry.
- North America is estimated as the second most dominant region in the global soldering in the electronics assembly market in 2023 just beside China.
- The combined US, Mexico, and Canada have a presence of several electronics manufacturers, such as Apple Inc, Intel Corporation, Plexus Corp., and Creation Technologies LP.
- These companies are consistently focused on the development of new and technologically advanced electronic products, which is significantly increasing the demand for soldering in electronics assembly, thereby contributing to the soldering in electronics assembly market growth.
- Moreover, soldering in electronics assembly market players in North America are Lucas-Milhaupt Inc, S-Bond Technologies LLC, Fusion Inc, Indium Corp, and Superior Flux & Manufacturing Co., among others.
- These companies are involved in the development of advanced soldering products, which is contributing to the soldering in electronics assembly market growth.
MRO
Market Overview
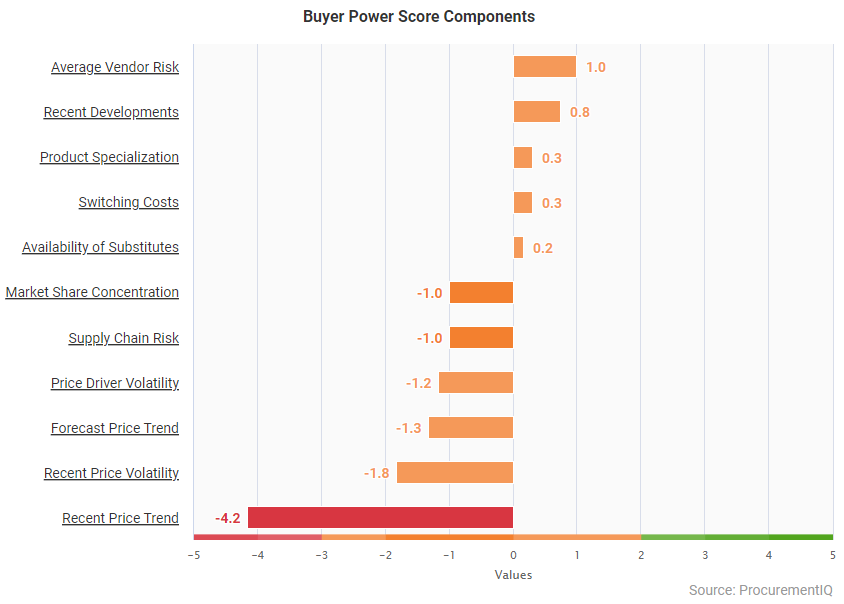
- Market conditions have not changed significantly from previous quarters. The trend shows buyer power score has still not attained the average of prior years, but stabilization is in sight
- Buyer power score fluctuations are driven by market conditions and the strength of the USD against other currencies. Example:
- If the previous quarter, there was a Good/Service purchase for $4M MXN it would be around the $190K USD(1 USD = 21MXN). Calculated at current rates, the same $4M MXN is now around $223K USD (1 USD = 17.9MXN).—an increase of 18% just due to the exchange rate.
- As a result, the market is trying to find local suppliers that can bill with the local currency, as a hedge against exchange rate impacts.
