By clicking the “I Accept” button, or by accessing, participating, or submitting any information, or using the Jabil Global Intelligence Portal or any of its associated software, you warrant that you are duly authorized to accept the Global Intelligence Portal Terms and Conditions on behalf of your Company, intending to be legally bound hereby, and your company shall be bound by the terms and provisions of the Global Intelligence Portal Terms and Conditions, accessible under the following link Portal T&Cs.
Jabil's Global Category Intelligence Archive
Global Category Intelligence
Q4 2024
Jabil's Global Category Intelligence Archive
Global Category Intelligence
Q4 2024
CAPEX, MRO, INFRASTRUCTURE
Automation
MARKET DYNAMICS
-
Global commodity prices remain flat or trend downward, keeping the market in a buyer’s favor. Automation parts lead times remain unchanged from the previous quarter, indicating stable supply conditions but persistent stock imbalances.
-
The global industrial automation market faces short-term challenges due to weak demand and a slow de-stocking process. However, long-term growth prospects remain positive, driven by automation’s potential to enhance supply chain resilience.
-
Automation investments in the automotive (especially EV) and electronics industries continue to be robust, particularly in Asia and the Americas, sustaining demand despite broader market uncertainties.
-
Many automation suppliers reported underperformance, primarily due to weak market demand and high stock levels, reflecting the broader economic slowdown and its impact on capital investments.
DEMAND TRENDS & FORECASTS
The global economy has continued to expand steadily, and the IMF projected global growth to be 3.2% for 2024 and 3.3% for 2025. The Global Industrial Automation market size is projected to reach USD 218 billion by 2027 at a CAGR of 8.2%. Although with long-term higher-than-GDP growth rate expansion, the Global Industrial automation market is experiencing short-term challenges due to weak market demand and customer slow de-stocking, especially in Europe and China.
-
In the United States, projected growth is revised downward to 2.6% in 2024, reflecting the slower-than-expected start. Growth is expected to slow to 1.9% in 2025 as the labor market cools and consumption moderates, with fiscal policy gradually tightening. The industrial automation market is experiencing significant growth in North America, particularly in the automotive and electronics sectors. Automation investments are increasingly focused on projects such as electronic shelf labeling in supermarkets and electric vehicle control unit manufacturing, which require substantial advancements in automation technologies to meet production demands.
-
In the EURO area, activity appears to have bottomed out. A modest pickup of 0.9% is expected for 2024, driven by stronger service momentum and higher-than-expected net exports in the first half of the year; growth is projected to rise to 1.5% in 2025. Automation investment seems low in the region. We’ve seen some automation investment for medical products.
-
For China, the growth forecast is revised upward to 5% in 2024, primarily due to a rebound in private consumption and strong exports in the first quarter. In 2025, GDP is projected to slow to 4.5%, and to continue decelerating over the medium term to 3.3% by 2029, because of headwinds from aging and slowing productivity growth. Automation investment is mainly in electric vehicles and new energy industries. Automation market competition is fierce for players, Chinese brands increase market shares against international brands due to lower cost, fast responding time and custom-tailor solutions. Most global brands adopt different pricing strategies that set China's price much lower than other regions to retain market share.
-
The forecast for growth in India has also been revised upward to 7.0% this year, reflecting carryover from upward revisions to growth in 2023 and improved prospects for private consumption, particularly in rural areas. With the electronics industry moving to the country, India is seeing increasing automation demand. For example, Apple doubled India’s iPhone production to USD 14 billion as it shifted from China, and automation suppliers are swarming into the country for new business opportunities.
-
Industrial automation has become increasingly essential for manufacturing companies to grow and prosper. Investments in industrial automation improve overall manufacturing business performance in many areas. Some technology trends are empowering innovation for industrial automation:
-
Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning. Properly applied AI and ML offer industrial companies enormous potential to significantly cut operating expenses, improve staff efficiencies, quality, productivity, and operations, and reduce maintenance and repair costs. AI technologies help achieve the goals of all industrial automation to increase productivity and efficiency. AI industrial applications properly designed with the right data can more effectively handle unforeseen scenarios in complex and rapidly changing environments based on patterns and trends in the data without being explicitly programmed for every possible scenario with little to no human interaction.
-
Hyperautomation: Hyperautomation is an advanced automation strategy for driving profound digital transformation and gaining a competitive advantage. It uses multiple technologies, tools, and platforms, including AI, ML, event-driven software architecture, robotic process automation (RPA), robotics, business process management (BPM), and low-code/no-code tool technologies.
-
In industrial manufacturing, hyper-automation is the digitalization and integration of the entire business, from plant process to business enterprise, including ERP, supply chain, logistics, and customer fulfillment.
-
-
Modular Design and Programming: Modular design and programming enable subject matter experts to create applications directly without writing code, resulting in superior-quality applications.
-
Industrial automation has many common functions and processes encapsulated in software modules and configured to meet application requirements. Industrial automation continues to move toward open-standard, modular-based design with standardization.
-
For example, JABIL designs and deploys proprietary Jabil Automation Gear (JAG) in its automation line, which is a flexible, modular, reconfigurable, and re-deployable automation platform.
-
-
Digital twins: The digital twin has become one of the most powerful concepts of Industry 4. 0. It is a higher level of closed-loop control that ideally incorporates all the factors of a manufacturing business that affect production efficiency and profitability, including incoming material quality, order flow, economic factors, customer orders, production plans, work-in-process (WIP) flows, and machine efficiencies. Digital twins are a virtual representation of a real-world process that is constantly updated with its real-time twin to achieve complete manufacturing closed-loop control that is optimized and responsive to changes.
-
Robotics: The cost and ease of use of robotics have changed dramatically, particularly with collaborative robots (cobots). The growing trend of modular industrial robot components, which can be used to assemble the optimal robot structures for different applications on an individual and flexible basis, is creating more possibilities. In addition, easy-to-use software tools allow people and plants to define robot actions without programming directly.
SUPPLY ANALYSIS
Most automation suppliers keep a pessimistic business forecast for the next few months due to weak demand, customer slow de-stocking situation, etc., while remaining optimistic for the mid-to-long term as they still believe industrial automation will play a big part in many industries. With increased production capacity and rather softening market demand, many suppliers provide short lead times and even ex-stock for some common parts.
- Lead time remains the same as last quarter:
- Industrial PC/PLC lead time is four to eight weeks,
- Robot lead time from six to eight weeks,
- Motion parts lead time of four to six weeks,
- Vision system lead time is around four weeks.
- Actuator lead time is around four weeks.
- For priority cases, lead time can be improved to two weeks, and some common parts are in stock.
-
Major Automation Industry Mergers and Acquisitions:
-
Stellantis N.V. spinoff Comau as part of its strategy. Stellantis N.V., one of the world’s largest automakers and mobility providers, and One Equity Partners (“OEP”), a middle market private equity firm, announced that OEP has signed a binding agreement to make a majority investment in Comau S.p.A. (“Comau”), a global technology company specializing in industrial automation and advanced robotics. The spinoff of Comau is part of the strategic agreement set during the merger between former FCA and Groupe PSA in January 2021 that formed Stellantis N.V. Financial terms of the private transaction were not disclosed. The transaction is expected to close by the end of 2024 and is subject to regulatory approvals and other customary closing conditions.
- Comau is a worldwide leader in delivering sustainable advanced automation solutions. With 50 years of experience and a global presence, Comau is helping companies of all sizes in almost any industry leverage the benefits of automation. Backed by a continuous commitment to designing and developing innovative and easy-to-use technologies, its portfolio includes products and systems for vehicle manufacturing, with a strong presence in e-mobility and advanced robotics and digital solutions to address rapidly growing markets in industrial sectors. The company’s offering also extends to project management and consultancy. Through the training activities organized by its Academy, Comau is committed to advancing the technical and managerial knowledge necessary to face the challenges related to automation and leverage the opportunities of a constantly changing marketplace. Headquartered in Turin, Italy, Comau has an international network of seven innovation centers and 12 manufacturing plants spanning 12 countries and employs 3,700 people.
-
Walmart and Fox Robotics Enter into Multi-Year Commercial Agreement
-
In April 2024 – Fox Robotics, the autonomous forklift company, announced that it had entered into a multi-year program agreement with Walmart after a 16-month proof of concept. Founded in 2017, Fox Robotics is leading the industry in autonomous pallet workflows to improve workplace safety and productivity in warehouses across the U.S. and Canada. The company develops, manufactures, and sells the world’s first autonomous trailer loader/unloader, the FoxBot. Fox Robotics is backed by some of the world’s most admired investors and companies, including BMW i Ventures, Walmart, Menlo Ventures, and Zebra Technologies. The program begins with rolling out 19 additional FoxBot autonomous forklifts across four high-tech Walmart distribution centers, with the potential for more, pending continued performance. As part of the partnership, Walmart also invested growth capital in Fox Robotics, obtaining a minority interest in the Company.
- The FoxBot forklift is the world’s first autonomous forklift designed to fully automate the warehouse loading dock. Since the company started selling its FoxBots in 2021, its installed base has autonomously processed more than 3 million pallet pulls for customers across North America. At the core of the FoxBot is a proprietary AI and machine learning system that serves as the robot’s brain, allowing it to make decisions dynamically and autonomously on everything from detecting pallet locations, stabilizing picked loads, and loading and unloading pallets with more care to avoid product damages commonly caused by manual forklifts.
-
-
AUTOMATION SUPPLIER UPDATES
Rockwell Automation to lay off 3% of the workforce
- Rockwell Automation will lay off 3% of its global workforce after announcing that sales have declined this year. That means roughly 900 employees will be cut.
-
The company had projected sales to grow between 0.5% and 6.5% but now expects losses between 4 and 6% for the year. Total sales in the second quarter of 2024 have declined by 6.5%, Rockwell CEO Blake Moret said on an earnings call on May 7. He said the company is “accelerating actions to bring costs in line.” “We will save USD 100 million in the second half of this year from accelerated actions being taken now, creating a beneficial starting point for fiscal year ’25,” Moret said. “We will see incremental savings of USD 120 million next year from these actions alone, plus a larger amount of additional savings from the more comprehensive program targeting sourcing, manufacturing, and SG&A (selling, general and administrative expenses),” he said. The company also said executives will not receive bonuses.
- Despite the good results in many of its usual businesses, Moret explained that Rockwell needs to reduce personnel to help offset persistently high inventories of its products—and subsequently lacking order—among machine-builder clients and other customers in the discrete and hybrid sectors it serves, such as automotive, e-commerce, food and beverage, and warehouse automation.
ABB Robotics and Discrete Automation order intake decreased by 19%
- The Robotics division recorded a slight positive order growth, supported by a positive development in the segments of general industry and warehouse logistics linked to consumer industries. This was, however, partially offset by the negative development in automotive and electronics.
-
Orders increased strongly in the Americas and declined at a single-digit rate in Asia, the Middle East, Africa, and Europe. Inventory levels in these channels are seemingly aligned with the current market situation.
-
Machine Automation orders declined sharply due to order normalization after earlier pre-buys and a softer underlying market. The division, which comprises approximately 1/3 of the business area revenues, is primarily exposed to the European market, where the machine builder segment is expected to remain under pressure for the remainder of this year.
-
ABB Robotics and Discrete Automation's Operational leverage on lower volumes put pressure on the Operational EBITA, which declined by 34% to USD 93 million, and the Operational EBITA margin, which dropped by 420 basis points YoY to 11.1%. • Lower production volumes triggered under-absorption of fixed costs in both divisions and the largest margin decline was recorded in Machine Automation.
-
Divisional mix hurt profitability as Machine Automation represented a lower share of revenues than last year. • In expectations of a challenging near-term market, Machine Automation has initiated cost actions to defend future profitability. Benefits from these measures are expected to start towards the end of this year.
