By clicking the “I Accept” button, or by accessing, participating, or submitting any information, or using the Jabil Global Intelligence Portal or any of its associated software, you warrant that you are duly authorized to accept the Global Intelligence Portal Terms and Conditions on behalf of your Company, intending to be legally bound hereby, and your company shall be bound by the terms and provisions of the Global Intelligence Portal Terms and Conditions, accessible under the following link Portal T&Cs.
Global Category Intelligence
Q2 2025
Global Category Intelligence
Q2 2025
The Emergence of Power Purchase Agreements in the Energy Industry
Background
The power purchase agreements (PPAs) industry refers to the contracts established between electricity generators and buyers for the sale and purchase of power. These agreements play a crucial role in the renewable energy sector, where they provide a financial mechanism for project developers to secure revenue streams and mitigate risks associated with their investments.
In the past decade, there has been significant growth in renewable energy deployment, driven by factors such as declining costs, policy support, and increased environmental awareness. PPAs have been instrumental in facilitating this growth by offering a framework for renewable energy project developers to secure long-term contracts for the sale of their electricity.
Global renewable energy power purchase agreements by sector, 2010-2021
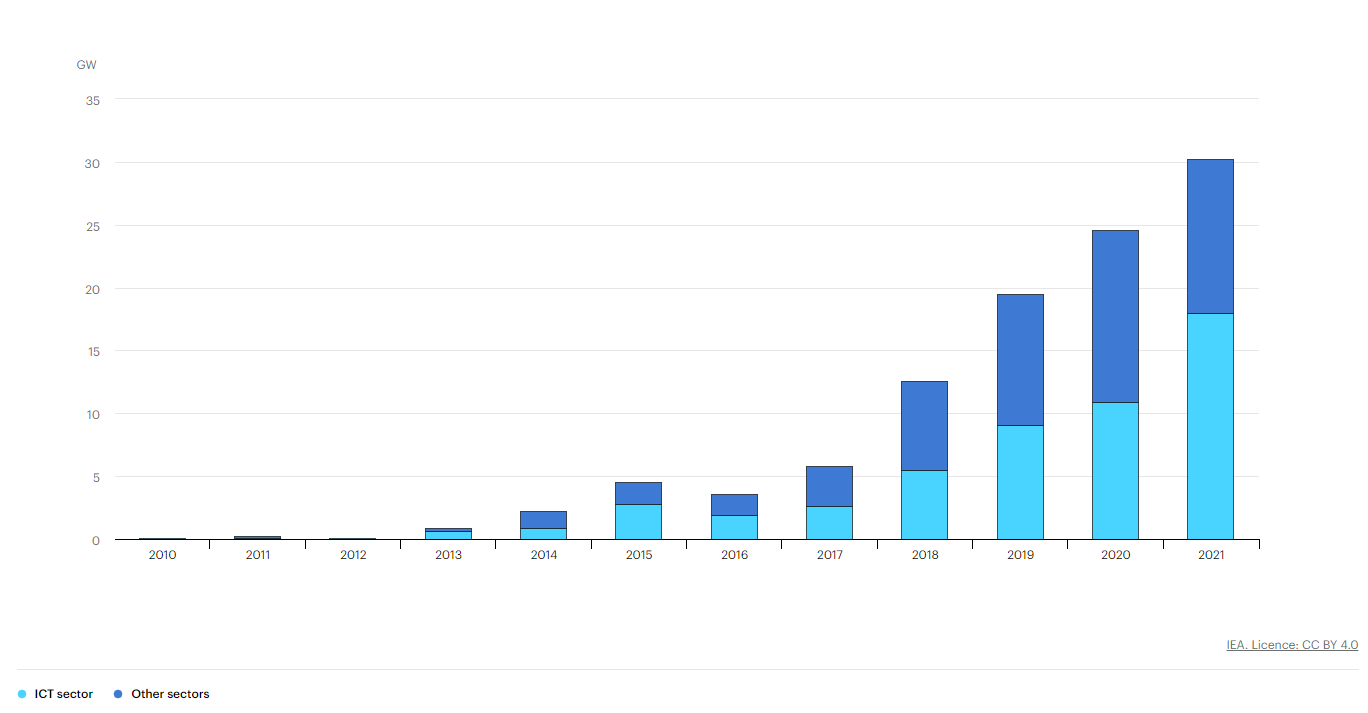
Figure 1: IEA, Global renewable energy power purchase agreements by sector, 2010-2021, IEA, Paris https://www.iea.org/data-and-statistics/charts/global-renewable-energy-power-purchase-agreements-by-sector-2010-2021, IEA. Licence: CC BY 4.0
Here are some key aspects of the power purchase agreements industry.