- Buyer power score fluctuations are driven by market conditions and the strength of the USD against other currencies. Example:
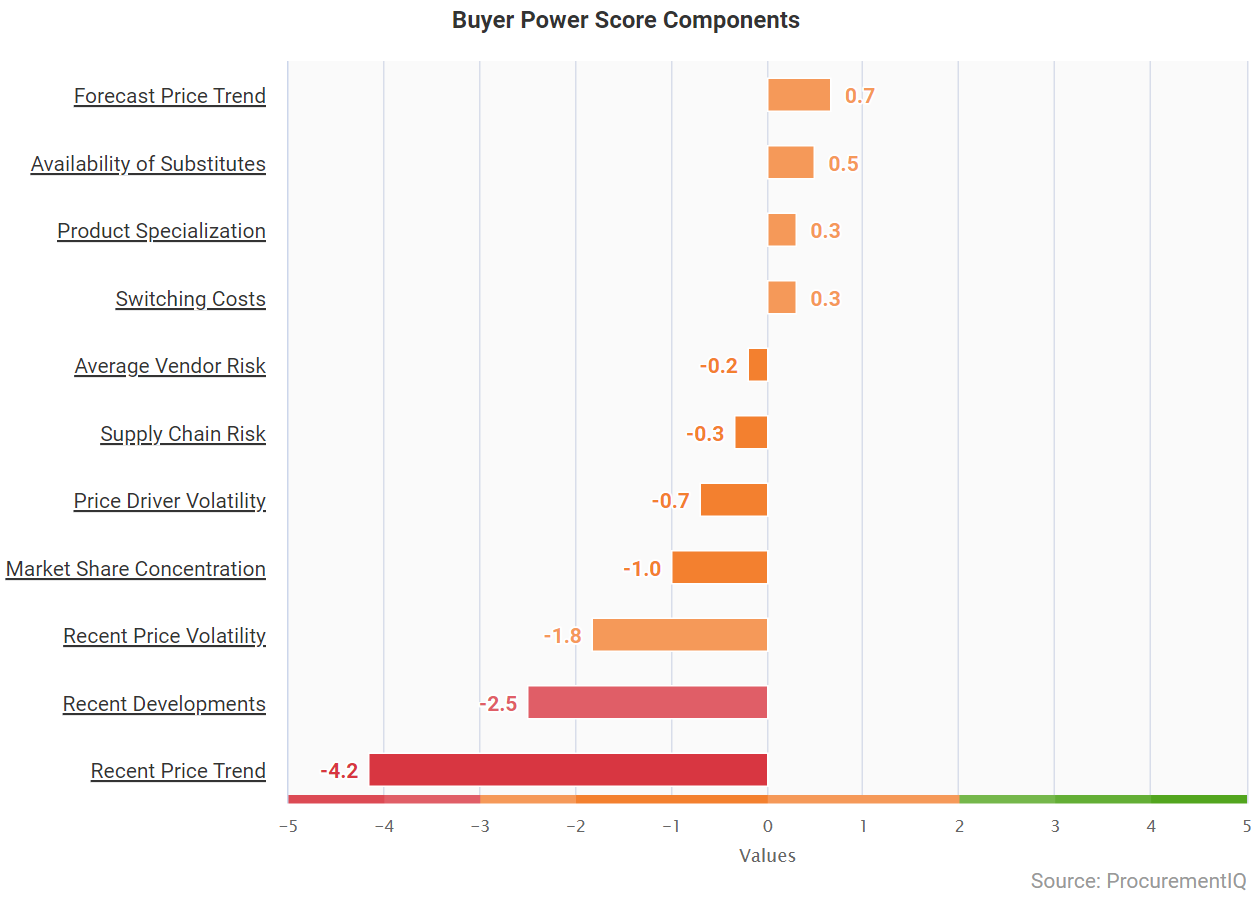
- Quick Compare: 15% power reduction on Forecast Price Trend indicator; 30% increase on Price Driver Volatility indicator. Supply chain risk increases significantly—by a factor of 3—as compared to the indicator from the previous quarter
- NOTE: A score of +5 indicates that a factor works in favor of buyer power, whereas a score of -5 indicates that a factor works in favor of supplier power. A score range of 0 equates to a neutral impact on buyer power.
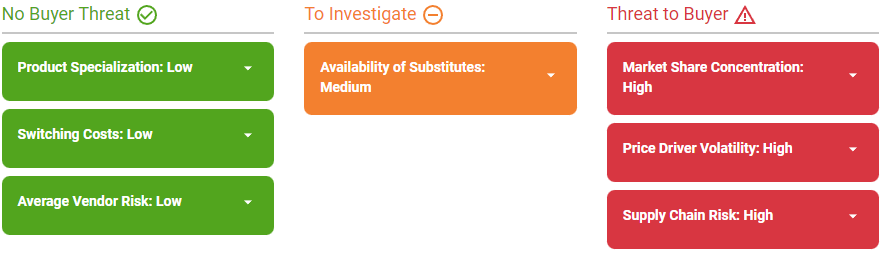
- Availability of Substitutes continues as a medium opportunity for the market.
- Substitutes as a key driver for MRO market conditions continue to drive options for supply and cost reduction for buyers. While low lead time is key, the most impacted areas in MRO are spare parts, due to these needing to come directly from the manufacturer.
- Supply chain risk continues to be an issue driving price volatility. Shortages and delays due to supply chain disruptions continue to impact existing orders and have the potential to affect operations directly if goods are not received in time.