-
Siemens to Hit Low End of Forecasts on Slow Automation Sales in Q3 2024
-
Factory automation, which has long driven growth in the Group, remains subdued—the recovery will take longer than expected. The reduction of customers' full inventories is dragging on, particularly in China. In addition, the resulting increase in competition is leading to price pressure in the region. The key Chinese market won’t improve until 2025. Orders in the automation businesses came in moderately lower in a challenging market due to ongoing elevated stock levels at customers.
-
The German manufacturer has set a minimum goal of comparable revenue growth of 4% for the group during fiscal 2024 ending in September. Digital Industries’ margin is expected no lower than 18%. The company had revised down its outlook for the unit in May after disappointing demand in China, with a global consumer pullback becoming more entrenched since. “We still have a muted market for automation,” Chief Executive Officer Roland Busch said in an interview with Bloomberg Television, adding that he expects the important Chinese market to improve next year, but “slowly.” Industrial companies are contending with weak business in China, where a deepening real estate crisis is weighing on spending and dragging down economic growth. Swiss rival ABB Ltd. last month reported a decline in orders for automation products in China, saying business in the country “continues to be negative overall.” Like ABB, Siemens said demand for electrification, such as from data centers, remained high.
PRICING TRENDS & INSIGHTS
Global commodity prices remain flat due to tightened monetary policy.
-
The Federal Reserve Open Market Committee (FOMC) held the federal funds rate steady at its current target range of 5.25% to 5.50%. While recent economic indicators show continued growth, the Committee remains cautious about inflation pressures.
-
Job gains have moderated, and the unemployment rate has risen slightly, though it remains low. Inflation has shown signs of easing but remains above the Fed's 2% target. The FOMC will continue to monitor economic data and assess the appropriate course of action for monetary policy.
-
-
Steel and copper are primary raw materials used in many types of automation parts, and changes in steel and copper prices can affect the prices of these parts.
-
Copper prices have increased 10% over the past 12 months. Copper is estimated to account for 5% of the total robot cost.
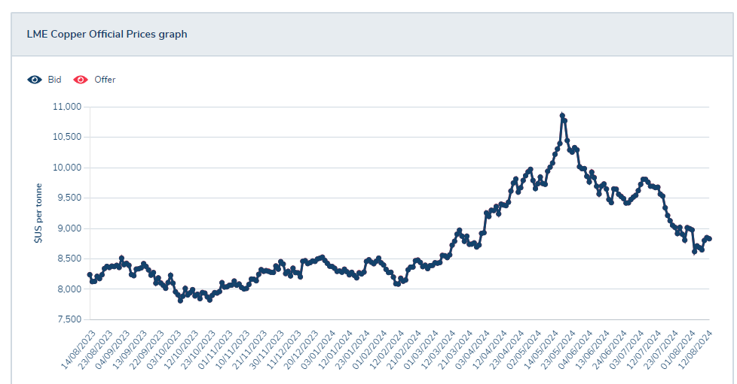
- Steel prices have fallen by 14% over the past 12 months. Steel is estimated to account for 10% of the total robot cost.
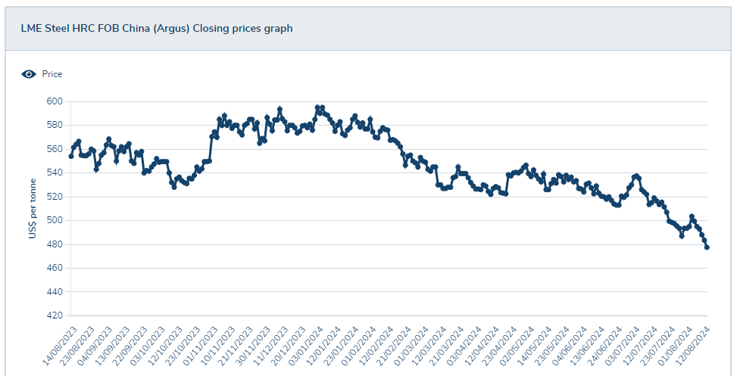
- Although copper prices increase and labor costs are generally increasing due to inflation, Automation part prices remain flat or even in a downtrend. Fierce competition in a soft market to retain market share and absorb underutilized factory capacity all lead to price reduction pressure. Automation suppliers find it difficult to pass on cost increases to the end customer and have to absorb them.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
-
Short-term Market Challenges: The global industrial automation market faces short-term challenges driven by weak demand and slow customer de-stocking, particularly in Europe and China. However, the long-term outlook remains positive, with expectations of continued growth as demand stabilizes.
-
Sector-Specific Investments: High levels of automation investment continue in the automotive (especially EV) and electronics sectors, with significant activity in Asia and the Americas. This trend is expected to drive incremental growth despite current market softness.
-
Commodity Pricing and Cost Pressures: Despite increased copper prices (+10%) and ongoing inflationary labor costs, automation part prices remain flat or slightly down due to fierce competition, excess production capacity, and suppliers absorbing cost increases to retain market share. This has created a favorable buyer's market for negotiations.
-
Stable Lead Times with Some Stock Availability: Lead times for key automation components have remained consistent since the previous quarter, with some suppliers offering short lead times or even ex-stock availability for commonly used parts. This ensures continuity in supply despite market pressures.
Additional Insights:
-
Major industry mergers and acquisitions, such as Stellantis' spinoff of Comau, suggest ongoing market consolidation and a focus on advanced automation solutions.
-
The Walmart-Fox Robotics partnership highlights the rising adoption of autonomous solutions for improved warehouse efficiency and productivity.
-
The challenges faced by automation giants like Rockwell Automation and ABB emphasize the need to adapt to changing market dynamics.
CAPEX, MRO, INFRASTRUCTURE
Warehouse Automation
OVERVIEW
The warehouse automation market is experiencing significant transformation driven by technological advancements, shifting labor dynamics, and evolving consumer behaviors.
The current landscape: As of 2023, the global warehouse automation market stands at an impressive USD 16.15 billion. But that's just the beginning. This sector is on a remarkable growth trajectory, with forecasts indicating a robust compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 19.4% over the coming years. This surge is a testament to the transformative changes happening within the industry.
At its core, warehouse automation refers to using technology to enhance and streamline warehouse operations. This involves automating various activities, from inventory handling to internal processes and outbound shipments.
The Benefits of Automation
Integrating sophisticated software and advanced technologies like robotics, sensors, and data analytics is at the heart of this transformation. The benefits of adopting warehouse automation include:
-
Efficiency: Automated systems significantly improve operational efficiency, reducing the time and labor required for various tasks.
-
Accuracy: Automation enhances inventory management and order fulfillment accuracy by minimizing human error.
-
Cost Savings: Over time, automation can lead to substantial cost reductions by optimizing resource allocation and minimizing operational disruptions.
-
Scalability: Automated systems can easily scale to accommodate growing business needs, making it easier to adapt to fluctuating demand.
The warehouse automation market is undergoing a major shift driven by technological advancements, changing labor dynamics, and evolving consumer behaviors. As we look to the future, the integration of cutting-edge technologies will continue to redefine warehouse operations, leading to increased efficiency, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness.
MARKET DYNAMICS
This sector is characterized by its fast-paced technological advancements and a significant rise in demand, primarily driven by the growth of e-commerce and labor market challenges.
Current Landscape of Warehouse Automation
-
Technological Advancements: The field of warehouse automation is advancing at an unprecedented rate. Innovations in robotics, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things enhance operational efficiency and performance. These technologies are not just incremental improvements but represent transformative shifts in warehouse operations.
-
E-commerce Growth: The rise of online shopping has dramatically increased order volumes and expectations for rapid delivery. Automation helps companies meet these demands by streamlining processes, managing inventory more effectively, and improving order accuracy.
-
Labor Market Challenges: Elevated labor costs and a shortage of skilled workers are pushing companies toward automation. By investing in automated solutions, businesses can reduce their reliance on manual labor, address labor shortages, and control costs more effectively.
-
Regulatory and Environmental Concerns: Companies also use automation to tackle regulatory and environmental issues. Automated systems can help ensure compliance with regulations and reduce the environmental impact of warehouse operations by optimizing energy use and minimizing waste.
DEMAND TRENDS & FORECASTS
Threat of New Entrants
The threat from new entrants or substitutes is relatively low. This is due to the market's division, established economies of scale, and the specialized knowledge required for designing, implementing, and integrating complex automation systems.
-
The warehouse automation market is rapidly advancing due to key drivers such as warehouse expansion and the need for labor cost reduction. The competitive landscape is characterized by demands for precision and speed, challenges related to adoption and branding, and strong supplier dynamics.
-
Continued innovation and strategic investment are crucial for navigating this evolving landscape. As technology progresses and market conditions shift, staying ahead of these trends will be essential for capitalizing on opportunities and maintaining a competitive edge.
-
The warehouse automation market is set for remarkable expansion, with significant growth in MRO services, Automated Guided Vehicles/Autonomous Mobile Robots (AGV/AMR), and picking services. Despite a slowdown in storage systems and WMS, the sector's future, with robust growth projections, looks promising. The competitive landscape emphasizes precision and rapid response, while challenges like slow technology adoption and high initial costs persist. Regional dynamics reveal strong growth in APAC, stable growth in North America, and moderate expansion in Europe, with varying market shares and investment opportunities across regions.
SUPPLY ANALYSIS
The global warehouse automation sector is characterized by a diverse supply base, encompassing over 700 companies that offer a broad spectrum of specialized solutions. Here's a detailed overview of the key segments and players in the industry:
Automated Guided Vehicles/Autonomous Mobile Robots (AGV/AMR):
-
Number of Companies: Approximately 200
-
Key Players:
- MIR: Specializes in flexible AGVs for various applications.
- Geek+: Known for its versatile AMRs and robotics solutions.
- Omron: Offers a range of AGVs with integrated safety features.
- Kuka: Provides advanced robotics and AGV solutions for complex environments.
- Market Characteristics: AGV/AMR solutions are increasingly integral to warehouse operations, supporting automation in material transport and logistics.
Material Handling Solutions:
Number of Companies: Around 90
-
Key Players:
- Dematic: Leading provider of comprehensive material handling solutions.
- Opex: Known for its innovative sorting and handling systems.
- Daifuku: Offers a broad range of material handling technologies.
- Kardex: Specializes in automated storage and material handling systems.
- SSI Schafer: Provides robust material handling solutions and systems integration.
Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (ASRS):
Number of Companies: Approximately 80
-
Key Players:
- Dematic: Offers a range of ASRS solutions for diverse storage needs.
- Opex: Provides automated systems for high-density storage.
- Daifuku: Known for scalable ASRS technologies.
- Swisslog: Delivers advanced ASRS solutions for various industries.
- Vanderlande: Specializes in high-performance ASRS systems.
- Jungheinrich: Offers efficient ASRS solutions for large-scale operations.
Warehouse Drones and Automatic Truck Loading Systems:
-
Number of Companies: Around 10 each
-
Key Players:
- Siemens: Provides solutions for automatic truck loading and warehouse drones.
- Honeywell: Offers advanced technology for warehouse drones and automated loading systems.
The global warehouse automation market is supported by a broad and diverse supply base, with numerous companies specializing in different segments. Although key players offer comprehensive solutions, their global reach varies, with regional coverage is more prevalent. Recent improvements in lead times have positively impacted market dynamics, aligning with investor targets and enhancing overall market efficiency. As the sector evolves, these trends will drive further growth and innovation in warehouse automation solutions.
-
Regional vs. Global Coverage: While major players offer end-to-end solutions, their coverage is often more robust regionally than globally. Many companies excel in providing comprehensive solutions within specific regions but may lack the global infrastructure to deliver the same level of service worldwide.