Participants: PPAs involve two main parties: the electricity generator (often renewable energy project developers) and the electricity buyer (utilities, corporations, or other entities). The buyers are motivated by various factors, including sustainability goals, cost savings, and regulatory compliance.
Contract Structure: PPAs typically define the terms and conditions of the electricity sale, including pricing, contract duration, delivery obligations, payment terms, and other relevant aspects. They can be structured as either physical or financial contracts.
Renewable Energy Focus: PPAs have been particularly prevalent in the renewable energy sector, enabling the development and financing of wind, solar, biomass, geothermal, and hydroelectric projects. These agreements provide revenue certainty to renewable energy developers, reducing their exposure to market price volatility and supporting project bankability.
Corporate PPAs: In recent years, there has been a notable rise in corporate PPAs, with large corporations entering into long-term agreements to procure renewable energy directly from generators. These agreements help corporations meet sustainability targets, reduce their carbon footprints, and demonstrate environmental stewardship.
Competitive Auctions: Many countries and regions have implemented competitive auction mechanisms for procuring renewable energy through PPAs. These auctions involve a bidding process where developers submit proposals with their desired PPA terms, including pricing, and the lowest-cost or most competitive projects are selected.
Policy Support: Government policies and incentives, such as feed-in tariffs, renewable portfolio standards, tax credits, and subsidies, have played a crucial role in facilitating the growth of PPAs and renewable energy deployment. These policy measures create favorable market conditions and encourage the signing of long-term contracts.
Top five corporate off takers of renewable energy power purchase agreements, 2010-2021
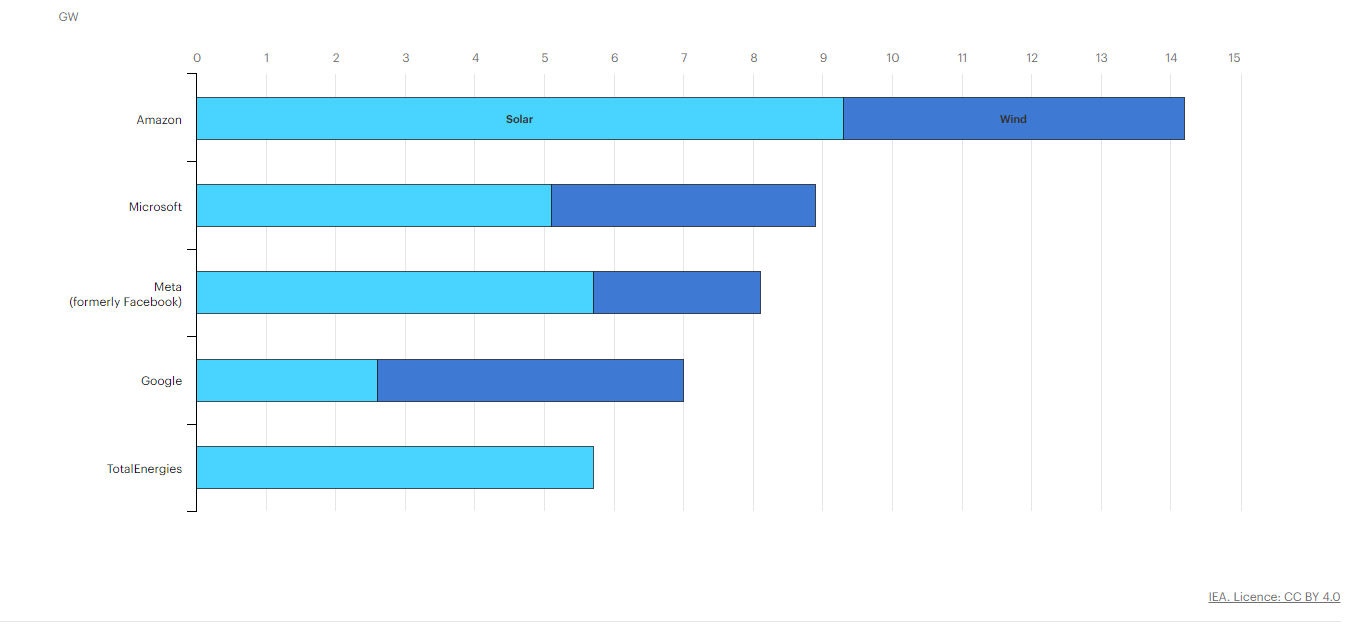
Figure 2: IEA, Top five corporate offtakers of renewable energy power purchase agreements, 2010-2021, IEA, Paris https://www.iea.org/data-and-statistics/charts/top-five-corporate-offtakers-of-renewable-energy-power-purchase-agreements-2010-2021, IEA. Licence: CC
Types of Power Purchase Agreements:
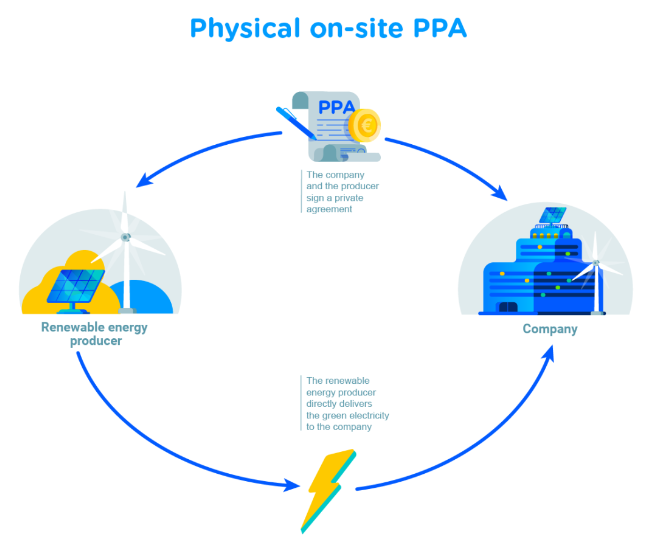 Physical on-site PPA Principle
Physical on-site PPA Principle
Green power generation solutions are installed directly on the company’s property, be it on rooftops, parking carports, or ground mounted. The electricity is then consumed on-site.
Figure 3: Total Energies - what is a PPA? (https://totalenergies.com/news/what-power-purchase-agreement-ppa)
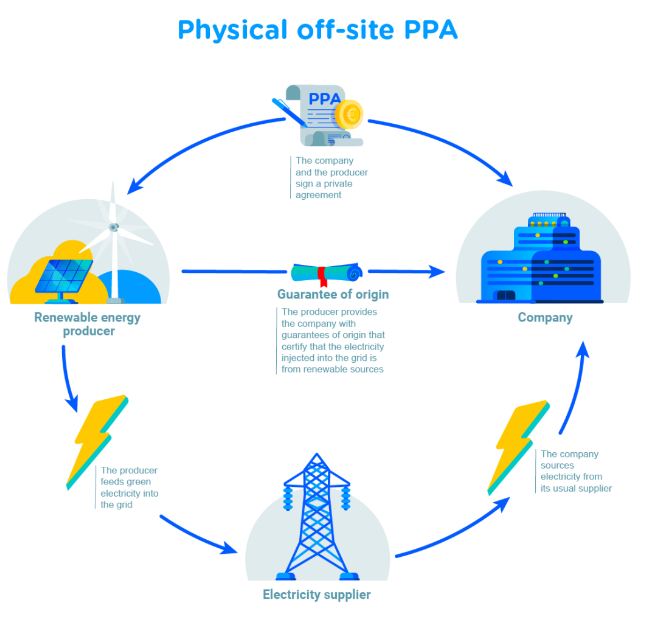 Physical off-site PPA Principle
Physical off-site PPA Principle
When the renewable energy producer is also the electricity supplier and the renewable facility is not in the customer’s immediate vicinity, the “problem” is overcome by injecting the energy produced by the renewable facility into the power grid and then using the grid to supply the customer with electricity. Guarantees of origin provide the customer with the assurance that it is contributing to the development of renewables.