- Consumables for machines like tips or drills, chemicals, and some customized items are challenging for factories, reducing their IOH (inventory on hand) and catalyzing the need for finding local suppliers and alternate items where possible.
Market Dynamics
- Substitutes continue to be a driver of market dynamics, requiring buyers’ analysis and consideration of testing and implementation costs, in addition to the time for evaluation.
- Nevertheless, some of the alternates in specialized items like chemicals or customized MRO goods may extend more than 6 months, therefore it is advised that buyers start with their analysis even as the benefit of the LTs, availability, pricing, and competition would help to avoid operations disruptions.
- Special cases will not allow the buyer to obtain alternates if the decision is on the final consumer (Buyer´s customer) and not on its own.
- Buyer is recommended to explore sub-commodities and review details for tooling, consumables, office supplies, PPE, tapes, etc. with the intention to see the competitor opportunities.
- Most items are purchased through distribution where margins are larger providing the opportunity to negotiate and reduce the cost directly by obtaining the CR or discounts for large volumes.
- Volume incentive programs should be explored by buyers—(i.e., rebates.)
- Benefit on the credit given to allow more cash flow with an increase in payment terms.
- Leasing continues to increase as a strategy by the companies for requirements, small tools, and now also for office furniture, helping buyers to reduce the impact on their cash flow.
- For over 70% of the MRO items (including spare parts), buyers need to implement negotiations with suppliers to secure fixed pricing. This can vary and could be monthly quarterly or yearly, depending on the items based on historical consumption.
- There might be some specific items that will benefit from a longer period of fixed pricing, as volatility may potentially drop pricing and impact P&L.
- Specialization is low in the market—except for some equipment brands and warranty policies)— giving buyers the opportunity to move between different competitors and suppliers, depending on the benefit to be obtained
- This is one of the reasons why agreements for commercial benefits (i.e., volume incentive bonuses, LTs, payment terms) are strongly recommended so that buyers have the opportunity and right to move demand from one source to another depending on the market conditions.
- Buyers could find solutions to their requirements, however as a result of internal administrative requirements, or if the agreement is not in place, the procurement of goods can be affected.
- Short lead times are good news in today’s market.
- “Just-in-time” orders are helping to reduce cash spent and days of inventory on-hand, not to mention reducing downtime risk.
- Buyers can also explore other sourcing options like vending machines with monthly invoicing, helping their MPR (material requirements planning), and cash flow as well as helping their Kanban inputting
- Vending machines can control the number of items that can be used by employees, reducing the cost of “leaks” and providing better control on spending by area and users.
- Medical, automotive, and 5G markets are being driven by growth MRO space requirements. Additionally, the general EMS market is ramping up, giving the market an increase in demand, but also stabilizing purchasing behavior.
- Buyers should reduce operational expenses by implementing process efficiencies like SLAs service-level agreements or vendor-managed inventory (VMI).
- General consumables and office supplies, which are subcategories of MRO, offer a wide range of substitute options that are typically managed internally for MRO inventory purposes.
- It is recommended that a Vendor Managed Inventory (VMI) system is implemented to assess the additional costs involved and reduce the “in-book” number.
- Buyers should negotiate an extension of payment terms to reduce the impact on their cash flow.
- Minimize impact upon cost (with the valuation of the carrying cost) by having the supplier carry over and assuring the material is on time for production.
- Negotiate safety stocks with suppliers.
- Suppliers should be continuously developing alternate items.
- Concentrate demand within key partners to better ensure supply.
- Develop local sourcing for general supplies, office supplies, and furniture and no customized tolling needs to be a day-to-day activity.
- Regional standardization is recommended
- Divide high-quality demand items across more than one supplier to protect against dependence on a single source
- Contingency plans should be created if goods are brought from different geographies, to protect against potential natural disasters or local disruptions as well as various geopolitical tensions in place around the globe.
- Majority of small/hand tools can be sourced with local suppliers, expanding demand, and gaining more leverage on negotiations, as well as getting reductions on “total cost” and lead times.
- This can also include some “customized” consumables like Tips, Drills, etc.