-
Lead Times and Investor Targets: Lead times across regions have improved significantly in recent months, reflecting enhanced operational efficiencies and better alignment with investor expectations. This improvement indicates the sector's ongoing efforts to meet growing demand and streamline implementation processes.
-
Diverse Supply Base: The warehouse automation sector benefits from a wide range of specialized suppliers, each focusing on different aspects of warehouse operations. This diversity allows for a variety of solutions tailored to specific needs.
Regional Insights
Asia-Pacific
- Growth Dynamics: APAC remains one of the highest-growth regions in the warehouse automation sector. Significant developments are occurring in India and China, where local representation of major suppliers in India is making installation and maintenance more cost-effective. Furthermore, government initiatives such as "Make in India" actively support sector growth.
- Market Leadership: China and the broader APAC region dominate the warehouse robotics market. This trend is expected to continue, with APAC predicted to be the fastest-growing region in the next 3 to 5 years.
North America
- Market Size: North America accounts for approximately 26.5% of the global warehouse automation market. The market size is projected to grow from USD 6.9 billion in 2024 to USD 14.9 billion by 2029, reflecting a robust compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 16.5%.
- Adoption Rates: The United States leads in automation adoption, with over 20% of warehouses utilizing automated systems. This high level of adoption underscores North America's significant role in driving the market.
Europe
- Market Size and Growth: Europe's warehouse automation market is estimated at USD 3.75 billion and is expected to grow to USD 7.25 billion over the next five years, with a CAGR of approximately 14.5%.
- Key Players: Germany and the Netherlands are prominent players in the European market, serving as major logistics hubs. Italy is also emerging as a key player, contributing to Europe's overall growth.
Latin America, Middle East, and Africa
- Market Share: These regions hold a smaller portion of the market but are experiencing ongoing developments and gradual growth. The pace of expansion varies, with each region progressing at its rate.
Supplier Commentary
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGV) / Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMR)
- Key Players: MIR, Geek+, Omron, and Kuka lead the AGV/AMR segment. These solutions are increasingly essential for material transport and logistics within warehouses.
Material Handling Solutions
- Key Players: Major providers include Dematic, Opex, Daifuku, Kardex, and SSI Schafer. These companies offer comprehensive solutions to optimize warehouse efficiency and throughput.
Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (ASRS)
- Key Players: Dematic, Opex, Daifuku, Swisslog, Vanderlande, and Jungheinrich are prominent in the ASRS market. ASRS technologies are crucial for maximizing storage density and retrieval speed.
Warehouse Management Systems (WMS)
- Key Players: Leading software vendors in this segment integrate automation solutions to enhance warehouse operations, including inventory management and order processing.
Navigation and Robotic Software
- Key Players: Companies specializing in navigation and control software play a crucial role in improving the accuracy and efficiency of warehouse robotic systems.
Automatic Identification and Data Capture (AIDC), Machine Vision, Imaging, and Wireless Technology
- Market Dynamics: These technologies support essential functions such as inventory management and data transmission, contributing to streamlined operations.
Micro Fulfillment and Piece Picking Robots
- Market Dynamics: These specialized robots cater to the growing demand in e-commerce for efficient micro-fulfillment centers and piece-picking applications.
Warehouse Drones and Automatic Truck Loading Systems
- Key Players: Siemens and Honeywell are notable players providing solutions in these emerging areas, offering innovative tools to enhance warehouse operations.
Supply Base and Global Coverage
- The warehouse automation sector benefits from a broad spectrum of specialized suppliers, each focusing on different aspects of warehouse operations. This diversity allows for tailored solutions that address specific needs.
- While many key players offer end-to-end solutions, their coverage tends to be more robust regionally than globally. This regional focus can affect the level of service provided worldwide.
- Recent improvements in lead times reflect better operational efficiencies and alignment with investor expectations. This progress indicates the sector's ongoing efforts to meet growing demand and streamline implementation processes.
PRICING TRENDS & INSIGHTS
The warehouse automation sector has experienced stable pricing conditions over the past quarter, but there are notable regional variations in negotiation power. The landscape continues to evolve with shifting financial structures, ROI expectations, and market growth potential.
-
Suppliers increasingly offer flexible payment arrangements, such as long-term closed-end leases (three to five years). These alternatives to large upfront investments are becoming more common.
-
Such flexible structures help enhance cash flow management for investors, making it easier to integrate automation solutions without substantial initial outlays.
-
High-Volume Operations: ROI for high-volume automated warehouse operations typically ranges between 18 and 60 months. This variation depends on the solutions implemented and the complexity of transitioning from manual to computerized systems.
APAC (Asia-Pacific) Region
-
In APAC, buyers currently hold a stronger negotiating position. This advantage influences prices and leads to more favorable payment terms for automation solutions.
-
Buyers' negotiating power in APAC contributes to competitive pricing and enhances investment conditions, leveraging the region's robust growth in warehouse automation.
EMEA (Europe, Middle East, and Africa) and the Americas
-
In contrast, buyers in EMEA and the Americas face limitations in negotiating prices and payment terms. Recent minor cost increases reflect broader market trends and inflationary pressures.
-
Despite these challenges, the slight price adjustments indicate the ongoing market dynamics and economic factors affecting the sector.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
-
Growth Potential: AGVs/AMRs are expected to grow significantly due to their role in improving material transport efficiency.
-
Market Projection: ASRS is projected to grow, offering substantial benefits in space utilization and labor cost reduction.
-
Growth Rate: The robotics segment is experiencing a high growth rate, with a CAGR of approximately 17.7%, underscoring its critical role in warehouse automation.
-
Fastest Growth: The Asia-Pacific region is poised for rapid growth, with substantial expansion opportunities in countries like China, India, Vietnam, and Malaysia. Local representation of major suppliers enhances cost-effective installation and maintenance.
-
Market Share: North America holds approximately 26.5% of the global market share, with continued growth driven by high automation adoption rates in the U.S. and Canada.
-
Moderate Growth: Europe is expected to grow moderately, with key players in Germany and other logistics hubs increasing interest in automation due to high labor costs.
-
Regional Variations: APAC buyers have stronger negotiating leverage than those in EMEA and the Americas. Suppliers are adapting by offering flexible payment options.
-
Impact on EMEA: In EMEA, currency volatility affects price predictability and investment decisions.
-
Opportunity: With only 20% of warehouses automated, there is significant room for growth and investment in automation technologies.
-
Trends: Suppliers are offering flexible payment structures, such as long-term leases, to improve cash flow management for investors.
-
Market Leaders: Major global players like Dematic, Daifuku, Honeywell, and Kuka dominate. Despite a competitive landscape, no single player offers comprehensive global coverage, highlighting regional strengths.
-
Focus Areas: Continued innovation in robotics, software, and automation solutions is essential. Companies are increasingly emphasizing software development and customized solutions.
-
Advancements: Advances in robotics, software, and navigation systems are driving the sector forward. Emerging technologies like micro-fulfillment robots, piece-picking robots, and automated drones contribute to market growth.
DEMAND COMMENTARY
- The global warehouse automation market is categorized by technology, industrial vertical, and region.
- Major global players in the market possess comprehensive portfolios, either independently or through collaborations with specialist subcontractors, which provide them with a significant advantage in service levels over smaller local or regional competitors.
- Market analysis and predictions indicate substantial growth in MRO services, AGV/AMR, and picking services sectors, with expected triple or double increases in market share over the next 3-5 years.
- Conversely, growth in storage systems and WMS activities is projected to slow down, with increases expected to be less than 70-80% compared to current market shares.
- Two primary growth drivers behind this trend include a rapid increase in warehouses and rising demand to reduce labor-related expenses.
- The competitive landscape necessitates precise accuracy and rapid response times in operations.
- Challenges include the slow adoption of automation technologies and the high initial investment required for robotics and operating 'dark' warehouses.
- Despite the advantages of automation solutions, such as flexibility, ROI, and reliability in breakdown situations, investors remain less familiar with them due to the sector's relatively weak branding effort.
- Despite the market expansion, negotiation power remains largely with suppliers, with procurement power fluctuating between low and medium.
- Top 6 suppliers maintain confidence in their capabilities, offering long-term value-added services to ensure profitability stability.
- Cost negotiation continues to pose challenges, and no significant changes have been observed.
- The threat of new entrants or substitutes is low due to market division, established companies' economies of scale, and the specialized knowledge required in design, implementation, operation, and integration.
- The global warehouse automation systems market:
- Valued at USD 14 billion in 2022, USD 22 billion in 2023, and expected to reach USD 25.7 billion in the current year.
- Projected to grow to approximately USD 54.5 billion by 2029, at a CAGR of around 16.2%.
- Forecasts suggest a remarkable increase to approximately USD 80-90 billion by 2030.
- Key segments include:
- Racking systems, including Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (ASRS), are software-controlled storage systems that enhance warehouse efficiency.
- The market is forecast to grow at a CAGR of approximately 12.6% over the next five years, from USD 16.25 billion to USD 30 billion by 2029.
- APAC remains the fastest-growing market segment in this category.
- Robotics in warehousing demonstrates an impressive CAGR of approximately 17.7%.
- Last year, the market was valued at around USD 6.5-6.7 billion and is anticipated to grow to approximately USD 15 billion by 2028.
- This growth solidifies robotics' strong global position and promising future in warehousing.
- Robotics market leaders include ABB Limited, Amazon Robotics LLC, and Honeywell Integrated.
- Packing segments, despite maturity, show the lowest vendor growth with a CAGR below 3%.
- Picking robotics vendors experience higher growth, approximately 25% CAGR.
- AGV/AMR (Automated Guided Vehicles/Autonomous Mobile Robots) represents a robust market with an 11.5% CAGR, forecasted to reach approximately USD 18.5 billion by 2028, indicating significant attractiveness for investment.
- APAC's growth centers around Vietnam and Malaysia are experiencing significant expansion opportunities.
- Local representation of major suppliers represents a significant advantage for automation solutions and ensures cost-effective installation and maintenance.
- India has emerged as a strong player in recent years, driven by growing interest in its manufacturing capabilities and improving infrastructure.
- India lacks dominant suppliers in automation, resulting in stronger negotiation power for buyers and intense competition among suppliers.
- Increasing supplier interest in India, supported by government initiatives like "Make in India" programs, will support the growth of its manufacturing sector.
- Currently, APAC and China dominate the warehouse robotics market and have the largest market share.
- The region is predicted to be the fastest-growing in the next 3-5 years, driven by strong adoption in South Korea, Japan, and China, which are eager to adopt new technologies. Jabil has established a robust presence in Malaysia and Vietnam.
- Market projections suggest the warehouse automation market could reach USD 10.5-10.75 billion by the end of this year, with a projected CAGR of 17.25%, reaching USD 23.75-24 billion by 2028.
- In Europe, despite widespread interest in efficient solutions, the warehouse robotics market remains relatively subdued.
- Key players such as Germany, the Netherlands, and other logistics hubs are more actively discussing new systems and warehouses.
- Suppliers are predominantly concentrated in the UK, Germany, and France, with Italy emerging as a growing player offering diverse solutions with reliable backgrounds.
- The market size for this region is approximately USD 3.75 billion, projected to grow to USD 7.25 billion over the next 5 years, reflecting a CAGR of approximately 14.5%.
- In North America, including the U.S. and Canada, the warehouse automation market accounts for approximately 26.5% of the global market, with an estimated USD 6.9 billion in 2024.
- This market share is expected to remain stable over the next 5 years, reaching USD 14.9 billion by 2029 at a CAGR of 16.5%.
- The retail sector continues to expand, fueled by the growing popularity of online shopping, which has become increasingly prevalent following lifestyle changes post-COVID-19.
- Adopting robotics in warehouses has bolstered business operations and effectively met customer demands.
- Rapid response times and cost-effective material management are crucial for business success.
- In the U.S., over 20% of warehouses now utilize automated warehousing equipment and systems.