Figure 4: Total Energies - what is a PPA? (https://totalenergies.com/news/what-power-purchase-agreement-ppa)
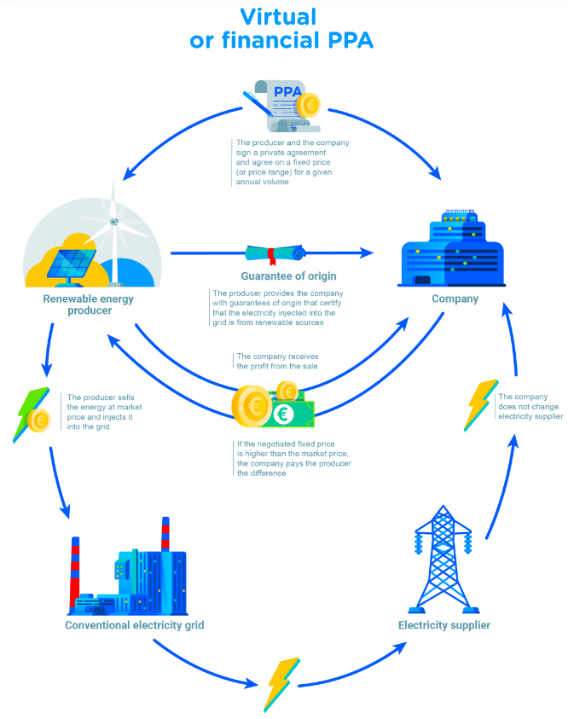 Virtual or financial PPA Principle
Virtual or financial PPA Principle
The producer and the buyer agree on a price (or price range) per kilowatt-hour for the supply of an annual volume of energy over a given period. This secures the investment, ensuring a regular income for the renewables project, but there is no physical delivery of electricity under this model. The energy produced is sold directly to the grid and the buyer benefits from the guarantees of origin associated with the production covered by the agreement. Another advantage of financial or virtual PPAs is that they come with a “contract for difference”, meaning that when the price on the highly volatile electricity market exceeds the price negotiated between the parties, the producer pays the difference to the buyer. In the opposite case, when the price per kilowatt-hour injected into the grid is below the price provided for in the contract, the buyer pays the difference to the producer. This is the most flexible type of PPA, especially when the renewable energy producer is not the customer’s electricity supplier.
Overall, the power purchase agreements industry continues to thrive, driven by the increasing demand for renewable energy, the decreasing costs of renewable technologies, and the commitment of corporations and governments to decarbonization efforts. PPAs provide a valuable framework for project developers to secure revenue streams, attract investments, and accelerate the transition to a more sustainable energy future.
Figure 5: Total Energies - what is a PPA? (https://totalenergies.com/news/what-power-purchase-agreement-ppa)
Jabil’s Perspective
The trend of increasing Power Purchase Agreement expansion will continue for the foreseeable future to accommodate the increasing demand for renewable energy and address environmental concerns. The benefits of these agreements are increasingly attractive to large corporations (especially with the volatility of energy markets over the past 2 years) as they give the ability to combine cutting electricity costs with lowering CO2 emissions which will both continue to be tightly monitored by customers and Governments globally.
It's essential to note that the specific landscape and trends in the PPA industry may vary depending on the region and its energy market dynamics. Recently, several traditional regulated energy markets typically seen in APAC and LATAM are also reforming their energy governing structures and introducing ‘dual markets’ whereby there will be the ability to buy through state-owned entities or through a deregulated market. These reforms give additional presence and opportunity for Power Purchase Agreements to become more prevalent in some of the biggest economies in the world, hence, increasing their global deployment.
Back to Top