- Larger suppliers should remain to be developed, by the country for example, and to ensure supply chain needs are met
- Office supplies, tapes, wraps, PKG products, and general items that are procured from general distributors, are suggested to be identified as repetitive purchases, and concentrated with appropriate partners—depending on the commercial agreements in place—to obtain the maximum benefit possible (i.e., cost, stock, delivery time, alternates, etc.)
- The list of key global industrial distributors continues to be:
- WW Grainger
- RS Components
- Sonepar SA
- WESKO
- Gastenal
- RS Hughes
- McMaster
- For OEM products, focus should be on negotiating long-term contracts with suppliers, including safety stock of spare parts, programmed maintenance inclusive, or training for internal workers to perform basic repairs and avoid down times and reduce repair costs.
- The increasing standardization of services and equipment is expected to accelerate the MRO market growth, providing buyers more purchasing leverage for negotiation.
PRICING SITUATION
- Construction markets have been affected due to the increase on interest requested, in addition to the policies some companies already might require.
- As specialization on a product is not a common issue PPE, office supplies, and consumables are items that can be mass-produced. The opportunity to have larger orders can reduce costs if the MOQ (minimum order quantity) is properly negotiated.
- PPE products have variations depending on the markets they are utilized in (i.e., re: thickness/gauge of powder gloves, types of plastics, etc.) Most suppliers offer similar products across each product line.
- Buyers should be strategic regarding timetables and schedules for procurement from distribution, as in some cases, (for example, gloves,) the manufacturer has enough capacity to deliver directly
- Buyers should also establish relationships and have side contracts with manufacturers, so if there is a need to have a distribution partner, there will be a price agreed to in advance, protecting against excessive markups.
- Medical and automotive industries work with different levels of certification depending on the product, which creates potential increases in costs from 15% or even 30% higher.
- The availability of substitutes provides an opportunity to increase buying power.
- Buyers should identify items that are not particularly sophisticated, like PPE, small tools, or consumables.
- For machine consumables it is recommended to do an assessment and evaluate options for local alternatives (screw tips, welding tips, drills, etc.)
- Logistics expenses are still affecting cost—up to 60% of the raw material cost.
- Geopolitical issues can highly impact transit concerns (driving an increase in Nearshoring to Mexico), as well as potentially drive speculation on some pricing increases between 6.5% up to 10% depending on the good.
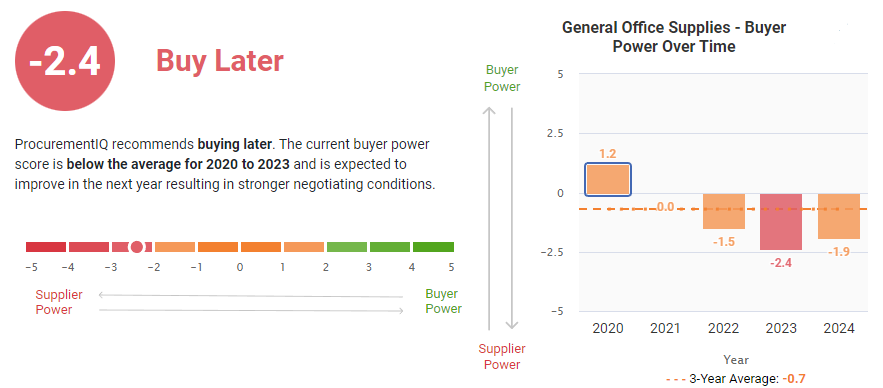
- MRO supplies are still increasing in price, putting pressure on buyers’ purchasing power.
- Buyers are advised to develop new suppliers (local suppliers should be explored) to grow along with them and prepare for future requirements. In time, this investment provides a “built-to-suit” solution at a lower cost.
- By creating their own list of specialized suppliers, new cost reductions can be met—starting from construction (where reductions are between 5% to 8%,) installations (3% to 5% CR,) office supplies (saving up to 20%,) just by adapting standard requirements to other materials or finished goods. Office furniture is a great example.
- Biggest suppliers, such as Fastenal, Grainger, MSC, etc. are committed to anti-corruption within their codes of conduct for suppliers.
- This gives buyers the opportunity to achieve the best possible pricing with more certainty and builds a relationship based on trust between buyers and their suppliers for negotiating potential markups.