- Customers benefit from a competitive market landscape that offers diverse pricing and solutions.
- However, market dynamics are becoming increasingly fragmented due to major global players such as Dematic Group, Daifuku Co. Limited, Swisslog Holding AG, and Honeywell Intelligrated.
- Europe is following American trends with a significant rise in e-commerce and automation demand due to high labor costs.
- Major global players are actively present in the European warehouse automation market despite potentially higher costs compared to the Americas or Asia
- The European market is estimated to reach USD 4.28 billion in 2024 and is projected to double by 2029, with a CAGR of approximately 14.5% over the next five years.
- Forecasted benefits include up to 85% savings in warehouse footprint and up to 65% reduction in operational costs.
- Globally, only about 5% of warehouses are fully automated, indicating substantial growth potential.
- DHL reports that 80% of its warehouses remain manually operated, with Europe's slightly higher level at around 15% automation.
- Germany stands out as one of the largest users of automated solutions globally.
- Market concentration in Europe is moderate, with representatives exhibiting medium competitiveness compared to other regions.
- Automation trends are shifting towards software and service solutions over hardware-centric approaches.
- Initially, there was a strong emphasis on installing systems and investing in robotics, but the focus has now turned towards software optimization.
- Understanding and enhancing software capabilities, including upgrades and module introductions, is crucial to maximize system benefits.
- Advanced systems have analytics capabilities to optimize material movements and pick-ups by identifying the shortest and fastest routes.
- There is a growing anticipation for increased interest in software development and customized programs tailored to specific needs.
- •APAC, India, and China continue to exhibit the highest growth rates among regions, while Europe and the USA show moderate growth.
- In terms of market share distribution:
- North America and Europe hold slightly less than half of the market share.
- APAC accounts for approximately one-third of the market share.
- The remaining market share is divided among LATAM, the Middle East, and Africa.
SUPPLIER COMMENTARY
- Over 700 companies operate in the global warehouse automation sector, offering a wide range of specialized solutions:
- Approximately 200 companies focus on Automated Guided Vehicles/Autonomous Mobile Robots (AGV/AMR), with key players including MIR, Geek+, Omron, and Kuka.
- Around 90 companies specialize in Material Handling Solutions, with leaders such as Dematic, Opex, Daifuku, Kardex, and SSI Schafer.
- Around 80 companies provide Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (ASRS), offering opportunities through Dematic, Opex, Daifuku, Swisslog, Vanderlande, and Jungheinrich.
- Approximately 50 companies focus on Warehouse Management Systems (WMS).
- About 40 companies specialize in Navigation and Robotic Software.
- Around 30 companies each are involved in Automatic Identification and Data Capture, Machine Vision, Imaging, and Wireless Technology.
- Roughly 20 companies each focus on Micro Fulfillment and Piece Picking Robots.
- About 10 companies are engaged in Warehouse Drones and Automatic Truck Loading Systems, with solutions offered by Siemens and Honeywell.
- The supply base is diverse, but key partners cannot provide comprehensive hardware solutions globally.
- Major players offer end-to-end solutions, yet regional coverage is more prevalent than global coverage.
- Lead times across regions have become more acceptable recently, meeting investor targets and reflecting significant improvements in recent months.
PRICING SITUATION
- There have been no significant changes in this area since last quarter, with negotiation power varying by region:
- In APAC, buyers hold the negotiating advantage, impacting prices and favorable payment terms.
- In EMEA and the Americas, buyers cannot influence prices, terms, or payment conditions, though slight increases have been observed recently.
- Suppliers are increasingly open to flexible payment structures, including long-term closed-end leases (3 or 5 years) as alternatives to upfront investments, enhancing cash flow management for investors.
- Typical ROI expectations for high-volume operations in automated warehouses range between 18 and 48 months, influenced by selected solutions and the complexity of transitioning from manual to automated operations.
- Implementing Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS) can reduce shopfloor area utilization by 60-80% (depending on building conditions) and cut labor costs by up to 50%.
- Currency fluctuations, particularly in the EMEA region, contribute to market price unpredictability.
- Despite high interest and readiness for automation, only approximately 20% of warehouses are currently automated, indicating substantial growth potential for the automation market.
- ROI calculations remain a critical criterion in warehouse automation decisions, and returns are improving as manual labor costs continue to rise.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- Maintaining a diverse Approved Vendor List (AVL) remains our recommended strategy, providing Requesters with enhanced commercial competitiveness, reliable supply access, and increased leverage.
- AVL implementation offers additional benefits over time, facilitating smoother maintenance, software upgrades, and system integrations with existing infrastructure and automated solutions.
- When defining specifications, prioritize Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to leverage advanced technologies, which can significantly improve accuracy in stocktaking and picking and enhance material traceability.
- Automation initiatives often focus on reducing labor dependency; however, strategic process improvement should be the primary goal, naturally leading to reduced headcount.
- Considering the unique variances in buildings, materials, warehouse layout, and operational needs, strategic planning is crucial, necessitating tailored and customized warehouse automation solutions.
- Suppliers have slightly improved response times and lead times, approaching pre-COVID conditions.
- ASRS and Conveyor systems remain highly beneficial in warehouse applications, and there is increasing interest in small parts storage and KIT management.
- The demand for efficient warehouse automation solutions continues to rise, highlighting the global importance of robust maintenance capabilities.
- Ensuring the availability of spare parts and skilled technicians is crucial; consider multi-year agreements at fixed rates to mitigate potential ROI impacts from unforeseen cost increases.
- Software management is critical; secure long-term IT support to ensure business continuity and leverage market intelligence to negotiate based on factual insights
CAPEX, MRO, INFRASTRUCTURE
MRO
MARKET DYNAMICS
Competitive Dynamics and Technological Innovations in the MRO Market
-
The Maintenance, Repair, and Operations (MRO) market is a crucial segment within manufacturing, ensuring smooth equipment and process operations. Similar trends affecting other manufacturing sectors, such as technological advancements and sustainability, influence this market. Automation and robotics, already transforming packaging, are now enhancing efficiency and cost-effectiveness in MRO activities. The push for eco-friendly materials in packaging mirrors the growing demand for sustainable MRO solutions that balance performance with environmental impact.
-
The MRO sector also adapts to broader manufacturing trends like digitalization and innovation. Integrating IoT and AI improves maintenance predictions and repair schedules, reflecting a shift toward data-driven decision-making. Innovations in materials and methods, similar to Jabil’s BluPrint coating technology, enhance equipment durability and reliability, aligning to reduce downtime and boost operational efficiency.
-
Companies should focus on cost management, operational efficiency, and sustainability to address challenges such as inflation, reduced consumer spending, and high interest rates. Adopting a Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) approach can uncover long-term savings opportunities. Leveraging technology and automation can optimize processes and reduce downtime while consolidating suppliers, forming strategic partnerships, enhancing pricing, and minimizing supply chain risks. Embracing sustainable practices drives efficiency and meets the expectations of eco-conscious consumers.
-
Companies should deliver value through personalized experiences and high-quality products in response to shifting consumer behavior. Analyzing consumer data can help tailor offerings and identify niche markets with strong demand. Effective financial management is crucial in a high-interest-rate environment to maintain liquidity and minimize debt. By implementing these strategies, companies can build resilience and position themselves for growth despite economic uncertainties.
-
The BluPrint coating technology, which utilizes Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD), marks a notable advancement in metal finishing. Applied after cutting apertures, this method enhances both performance and durability. It generates partially ionized metal vapor, which reacts with gases to form a thin, uniform metal-based film on the substrate. This process, conducted within an inert argon environment in an atomic reactor, deposits the coating atom by atom, ensuring precise and consistent coverage. The result is a finish that is highly resistant to harsh chemicals and abrasives, providing a durable bond that enhances the longevity and reliability of the coated materials.
-
BluPrint technology offers several key benefits that contribute to its superior performance. It improves paste release in miniature components, increases process repeatability, and extends intervals between stencil cleanings. The technology also enhances printing speed, reduces squeegee pressure, and decreases the frequency of stencil washings. BluPrint significantly improves first pass yield from 80% to 95%, with design enhancements reaching up to 100%. Additionally, it extends stencil cleaning intervals from every four to every 16 hours, thereby reducing maintenance frequency and enhancing overall operational efficiency.
DEMAND TRENDS & FORECASTS
It is important to understand the critical factors that shape the market dynamics in the manufacturing sector for packaging innovations.
- Technological advancements are advancing the development of more efficient and adaptable packaging methods.
- Sustainability trends are driving the adoption of eco-friendly materials and practices.
- Regulatory changes are impacting packaging design and materials, and
- Shifting consumer preferences guides the industry towards greater convenience and functionality solutions.
- Staying competitive in this rapidly evolving landscape requires a thorough understanding of these dynamics.
The Trends in Packaging Innovation
The chart below illustrates trends in packaging innovation from 2018 to 2024, highlighting five key areas:
- Sustainability: This has seen remarkable success, reaching unprecedented levels of adoption by 2024, a promising sign for the future of our industry.
- Digitalization: This shows a steady increase, reflecting the growing integration of digital technologies in packaging.
- Design Innovation: It also exhibits a notable rise, focusing on enhancing the consumer experience and creating emotional connections.
- Automation and Robotics: This has progressed considerably, improving efficiency and reducing costs in packaging production.
- Personalization and Augmented Reality: Although they started later, they have experienced accelerated growth, driving more immersive and personalized shopping experiences.
These trends highlight a clear shift towards adopting advanced technologies and sustainable practices in the packaging industry. In this area, buyers should actively seek to develop projects to enhance the performance of existing materials.
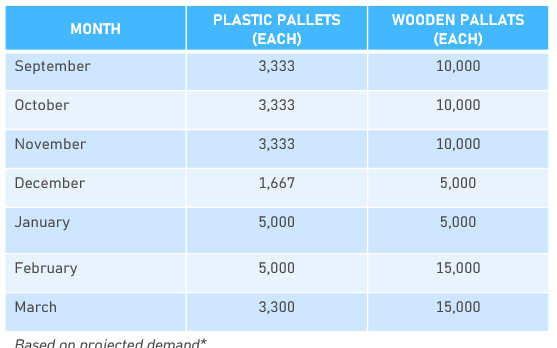
- As noted above, one of the key innovations is the implementation of plastic pallets in warehouses. This initiative exemplifies how leveraging these emerging technologies can improve performance and efficiency in packaging operations.
-
The charts below illustrate the hypothetical projected demand for the project, revealing a significant trend toward the use of plastic pallets.
-
This shift is driven by plastic pallets' superior maintenance benefits and extended service life, which are perceived as more advantageous despite their higher initial cost.
SUPPLY ANALYSIS
Key Dynamics Shaping Packaging Innovations in Manufacturing
-
In the evolving MRO supply landscape, companies increasingly focus on supply chain resilience and strategic partnerships to navigate market complexities. Suppliers are enhancing their competitiveness through technological advancements, such as advanced stencil technology, and their supply chain strategies are reassessing to ensure steady product availability and cost stability. For example, suppliers like Fastenal and MSC are leading the way with onsite programs that offer integrated and responsive service, streamlining MRO processes and reducing the total cost of ownership.
-
The market is also witnessing a notable shift towards sustainability and digital transformation. Adopting digital tools like predictive maintenance platforms and AI-driven inventory management systems improves demand forecasting and minimizes supply chain disruptions. Simultaneously, emphasizing sustainable materials and energy-efficient solutions is becoming a key differentiator as companies focus on corporate social responsibility. Suppliers integrating these elements meet regulatory requirements and position themselves as valuable partners in achieving long-term operational and environmental goals. Balancing innovation with sustainability is essential for thriving in the competitive MRO market.
-
The manufacturing sector, crucial to the global economy, faces significant environmental challenges, particularly concerning resource use and waste production. To address these, buyers are aligning with key environmental and social issues. Our approach involves collaborating with stakeholders and suppliers to minimize environmental impact while promoting innovation and sustainability.
-
In the MRO industry, emphasizing packaging innovations is vital for improving efficiency, sustainability, and customer satisfaction. By partnering with suppliers who provide biodegradable and recyclable materials, we aim to reduce landfill waste and support a circular economy. Initiatives like smart warehouses and the use of cutting-edge materials underscore our commitment to sustainable and efficient operations. These efforts also offer suppliers opportunities to contribute through smart packaging and QR code solutions, further advancing sustainability objectives.
Innovations in Stencil Technology
- For example, Stentech’s BluePrint coating technology represents a significant leap in metal finishing. Using Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD), this technology applies a durable metal-based coating atom by atom, providing exceptional precision and longevity. BluePrint enhances paste release in miniature components, improves process repeatability, and extends stencil cleaning intervals, making it a crucial innovation for modern manufacturing and significantly improving both efficiency and reliability.
PRICING TRENDS & INSIGHTS
-
Companies effectively manage rising costs and supply chain complexities in the current MRO pricing environment. Jabil is leading efforts to streamline certification processes for alternative products at its Healthcare sites. By strengthening supplier relationships and leveraging digital tools like blockchain, Jabil aims to expedite certifications, reduce delays, and cut costs. This proactive approach is vital for integrating alternative products efficiently in a market where cost control and compliance are critical.
-
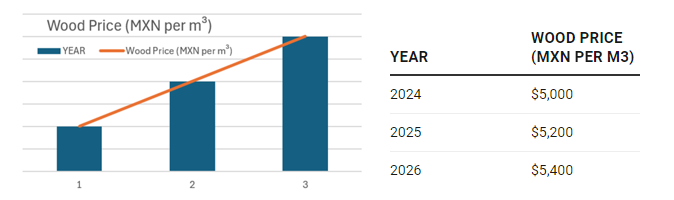
External factors, including global supply chain disruptions and local market dynamics, also affect MRO pricing. For instance, the pallet wood market in Mexico is experiencing significant price hikes due to international competition, environmental issues, and logistical challenges. These factors increase costs for essential materials like wood pallets, impacting operational expenses and supply chain efficiency. To stay competitive, companies must adapt by consolidating purchases, using recycled materials, and negotiating better supplier terms.
-
A comprehensive approach to cost management, focusing on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), has become essential. TCO evaluates all expenses associated with a product or system throughout its lifecycle, including purchase, operation, maintenance, and replacement. This approach clarifies long-term financial impacts and helps organizations make informed, sustainable investments that align with their strategic objectives. By focusing on TCO, companies can uncover opportunities for savings, reduced maintenance needs, and lower environmental impacts.
-
Organizations are increasingly adopting cost-effective alternatives like generic or reconditioned products, which can offer up to 30% savings compared to branded or new items. However, implementing these alternatives requires careful planning, quality control, and effective change management to meet performance standards and manage potential supply chain disruptions.
-
Strategic sourcing and supplier relationship management are also utilized to negotiate better terms with MRO suppliers. Consolidating purchases and establishing long-term partnerships can leverage economies of scale and improve pricing. Despite these efforts, challenges related to certifications for new alternative products, especially in healthcare, persist. These challenges result in delays and bottlenecks, necessitating improved supplier relationships and streamlined certification processes. Enhancements in communication, digital certification tools, and blockchain technology are being explored to address these issues and accelerate product integration.
-
In 2024, the pallet wood market in Mexico faces substantial price increases due to a combination of global and local factors. According to the European Federation of Wooden Pallet and Packaging Manufacturers (FEFPEB), rising wood prices are driven by a Russian ban on log exports, intense international competition, environmental issues like bark beetle infestations, and logistical challenges such as shipping container disruptions. Locally, high pallet demand, driven by logistics needs and sustainability practices, exacerbates the price surge. Forecasts suggest prices will continue to rise due to competition for recycled materials, impacting operational expenses and supply chain efficiency for companies relying on pallet wood.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- The MRO market increasingly adopts smart machines and onsite programs to enhance inventory management, leveraging vending point-of-use solutions and vertical storage units to address control process challenges.
- MRO suppliers face challenges such as navigating complex regulations, controlling costs while maintaining safety and quality, and improving supply chain resilience in response to global disruptions.
- Advanced inventory management systems lead to substantial Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) savings, boosting competitiveness and allowing strategic resource allocation.
- PLP technology revolutionizes stencil roll cleaning, significantly enhancing screen printer maintenance.
- A major benefit of PLP technology is the 50% reduction in solvent usage, eliminating waste and boosting efficiency.
- The global packaging market, valued at USD 6.65 billion in 2015, is expected to grow at a CAGR of 8.91% from 2016 to 2024, driven by the increasing use of smart packaging and the growing outsourcing trend among companies.
- Fastenal and MSC are in charge of onsite programs, setting a new standard in the MRO sector with their commitment to smart technology and onsite management.
- MSC Industrial Supply Co.'s recent acquisition of Buckeye Industrial Supply Co. and True-Edge Grinding Inc. strengthens its position as a prominent multichannel supplier of MRO products and services.
- The packaging markets in Canada and Brazil are expected to experience significant growth, driven by thriving industries such as pharmaceuticals and cosmetics, leading to increased demand for contract packaging services.
CAPEX, MRO, INFRASTRUCTURE
Surface Mount Technology
MARKET DYNAMICS
-
The Surface Mount Technology Equipment Market was valued at USD 7.1 billion in 2023. The industry is projected to grow from USD 7.7745 billion in 2024 to USD 14.7 billion by 2032, exhibiting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.29% during the forecast period (2024 - 2032). Increased demand for miniature consumer electronics products and those highly used in home projects are the key market drivers enhancing the market growth.
The demand for smaller and lighter electronic devices, such as smartphones, wearables, and IoT devices, is augmenting the need for miniaturized electronic components and high-density PCB assemblies. SMT enables the placement of tiny surface mount components, thereby contributing to the trend of miniaturization.
-
SMT Equipment End-User Insights. Based on end-users, the Surface Mount Technology Equipment Market segmentation includes telecommunication, consumer electronics, automotive, and medical. The consumer electronics segment generates the most income due to its advantage over conventional through-hole technology, including smaller form factors, quicker production schedules, and higher efficiency; SMT is frequently employed in manufacturing consumer electronics.. Automated assembly lines can process large PCBs, allowing businesses to mass-produce consumer devices.
-
SMT Regional Insights. By region, the study provides market insights into North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and the Rest of the World. The North American Surface Mount Technology Equipment market will dominate this market, owing to increased demand for consumer electronics. In addition, the growing range of high-performance inter-connected devices and other related technologies has also been driven by the need for digital streaming content, which will boost the market growth in this region.
India is reportedly easing curbs on Chinese investments.
-
New Delhi is considering relaxing restrictions on Chinese investment in specific sectors. India may allow Chinese companies to invest in areas where the country lacks expertise, such as solar panels and battery manufacturing. This move aims to boost domestic production. However, sources told Reuters that India will strictly control Chinese investments in sensitive sectors like electronics and telecommunications. The decision to open up specific areas to Chinese investment will be made on a case-by-case basis.
-
According to the Economic Survey 2024 released by the Finance Ministry of India, India is shifting its focus towards attracting foreign investment from China as a key strategy to enhance its global electronics exports, according to the Economic Survey 2024. By encouraging Chinese companies to invest in India's electronics sector, the government aims to develop a robust domestic supply chain and increase the value added within the country's electronics manufacturing ecosystem. By encouraging Chinese companies to set up operations in India, the country can add more value to the manufacturing process, and export finished products to markets like the US and Europe. This strategy aims to reduce India's reliance on imports from China and address the growing trade deficit.
-
The Economic Survey 2024 highlights the need for India to carefully balance imports from China with capital inflows from the same country.
-
According to earlier reports by Bloomberg and Reuters, the Indian government plans to expedite visa processing for Chinese engineers and technicians, which is crucial for installing Chinese-made machinery in Indian factories. The current visa issuance time is five months à 30 days. The government plans to issue faster business visas for technicians across 14 high-tech electronics manufacturing sectors.
-
Industry demand fell slightly, dropping to a neutral level between expansion and decline.
-
Demand fundamentals weakened for the fourth consecutive month, falling to the lowest level.
-
Demand was dragged lower by weaker backlogs and weaker new orders.
-
-
Cost pressures eased in July.
-
The Labor Costs Index dropped two more points this month, and the Material Costs Index fell five points.
-
The Labor Costs Index set a record low in July. However, both indices remain in expansionary territory, suggesting that most businesses continue to face cost pressures.
-
-
The industry outlook fell slightly, dropping to the lowest level in a year.
-
The industry outlook remains strongly positive, though it continues to soften.
-
-
The impact of CHIPS Act awards has on semiconductor capital spending over the next few years. Companies would certainly have built these factories without CHIPS money. Companies plan fabs based on their capacity needs to meet their business plans. The CHIPS funds likely impacted the location of some of the wafer fabs. Without the CHIPS Act money, TSMC and Samsung may not have located their new fabs in the US. The effects of the CHIPS Act awards are not likely to be significant in 2024 but will likely boost 2025 CAPEX (capital expenditures).
-
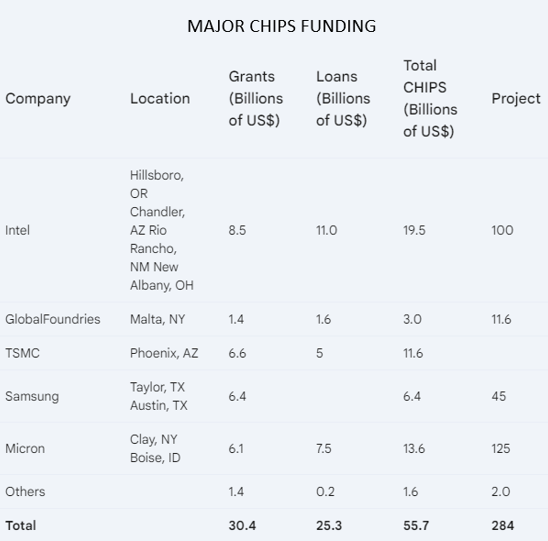
The U.S. is not the only country that has subsidized its semiconductor industry. According to Bloomberg, planned semiconductor investments include USD 46 billion from the European Union (EU), USD 21 billion from Germany, USD 142 billion from China, USD 55 billion (in tax incentives) from South Korea, USD 25 billion from Japan, USD 16 billion from Taiwan, and USD 10 billion from India.
-
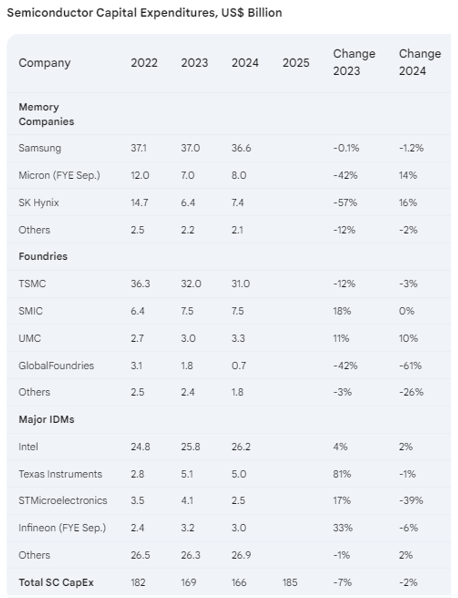
Our Semiconductor Intelligence estimate of total semiconductor CAPEX in 2024 is USD 166 billion, and we project an 11% increase in CAPEX in 2025 to reach USD 185 billion.