- Raw material costs continue to increase, affecting the price of goods:
- The producer price index for electrical equipment tends to increase by over 20% on a yearly basis
Supply Analysis
- High-level suppliers provide buyers with reduced risk of financial issues or supply disruptions, as buyers can lean on their partners for some VMIs without the constraint of being short due to lack of solvency.
- On the other hand, there may potentially be greater supply chain risks due to high-volume suppliers driving incremental shortages or price increases.

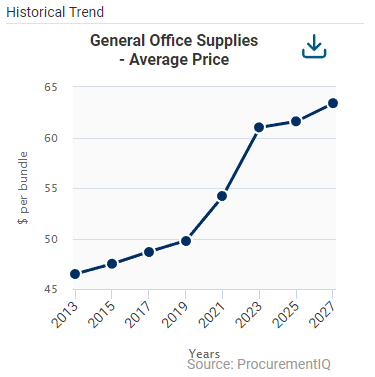
- People (headcount) issues and the difficulty in hiring additional workforce is impacting producers. 34% of the ISM survey’s respondents who are hiring indicated difficulty filling vacancies, up from 28% a month earlier.
- Remarking the previously mentioned local vendor and inventories managed by them will help to reduce this impact
- Substitutes will create new opportunities for avoiding logistics delays
- Turnover rates remain high, demonstrating severe tightness in the job market.
- MRO key partners play an important role in supply chain management by reducing LTs, obtaining lower costs by consolidating demand, and reducing the carrying cost of self-procurement.
- This may not be the case in all commodities or regions, so buyers are strongly advised to do a periodical evaluation and contact manufacturers to review if distribution can be directly with them, thereby avoiding 3rd party markups.
- QBRs (Quarterly Business Reviews) for key suppliers (in LT reductions, price reductions, suggestions for alternates, rebates) have now become a standard practice for MRO strategy by reducing subjective perceptions and moving towards quantitative, measurable KPIs.
- Intended to cost out efficient improvements and a more productive supply chain—also pushing suppliers to identify more proactive CR areas.
- MRO buyers should consolidate the number of suppliers providing 80% of their spending.
- “Emergency” or “one-time” MRO distributors and integrators should be around 12% - 15% of the suppliers and service 80% of their overall spend.
- Evaluate low specialization items; implement strategies with partners that can be developers without negatively affecting operations.
- Short buying LT, from RFP creation to implementation (for strategic purchases, the timing helps buyers avoid shortages and reduce cost by not absorbing price change impacts.)
- Shortages are one of the most significant impacts—causing production delays, additional communication, rush orders, and higher MRO costs.
- Should be maintained at less than 1% on a daily or weekly basis.
- This should be driven according to the category and per implementing the right mitigation strategy, such as vending machines, days of stock, local suppliers for responses just-in-time, and revisions of the Kanban numbers vs forecast consumption.
Key Takeaways
- Market conditions have not significantly changed, but there are signs of stabilization. Buyer power scores have fluctuated due to market conditions and currency exchange rates.
- The US market has impacted buyer purchasing power but not as much as expected, creating a more confident purchasing environment for buyers.
- Availability of substitutes is a medium opportunity in the market, especially in MRO where spare parts can be sourced locally to avoid currency exchange rate impacts.
- Supply chain risk has increased significantly, with three times the indicator from the previous quarter. Delays and disruptions in the supply chain can affect operations and push buyers to find local suppliers and alternate items.
- "Nearshoring" from Asia to Latin America and Europe has impacted land availability and demographic requirements, such as labor costs and green energy initiatives.
- Buyers should explore and analyze substitutes for MRO items, considering the testing and implementation costs. They should also concentrate demand with key partners and negotiate agreements for commercial benefits, such as volume incentives, extended payment terms, and leasing.
- Buyers can source small/hand tools and general items from local suppliers to expand demand, negotiate better pricing, and reduce lead times.
- Negotiating long-term contracts with suppliers for OEM products and ensuring the supply of spare parts can help reduce costs and avoid production disruptions.
- Conducting QBRs with key suppliers can support cost-efficient improvements and a more practical supply chain.
- Buyers should consolidate the number of suppliers to manage around 80% of their spend, while emergency or one-time MRO distributors and integrators should make up 12%-15% of their overall suppliers.
- Managing shortages is crucial, and they should be maintained at less than 1% on a daily or weekly basis to avoid production disruptions. Mitigation strategies should be implemented based on category-specific needs.
Back to Top