-
Two major memory companies, SK Hynix and Micron Technology, are planning double-digit CAPEX increases in 2024, while Samsung is guiding for a slight decrease. SK Hynix and Micron are projecting significant CAPEX growth in 2025, with SK Hynix at 75% and Micron at 47%.
-
The dominant independent foundry company, TSMC, plans a 3% cut in 2024 CAPEX and a 10% increase in 2025 based on the mid-point of its guidance. S
-
MIC expects no change in CAPEX in 2024, while UMC plans a 10% increase. GlobalFoundries will cut CAPEX 61% in 2024 but should increase it significantly in 2025 as it begins constructing its USD 11.6 billion wafer fab project in Malta, New York.
-
The largest integrated device manufacturer (IDM), Intel, projects a 2% increase in 2024 CAPEX. Texas Instruments is sticking to its plan to spend an average of USD 5 billion on CAPEX over the next few years. STMicroelectronics and Infineon Technologies plan CAPEX cuts in 2024 after strong increases in 2023.
-
Our forecast of 11% growth in 2025 semiconductor CAPEX may be conservative. The plans from TSMC, Micron, and SK Hynix account for two-thirds of the USD 19 billion CAPEX increase from 2024 to 2025.
-
Samsung, the largest spender, will likely increase its CAPEX substantially in 2025 to maintain its memory market share and increase its foundry business, which is second to TSMC.
-
In its June 2024 forecast, SEMI projected a 17% increase in spending on 300mm fab equipment in 2025 after a 6% increase in 2024. WSTS’ June 2024 forecast called for semiconductor market growth of 16% in 2024 and 12.5% in 2025. Our upside projection is a 20% increase in 2025 CAPEX.
-
The automotive industry also played a significant role in the EMS market. The need for electronic components and systems has surged as vehicles become more technologically advanced. EMS providers serving the automotive sector have been integral in manufacturing critical electronic components, including control units, sensors, and infotainment systems, contributing to the market’s overall growth.
-
In Heavy Industrial Manufacturing, Electronics Manufacturing Services (EMS) providers have been essential partners in producing electronic solutions for heavy machinery and equipment. This sector’s reliance on electronics for automation and control systems has led to the steady growth of the EMS market, with EMS companies contributing to the development of advanced industrial electronics.
-
Aerospace and defense are other key industries that have expanded the EMS market. The stringent quality and reliability standards in this sector have necessitated the involvement of EMS providers to manufacture specialized electronic components and systems, including avionics and communication equipment.
-
Healthcare, IT, and Telecom have all seen notable growth in electronic manufacturing requirements. In the healthcare sector, EMS companies have been instrumental in producing medical devices and equipment, contributing to advancements in healthcare technology. EMS providers have played a crucial role in manufacturing networking, communication, and computing components in the IT and Telecom sectors, supporting the digital revolution.
DEMAND TRENDS & FORECASTS
The 2024 economy remains soft, which can significantly impact the Surface-Mount Technology (SMT) space in various ways. Here's a breakdown of how economic changes might affect SMT and how the market shift from a seller to a buyer's market plays; the effects on the SMT space: There is an observation from most suppliers that they receive the same order to survive. Customers expect more but pay less for the products outsourced to EMS. The optimization of processes, materials, or equipment to make the operation cost cheaper and maximize profit. All in all, it is a vicious cycle.
-
Companies may delay or scale back investments in new SMT equipment and technology. The companies are more cautious about spending capital. This can lead to a slowdown in the purchase of new SMT machine or new related technologies, which could impact manufacturers and suppliers in the SMT space.
-
Changes in Electronics will cause Consumer and industrial demand for electronic products decrease. This, in turn, affects the SMT industry, which relies heavily on producing electronic components.
-
Pricing Pressure Increased competition and reduced budgets can lead to pricing pressure on SMT products and services. With less capital and decreased demand, companies might face pressure to lower prices to maintain competitiveness. This can affect profit margins for SMT manufacturers and suppliers.
-
Economic downturns can lead to disruptions in the supply chain, such as the availability and cost of raw materials and components, causing potential delays and increased costs in the SMT production process.
Buyers will optimize the opportunity in the SMT space:
-
The shift to a buyer's market increases competition among SMT suppliers.
-
In a buyer's market, however, the oversupply of SMT products or reduced demand shifts the power to buyers, who can negotiate better terms and prices.
-
If buyers have more leverage in negotiating prices and terms, they can negotiate more favorable contracts, potentially lowering costs for SMT components and services.
-
SMT may need to differentiate themselves through additional services or value. SMT suppliers might need to offer enhanced services, better support, or more innovative solutions to attract and retain customers
-
Both buyers and suppliers will focus on cost efficiency. Suppliers will aim to streamline operations and reduce costs to maintain profitability despite lower prices and tighter margins.
Strategic Collaboration with SMT Supplier
-
Adapt Product Offerings: Companies may need to adjust their product lines to meet the market’s changing needs, such as offering more cost-effective or technologically advanced solutions.
-
Enhance Customer Relationships: Building strong customer relationships can help retain business and gain a competitive edge in a buyer’s market.
-
Innovate and Diversify: Investing in research and development to innovate and diversify offerings can help SMT companies stay relevant and competitive.
A softening economy affects SMT by reducing capital expenditure, altering demand, and creating pricing pressures. The shift from a seller’s to a buyer’s market further emphasizes the need for Supplier Relationship development SMT companies to adapt their strategies, focusing on cost efficiency, value-added services, and strong customer relationships. The companies that build on AI or use AI will survive, and those who are still not on this wagon are the ones that are suffering now.
1. Market Trends and Demand Drivers:
-
Technological Advancements: Innovations in electronics, such as miniaturization and increased complexity, drive the need for advanced SMT equipment that can handle smaller and more complex components.
-
Consumer Electronics Growth: Increasing adoption of smart devices, wearables, and home automation systems fuels SMT demand.
-
Automotive Industry: Advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and electric vehicles (EVs) are driving demand for sophisticated SMT applications
-
Electronics Growth: The demand for consumer electronics, automotive electronics, and IoT devices drives SMT equipment demand. As these markets grow, so does the need for SMT assembly.
-
Industry Trends: Emerging trends like 5G technology, electric vehicles, and smart home devices can influence demand. For instance, increased adoption of 5G might lead to higher demand for SMT equipment to produce related components.
-
Product Lifecycle: New product introductions and lifecycle changes in electronics can spike demand depending on the season.
2. Challenges:
-
Supply Chain Disruptions like component shortages, geopolitical tensions, and logistics problems can affect forecast accuracy. Component Availability and raw materials can impact SMT equipment production and sales. Disruptions in the supply chain can affect the overall market. Lead times and costs for SMT equipment and changes in manufacturing costs can influence purchasing decisions.
-
Keeping up with the fast-paced evolution of electronics technology and market demands.
-
Fluctuations in economic conditions and consumer confidence can impact forecasts.
3. Regional Factors and Customer-centric:
-
Develop regional Manufacturing Hubs in countries with strong electronics manufacturing industries, such as China, Taiwan, South Korea, and Japan, which often have higher demand for SMT equipment.
-
Regional economic stability and growth can impact electronics manufacturing activities and SMT equipment demand.
4. Technological Trends:
-
Integrating automation and AI (artificial intelligence in SMT processes can affect equipment demand. Advanced automation can drive demand for high-precision and high-throughput SMT machines.
-
There’s a growing emphasis on energy-efficient and environmentally friendly manufacturing processes. SMT equipment that meets these criteria might see increased demand.
Market Forecasts
-
Market research reports and industry analyses provide forecasts based on current trends and future projections. Reports from firms like Gartner, IDC, or industry-specific analysts can offer detailed insights.
-
Reviewing historical sales data and growth patterns helps understand and predict future demand.
Strategic Demand Approaches
-
Flexible Manufacturing: Adapt production capabilities to respond to fluctuating demand and market conditions.
-
Scenario Planning: Develop multiple demand scenarios to anticipate varying market conditions and prepare accordingly.
-
Digital Engagement Shift: The SMT market transforms how businesses connect with consumers by leveraging digital platforms and interactive technologies, enhancing customer experiences and brand loyalty.
-
Customization Trend: Increasing demand for personalized products drives innovation in the SMT market, creating opportunities for businesses that can meet these tailored preferences.
-
Strategic Collaborations: Companies are forming alliances to expand capabilities, access new technologies, and more effectively enter new markets.
-
EMS Market Growth: The EMS sector supports OEMs by offering design, manufacturing, assembly, testing, and logistics services driven by product complexity, cost optimization, and the need for faster time to market.
-
Automation and Industry 4.0: SMT inspection systems are central to the automation trend, improving quality control, reducing manual interventions, and boosting production resilience.
-
Market regulations and political factors will shape the PCB industry in the coming year. Shifts in international politics and trade conflicts are expected to have a lasting impact on the electronics technology sector. To navigate these opportunities and challenges, businesses must bolster their resilience while closely monitoring customer trends and geopolitical developments, ensuring they can adapt their strategies with agility.
-
Significant growth opportunities exist for SMT placement in advanced electronics, particularly in emerging markets like South Asia. As Industry 4.0 and IoT drive increased connectivity and automation, the demand for advanced SMT placement equipment is projected to rise. These machines, known for their precision and speed, are well-suited for highly automated manufacturing environments.
SUPPLY ANALYSIS
Key Supplier Lead Time Analysis:
|
Supplier |
Lead Time |
|
FUJI |
Eight weeks |
|
ITW |
Four weeks |
|
Vitrox |
AOI: 4-6 weeks, AXI: 8-12 weeks |
|
Koh Young |
4-6 weeks |
-
The Red Sea Crisis of 2024 significantly disrupted global supply chains, forcing ships to take longer routes and increasing shipping costs. This impacted international trade, economies, and consumer prices.
-
To mitigate future disruptions, businesses should diversify routes, conduct risk assessments, and strengthen international cooperation. Other strategies include:
-
Technology investments: Invest in technology solutions that improve supply chain visibility, resilience, and responsiveness.
-
Inventory Management: Maintain adequate inventory levels to buffer against disruptions and minimize the impact on operations.
-
- SMT lead time is within control due to soft demand in the second half of 2024.
- Foster the transformation partnership with strategy SMT partners and drive level up on Tier 2 vendors on alternative sources in the future. This will avoid the LT issue.
- The customer's investment strategy will determine the global strategy. Supporting partners/Customers is crucial for long-term investment and eliminates a lot of non-value activity (NVA).
The outlook for the Next Six Months:
The EMS market is expected to grow and evolve in the coming months. To navigate the challenges and opportunities ahead, businesses should closely monitor market trends, adapt their strategies, and focus on building resilient supply chains.
India:
- Market Expansion: India's EMS market will likely expand, but growth may vary depending on specific customer requirements and preferences.
- Local EMS: Monitor local EMS providers, such as Tata, Dixon, and Padget, for potential opportunities.
Global EMS:
- Recovery: The global EMS market is expected to recover in 2025, driven by reduced inventory levels and the release of new technology products.
- Challenges: Current challenges include excess inventory and a potential lack of major technology releases in the second half of 2024.
Southeast Asia:
- Nearshoring and Reshoring: The region will continue to benefit from companies relocating manufacturing operations from China.
- Competition: Competition among EMS providers in Southeast Asia will be intense and influenced by customer strategies and preferences.
Risk Mitigation and Supply Chain Resilience:
- Alternative Sourcing: Develop strategies to mitigate risks and ensure a reliable supply chain.
- Customer Support: Closely support customers during potential supply chain disruptions.
China:
- Domestic Focus: China's EMS market will likely focus more on domestic customers.
- Offshore Expansion: Some Chinese EMS providers may explore opportunities for offshore expansion, but this will depend on various factors.
PRICING TRENDS & INSIGHTS
Various factors, including technological advancements, market demand, and economic conditions, can influence surface-mount Technology (SMT) equipment pricing trends. Here’s a look at some key trends and future insights: Prices for semiconductors, a key component in SMT, can fluctuate based on supply and demand, technological advancements, and geopolitical factors. Recent trends show a general price increase due to supply chain constraints and high demand for electronics.
1. Technological Advancements: Increased Automation in SMT equipment can lead to higher upfront costs but improved efficiency and lower labor costs over time. Expect prices for highly automated systems to rise, but their cost-effectiveness may offset this. Equipment with advanced features like AI-driven quality control, enhanced precision, and better flexibility may command higher prices. However, these features can also lead to cost savings and higher yields in the long run.
2. Market Demand: As demand for electronics continues to grow, particularly in sectors like automotive, consumer electronics, and industrial applications, demand for SMT equipment is likely to increase. This can drive prices up, especially for high-capacity or specialized equipment. As electronics become smaller and more complex, the need for advanced SMT equipment capable of handling finer pitch components and higher-density boards will likely drive up prices.
3. Economic Conditions: The prices of raw materials used in SMT equipment can fluctuate due to global economic conditions. For instance, shortages or price increases in metals or semiconductors can impact SMT equipment costs. Global supply chain issues, like those experienced during the COVID-19 pandemic, can affect availability and prices. While the situation has improved, future disruptions could still influence pricing.
4. Geopolitical Factors: Tariffs, trade restrictions, and other geopolitical factors can impact the cost of SMT equipment, especially if components or machinery are imported. Changes in trade policies may lead to price fluctuations. As we know, the US election will happen very soon.
5. Innovation and Competition: As more manufacturers enter the SMT equipment market, increased competition can decrease prices, particularly for more standardized and less advanced equipment. Companies’ differentiation on investing heavily in R&D may offer more advanced solutions at a premium. However, they might also provide better performance and efficiencies, which can justify higher prices.
Future Pricing Insights
-
Integration with Industry 4.0: Expect more SMT equipment integrating with Industry 4.0 concepts, such as smart factories and IoT. This integration could lead to higher prices initially but offer significant long-term benefits.
-
SMT will experience the growing demand for consumer electronics, automotive applications, and IoT devices, driving the need for SMT components. This increased demand can lead to higher prices and potential shortages of specific components.
-
Sustainability: A push may be toward more sustainable and energy-efficient SMT equipment. While these options might come at a premium, they could provide cost savings and environmental benefits over time.
-
Global Production Shifts due to Geopolitical and Economic Influences: As global manufacturing hubs shift, particularly towards regions with lower labor costs or more advanced technological capabilities, the dynamics of SMT equipment pricing could change.
-
Advances in SMT technology, such as improved soldering techniques and more precise placement machines, are helping to enhance efficiency and reduce costs. However, the initial investment in these technologies can be high.
While SMT equipment costs are likely to rise due to advancements and increased demand, innovations and competition may help mitigate some of these increases. Monitoring market trends and technological developments will be key to understanding future pricing.

KEY TAKEAWAYS
-
The upcoming US election will have global implications, making selective investment and partnership planning with customers crucial for long-term strategies.
-
The integration of robotics and AI in SMT is advancing rapidly. Machines are expected to operate autonomously, making faster, more intelligent decisions to optimize the SMT process.
-
Focusing on partnerships with SMT suppliers at the market share level will drive cost efficiency and competitive advantages.
-
The global EMS industry’s SMT sector is expected to face softness in the second half of 2024, with scattered investments driven by capital expenditure surpluses unable to meet emerging demands.
-
AI and machine learning will transform SMT over the next three years, driving predictive maintenance, inventory management, quality control, and supply chain optimization.
-
Collaborating with global AI-focused SMT partners is essential to meet the demand for consistent quality in EMS offerings and align with the "factory of the future" vision.
-
Diversifying and qualifying alternative sources is necessary to prepare for potential supply chain disruptions, particularly those originating in China.
-
Foreign EMS companies increasingly avoid expansion in China due to their customers' concerns about over-reliance on the region.
-
AI-driven procurement strategies, focusing on supply chain value differentiation and rebate incentives, will remain vital as global labor and material costs rise.
-
Investing in AI-based equipment training for staff will pay dividends when business conditions improve and new opportunities arise.
-
This year poses significant challenges for major SMT brands as Chinese distributors expand their sales and service presence across Asia. This shift is partly due to loosening government restrictions that previously hindered such growth.
-
Increasing demand for products built outside China is prompting Chinese and Taiwanese contract manufacturers (CMs) to relocate to South Asia, India, and Mexico. Many of these companies must establish local operations starting from the ground up. Taiwanese firms, in particular, are facing regulatory challenges that have pushed them to outsource to India’s local EMS providers.
-
Strategic sourcing is no longer just about finding the cheapest supplier. It’s a balancing act between cost, risk, quality, and reliability.
-
Effective strategic sourcing allows organizations to maximize the value of their purchasing decisions, aligning their procurement strategies with broader operational goals.
-
It also helps mitigate supply chain risks, ensure the timely availability of materials, manage inventory, and efficiently meet consumer demand.
-
In 2024, sourcing has become increasingly complex, requiring careful management to fit all the puzzle pieces together for maximum benefit. Developing and maintaining an up-to-date supplier tiering strategy will be essential to navigating these complexities and minimizing risks effectively.
-
As the SMT industry faces an evolving landscape shaped by geopolitical shifts, supply chain disruptions, and technological advancements, businesses must adopt strategic partnerships and embrace AI-driven solutions to remain competitive.
-
The relocation of manufacturing to emerging markets, particularly in South Asia, India, and Mexico, highlights the urgency of developing resilient, localized operations. At the same time, strategic sourcing will play a critical role in navigating rising risks and supply chain complexity.
-
Considering these factors, organizations that invest in automation, partnerships, and comprehensive sourcing strategies will be well-positioned to capitalize on new growth opportunities while mitigating the challenges ahead.
-
China and Taiwanese contract manufacturers (CMs) are relocating to Southeast Asia, bringing their preferred brands of SMT equipment, largely China-made. This shift has disrupted the sales process in Asia and is expected to continue.
CAPEX, MRO, INFRASTRUCTURE
Solder
MARKET DYNAMICS
-
The electronics industry's solder consumption in 2024 is projected to grow moderately. Rising demand in key sectors like mobile technology, touchscreens, and medical systems is driving this growth.
-
The global solder market, including solder used in circuit boards and other components, is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.0% through 2031. However, some concerns persist among key industry players and suppliers regarding a possible contraction in electronics demand.
-
The electronics market is facing an extended slowdown period with unstable demand. A "wait and see" approach is being observed globally due to two key factors:
-
US Elections: Investors are on edge, especially given former President Trump's stance on protecting US businesses and potential tariff increases on commodities, including metals from China.
-
Federal Reserve Policy: The Fed's decision to maintain interest rates between 5.25% and 5.5% has led to speculation about potential rate cuts, which could significantly affect monetary policy by September.
-
-
In Asia, the situation is equally tense. Investors are concerned about the sluggish recovery of the Chinese market as reduced consumer demand and lower government spending continue to stifle growth. The Chinese economy grew by 5% in the first half of the year, hitting the government's target, but concerns linger about future performance.
-
While demand for solder has softened, prices continue to rise, mainly due to fluctuations in the cost of metals like silver and tin. Silver, highly sensitive to global market conditions and investor sentiment, remains volatile, while tin prices are unstable due to supply disruptions and market speculation.
The global Electric Vehicle (EV) market is expected to drive significant demand for solder by 2025. EVs, including battery electric vehicles (BEVs), plug-in hybrids (PHEVs), and fuel cell vehicles (FCEVs), could account for 8-10% of global vehicle sales, bolstered by stricter environmental regulations and advances in battery technology.
-
China will continue leading the global EV market, driven by strong government support, local manufacturing, and consumer demand.
-
Due to CO2 targets and subsidies, Europe is expected to experience robust EV growth, with EVs making up a substantial share of new car sales by 2025.
-
North America is projected to see slower but steady EV adoption, aided by infrastructure development and the availability of more affordable EV models.
By 2026, electric vehicles may account for more than 25% of global new car sales, further driving demand for materials like solder, especially in automotive electronics.
DEMAND TRENDS & FORECASTS
-
The industry continues to drive global demand for metals used in soldering processes, primarily tin, silver, and copper. As the sector grows, the analysis of the demand for these metals must consider various factors, including the growth of the electronics industry, metal supply and demand, and economic and technological trends.
-
The global tin market has experienced significant changes in recent months due to various economic, geopolitical, and technological factors. Please see below an overview of the current state of the tin market, the factors that have recently influenced its demand, and future prospects.
-
In 2024, global demand for tin has grown moderately, with a 4% increase compared to the previous year. This growth is due to the ongoing expansion in consumer electronics, automotive, and technological
-
infrastructure sectors. The surge in the manufacturing of electronic devices, along with the increasing miniaturization of components, has driven sustained demand for tin solders.
-
Tin production worldwide is concentrated in a few countries. Major producers include China, Indonesia, Myanmar, and Peru. China remains the largest producer and consumer of tin, with a significant portion of its production allocated to the electronics and soldering industries. Global tin supply has faced challenges due to disruptions in the supply chain and mining restrictions in some key countries.
-
Supply Chain Disruptions: Tin supply chain disruptions in global logistics have affected the industry. Factors such as issues with maritime transport, labor strikes in producing countries, and export restrictions have created bottlenecks in tin supply. These problems have led to price increases and greater market volatility.
-
Regulations: Pressure to improve environmental practices and reduce the impact of mining has increased. particular in Myanmar, where tin mining is significant, new environmental regulations have limited production capacity. These restrictions have reduced global supply and contributed to rising tin prices.
-
Geopolitical Instability: Political instability in tin-producing countries, such as Myanmar, has affected the metal's production and export. Political tensions and government restrictions have created market uncertainty and influenced availability.
-
Raw Material Price Fluctuations: The prices of raw materials, including metals, have been volatile due to global economic factors. Inflation, fluctuations in the value of the US dollar, and international trade tensions have influenced tin prices, affecting both producers and consumers.
-
Silver is primarily used in small quantities in solder alloys due to its excellent electrical conductivity and resistance to corrosion. Its supply is influenced by several factors: Production: Most silver is extracted as a byproduct of copper and lead. This means that silver supply is closely tied to the production dynamics of these primary metals.
-
Demand and Financial Market: Silver is also used in jewelry and as an investment. Due to speculation in financial markets and industrial demand, silver's price fluctuations can be highly volatile.
-
Global demand for metals such as tin, silver, and copper in the solder industry remains strong in 2024, driven by growth in the electronics industry and expansion into specialized applications. Each metal has unique characteristics that affect its demand, and forecasts indicate sustained growth in the short term. However, price volatility, environmental concerns, and trends toward sustainability could impact market dynamics in the long term. Supply managers must stay alert to these trends to adjust their strategies and mitigate potential risks while exploring emerging opportunities in an evolving market.
SUPPLY ANALYSIS
-
The current landscape features several emerging trends and new acquisitions that could impact the supply of metals used in electronic soldering:
-
New Investments in Mining: Investment in new mines and exploration projects is rising. Companies seek to secure long-term supply sources by acquiring mining properties and entering into supply agreements. While these investments can help stabilize supply, they may also increase initial costs and associated risks.
-
Recycling and Circular Economy: Metal recycling is becoming more important due to heightened pressure to reduce waste and environmental impact. Advanced recycling technologies enable the recovery of valuable metals from electronic products at the end of their life cycle. This trend may contribute to a more stable supply of metals, easing some of the pressures on primary mining.
Trends and Advances in Solder
Development of New Solder Alloys
-
Lead-Free Alloys: As environmental regulations tighten and restrictions on lead usage increase, lead-free alloys have become more prominent. The most common are tin-copper (Sn-Cu) and tin-silver-copper (Sn-Ag-Cu) alloys. But we're also seeing new formulations that enhance fluidity and resistance to fatigue in electronic applications. These lead-free options provide a solid alternative to lead, offering comparable performance and reliability.
-
Bismuth-Based Alloys: Bismuth is being used as a lead substitute in certain soldering applications. Alloys like tin-bismuth (Sn-Bi) are known for their low melting points, making them suitable for heat-sensitive components. While bismuth is more expensive than lead, its unique properties can justify the cost for specific uses.
Advanced Soldering Technologies
-
Lead-Free Reflow Soldering: Reflow soldering technology has made significant strides to accommodate lead-free alloys. Modern reflow processes are optimized to handle higher temperatures and longer cycle times, ensuring the quality and reliability of solder joints in electronic components.
-
High-Speed Soldering Technologies: Advances in soldering technology, including wave and selective soldering, have introduced high-speed processes that boost efficiency and reduce production costs. These cutting-edge methods are crucial for managing large production volumes with high precision and quality.
Sustainability and Recycling
-
Metal Recycling: The push toward a circular economy drives the recycling of valuable metals from discarded electronic products. Advanced recycling technologies can recover tin, silver, and copper from old devices, reducing the need for new mining and lessening environmental impact.
-
Using Recycled Materials in Soldering: There's growing interest in incorporating recycled materials into solder production. This not only supports sustainability but can also help stabilize metal prices by decreasing the demand for newly mined resources.
Innovations in Soldering Materials
-
Enhanced Properties: Researchers are developing new solder materials with improved properties, such as better thermal fatigue resistance and enhanced electrical conductivity. These innovations are designed to boost the durability and reliability of soldered connections in electronic devices.
-
Development of New Solder Alloys and Materials: Research is ongoing to develop alternative alloys that could reduce reliance on rare or expensive metals. For instance, solder materials based on zinc and bismuth could offer viable and cost-effective options.
-
The trend towards developing new alloys and welding materials is an exciting opportunity. The industry must be prepared to adapt to these changes and take advantage of innovations to remain competitive and meet the demands of the global market.
-
The sintering paste is key in the EV industry due to its excellent performance in hot and stressed environments.
-
Sintering solder is widely used in high-power and high-temperature applications, particularly in the automotive industry for electric vehicles (EVs), where components like IGBT modules (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors) and power LEDs require highly reliable connections that can withstand significant thermal cycling and mechanical stress. It is also used in telecommunications, industrial electronics, and renewable energy systems.
-
Sintering solder, also known as sintering paste or sintered solder, is a specialized material used in advanced electronics manufacturing, particularly in applications requiring high reliability and excellent thermal and electrical conductivity. This solder type differs from traditional soldering methods, which involve melting the solder to create a bond. Instead, sintering solder consists of a process where the solder particles are fused under heat and pressure without fully melting.
-
Composition: Sintering solder typically consists of metal particles, often silver, mixed with organic binders and solvents. These materials are formulated into a paste that can be applied to the surfaces to be joined.
-
Process: During the sintering process, the paste is applied to the electronic components, and then heat (typically below the metal's melting point) and pressure are applied. This causes the metal particles to bond at the molecular level, creating a strong, conductive joint. The organic binders and solvents evaporate, leaving behind a solid metal structure.
-
High-Power Electronics: As the adoption of electric vehicles continues to grow globally, the need for high-power electronics, such as IGBT modules and SiC devices, is increasing. These components require reliable, thermally conductive, durable joints that sintering solder paste can provide.
-
Thermal Management: Sintering solder paste is crucial in managing the heat generated by power electronics in EVs. With the push towards higher efficiency and longer range, the demand for advanced thermal management solutions is expected to drive significant growth in the use of sintering solder paste in the automotive sector.
Advancements in 5G and Telecommunications
-
High-Frequency Devices: The rollout of 5G technology requires components that operate at higher frequencies and generate more heat. Due to its superior thermal and electrical conductivity, sintering solder paste is increasingly used to assemble these high-frequency devices.
-
Miniaturization: As electronic components become smaller and more powerful, reliable, void-free connections become critical. Sintering solder paste provides the precision and performance needed for these applications.
Growth in Renewable Energy
- Solar and Wind Power: The renewable energy sector is expanding rapidly, particularly solar and wind power. Power conversion and management systems in these applications often utilize sintered joints for their durability and ability to handle high power densities, driving further demand for sintering solder paste.
Aerospace and Defense
-
Harsh Environments: Aerospace and defense applications require materials that can withstand extreme conditions, including high temperatures and
-
mechanical stress. Sintering solder paste is well-suited for these environments, leading to increased use in producing military-grade electronics and avionics systems.
Technological Innovations
-
Development of New Materials: Continuous research and development in sintering materials, including lower-temperature processes and new alloy compositions, are expected to expand the range of applications and increase adoption across various industries.
-
Improved Manufacturing Processes: Advances in manufacturing technologies, such as the development of pressure-less sintering and hybrid bonding techniques, are making sintering solder paste more accessible and cost-effective, further boosting demand.
Challenges and Considerations
-
Cost: Sintering solder paste is generally more expensive than traditional solder materials, which may limit its adoption in cost-sensitive applications.
-
Process Control: The sintering process requires precise control of temperature, pressure, and environment, which can be challenging and may require specialized equipment.
PRICING TRENDS & INSIGHTS
-
The supply and prices of key metals used in electronic soldering are influenced by several interconnected factors, such as price fluctuations: Metal prices can be highly volatile, driven by shifts in supply and demand and speculation in financial markets. These price swings directly affect the cost of solder and can influence the overall production costs of electronic devices. Environmental and regulatory policies can also impact metal production by imposing stricter controls on mining and processing. These regulations can limit supply and drive up costs. Given the global nature of metal markets, international policies also play a significant role.
-
Technological Innovations and Alternative Materials: Advances in technology and the development of alternative materials can affect the demand for traditional metals. For instance, the shift towards lead-free solders or more eco-friendly soldering materials may reduce the need for tin and silver in certain applications.
IMPORTANCE OF TIN
-
Since tin prices rose aggressively in March, the global market has seen a series of developments that have influenced the price dynamics and supply of this critical metal for electronic soldering.
-
The increase in tin prices that began in March was driven by a combination of factors such as rising demand due to the global economy recovered and the demand for electronic products surged, especially with the rise in remote work and digitalization, the need for tin in soldering applications also grew significantly.
-
Supply Chain Disruptions: The COVID-19 pandemic caused major disruptions in the supply chain, affecting both the production and transportation of tin. These disruptions intensified market tensions and contributed to price increases.
-
Production Restrictions: Stricter environmental regulations and restrictions in major producing countries like China and Myanmar have limited the ability to extract and process tin. This has added pressure to prices by constraining supply.
The price of tin has been quite volatile recently due to several factors:
-
High Global Demand: The demand for tin remains strong, driven by its crucial role in the electronics industry. However, supply is constrained because production is concentrated in just a few countries. Additionally, extracting tin is becoming more challenging due to depleting reserves and rising mining costs.
-
Environmental Restrictions: Stricter environmental regulations in major producing regions impact the ability to extract tin. While these regulations aim to reduce environmental damage, they also limit tin supply, contributing to price fluctuations.
-
Financial Markets: The volatility of tin prices is also influenced by financial markets. Speculation and futures contracts can exacerbate price swings, affecting short-term costs for solder manufacturers.
-
The tin market is facing several challenges that impact both supply and prices. Tin production remains concentrated in a few key countries. For instance, Myanmar, a major player, has seen its supply affected by political instability and export restrictions, while countries like China and Indonesia are also struggling with mining and environmental issues. The tin mining industry faces rising operational costs and difficulties due to depleting reserves and the need for more advanced and expensive extraction technologies. Additionally, speculation in financial markets and new regulatory policies to reduce environmental impacts contribute to price volatility by restricting supply and increasing costs.
-
Looking ahead, tin prices are expected to remain unstable soon. Investments in new mining projects and advancements in recycling technologies may help stabilize supply and moderate prices over the long run. However, environmental pressures and market dynamics will continue to play significant roles in shaping the price of this valuable metal.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
Tin:
-
The situation around tin production in Myanmar has become increasingly precarious, leading to major disruptions in the global supply chain. In August 2024, Wa State, a critical tin-producing region, suspended all mining activities. This decision aims to conserve dwindling resources after years of extensive and environmentally harmful mining. Given that the Wa region contributed over 70% of Myanmar's tin production, this halt is significant, making Myanmar one of the top global tin producers.
-
As a result, tin prices spiked—up by 17.5% on the Shanghai Futures Exchange and 11% on the London Metal Exchange—anticipating tighter supply conditions. This disruption is particularly concerning for China, which relies heavily on Myanmar's tin. Industries dependent on tin, such as electronics and automotive manufacturing, are now grappling with supply shortages and heightened market uncertainty.
Silver:
-
Global silver demand is expected to hit 1.2 billion ounces in 2024, a record high. This surge is primarily driven by industrial applications, particularly in the photovoltaic (solar) and automotive sectors, where silver's conductivity is indispensable. Despite a projected 4% increase in mine production, the supply will not be sufficient to meet rising demand, leaving the market in deficit.
-
Key silver-producing countries, including Mexico, Russia, and Chile, face risks that could further tighten supply. Disruptions from community disputes or government interventions could result in mine closures or production halts, further straining the market. Additionally, potential trade policy changes or geopolitical tensions could lead to export restrictions or sanctions, increasing costs for importing nations and driving up global silver prices.
-
Amid these challenges, silver prices are already rising due to broader global instability, including trade tensions between the US and China and recession fears. This uncertain environment prompts buyers to hedge against price volatility, locking in prices to manage risks and potentially capitalize on market fluctuations.
Solder:
-
The solder paste market, a key component in electronics manufacturing, is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 2.5% from 2024 to 2031. The market size in 2024 is estimated at USD 735 million, with growth driven by increasing demand in consumer electronics, automotive, and telecommunications sectors.
-
Shift to Lead-Free Solder: Regulatory and environmental pressures are accelerating the transition from lead-based to lead-free alternatives, especially due to compliance requirements like RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) in Europe and North America. This shift poses challenges, as lead-free options can be costlier and technically more demanding, forcing suppliers to innovate to meet regulatory and quality demands.
-
Short-Term Risks:
-
Price Volatility: The raw materials for solder, particularly tin and silver, are subject to significant market fluctuations, which could lead to price instability.
-
Supply Chain Disruptions: Ongoing geopolitical tensions and logistical challenges could delay or reduce the supply of solder materials.
-
Regulatory Shifts: The move toward environmentally friendly and lead-free solder drives costs and requires significant adjustments in manufacturing processes.
-
-
Establishing agreements that protect both sides of the supply chain is crucial for medium and small companies. Effective inventory management and the negotiation of safety stock arrangements can help mitigate supply chain disruptions. Additionally, the complexity of managing solder paste, which has stringent storage requirements and expiration concerns, underscores the importance of working closely with distributors to avoid potential mishandling.
-
Top Suppliers of Solder and Flux:
-
AIM: A leader in both leaded and lead-free solder materials.
-
Indium Corporation: Offers specialized solder paste products for advanced electronics manufacturing, including automotive and semiconductor applications.
-
Alpha Assembly Solutions (a subsidiary of Alent, plc): Known for innovative formulations in solder paste, serving a wide range of electronic applications.
-
-
Top Distributors of Specialty Chemicals:
-
Krayden, Inc. specializes in adhesives, sealants, and coatings for multiple industries, including electronics and aerospace.
-
Ellsworth Adhesives: Provides high-tech solutions for medical devices and aerospace industries.
-
EIS Electrical Insulation Suppliers: A long-standing leader in specialty distribution, serving industries ranging from electronics to alternative energy.
-
Back to Top


