By clicking the “I Accept” button, or by accessing, participating, or submitting any information, or using the Jabil Global Intelligence Portal or any of its associated software, you warrant that you are duly authorized to accept the Global Intelligence Portal Terms and Conditions on behalf of your Company, intending to be legally bound hereby, and your company shall be bound by the terms and provisions of the Global Intelligence Portal Terms and Conditions, accessible under the following link Portal T&Cs.
Sector Market Report
Wireless Infrastructure
Sector Market Report
Wireless Infrastructure
Get an in-depth analysis of the current state, trends, and future of the wireless infrastructure technology market, including insights into key drivers, changing product lifecycles, and manufacturing challenges.
Wireless Infrastructure Market
Introduction
2024 marks a pivotal point in the evolution of the wireless infrastructure market. As our reliance on data consumption and seamless connectivity grows, the underlying network that supports the demand is undergoing significant transformation. This report delves into the key trends, challenges, and opportunities shaping the wireless infrastructure landscape over the next year.
The emergence of Open Radio Access Networks (Open RAN) is a game-changer. It promises to shift the wireless network landscape by fostering greater flexibility and interoperability. Unlike traditional, closed RAN systems, Open RAN allows network operators to mix components from different suppliers, offering greater flexibility in network design. This approach could potentially lead to cost savings and innovation while promoting vendor neutrality and fostering competition within the market.
However, the adoption of Open RAN is not without its challenges. A significant hurdle is the initial cost associated with Open RAN technology. Traditional radios rely on cost-effective Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs), while Open RAN currently utilizes more expensive Field-Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs). The challenge lies in determining if cost-effective ASICs can deliver the same functionality as FPGAs in the Open RAN architecture. Additionally, achieving economies of scale for Open RAN depends on widespread adoption. If initial uptake is lower than expected cost reduction through mass production might be hindered, impacting the technology's viability for some network operators.
As the technology matures, network operators are poised to reap significant benefits through reduced Capital Expenditure (CAPEX) and Operating Expenditure (OPEX). The increased flexibility and vendor neutrality offered by Open RAN allow for more efficient network design and potentially lower maintenance costs. Additionally, ORAN opens doors for innovation within the industry, as more minor, niche players can contribute their expertise without being locked out by proprietary technologies from major vendors. This potential for cost savings and increased innovation should inspire optimism about the future of wireless infrastructure.
Beyond technological advancements and geopolitical shifts, the wireless infrastructure industry increasingly focuses on sustainability. As data consumption rises, so does wireless networks' energy footprint. Network operators and OEMs alike are prioritizing solutions that minimize energy consumption. This could involve selecting suppliers committed to sustainable practices throughout their supply chain and designing components with lower power requirements. The rise of green initiatives and government regulatory pressure also push the industry towards more sustainable solutions.
A dynamic interplay of technological advancements, evolving business models, and geopolitical considerations characterize the wireless infrastructure landscape. With the rise of ORAN promising increased flexibility and cost savings, the industry is poised for a paradigm shift. However, initial cost concerns and the challenge of achieving economies of scale remain hurdles that must be addressed. Additionally, the geographical diversification of manufacturing and a growing focus on sustainability are shaping the industry's current trajectory. The companies that can adapt to these changes and embrace innovation will be best positioned to succeed in this ever-evolving market. This report will delve deeper into these key trends, exploring their implications for stakeholders within the wireless infrastructure ecosystem.
Wireless Infrastructure Market
Overview
Market Outlook
The wireless infrastructure market is booming and is projected to reach USD 286.18 billion by 2028 (Data Bridge Market Research). This significant growth, estimated at a compound annual rate of 7.02%, is fueled by several key factors. Operators are heavily investing in deploying high-speed networks. This push for better connectivity, driven by the global demand for high-speed mobile internet and 4G connections, is a significant driver of market expansion. The burgeoning 5G technology rollout in developing nations also creates significant opportunities.
The number of smartphone and mobile broadband users is exploding, leading to a surge in demand for network infrastructure devices and technologies. Small and medium enterprises (SMEs) and various industries also drive this growth by increasing reliance on robust wireless connectivity. Rapid advancements in technology and infrastructure development are propelling the market forward. Government initiatives promoting wireless network infrastructure in developed and developing economies further contribute to this growth. With their high demand for improved connectivity, emerging economies represent exciting new markets. A confluence of factors will drive significant growth in the wireless infrastructure market in the coming years. This report delves into the current landscape, future projections, and key trends shaping this dynamic market.
Operator Investments in High-Speed Networks are increasingly deploying high-speed networks to cater to the ever-growing demand for mobile data and internet connectivity. This translates to a surge in demand for wireless infrastructure solutions. The widespread adoption of 4G and the burgeoning deployment of 5G technology drive the need for advanced wireless infrastructure. 5G, with its ultra-fast speeds and low latency, opens doors to many innovative applications across various industries. Governments across the globe are actively promoting the development of wireless network infrastructure, recognizing its critical role in fostering economic growth and social progress. This includes initiatives in both developed and developing nations. Developing economies present a lucrative market for wireless infrastructure solutions due to their rapidly growing populations and increasing demand for mobile connectivity.
However, the wireless infrastructure market witnessed a slight downturn in 2023, primarily attributed to the significant expansion of 5G networks and the current network maturity. This led industry leaders to limit their capital expenditures (CapEx), deferring construction and site deployment initiatives into late 2024 and early 2025. According to Teral Research, the global market contracted by 9% year-over-year in 2023, with the US market experiencing its steepest decline in history.
The research and development required to create cutting-edge wireless infrastructure solutions come at a significant cost, which can be a barrier for some market players. As reliance on wireless connectivity grows, so do concerns about data privacy and network security breaches. Addressing these concerns is crucial for sustained market growth. The availability of radio frequency spectrum is a finite resource. Spectrum scarcity can pose a challenge to the further expansion of wireless infrastructure.
The wireless infrastructure market is currently experiencing a period of adjustment, marked by a slowdown in growth compared to previous years. This is largely due to the completion of major 5G network deployments and the ongoing transition to standalone 5G architecture. Additionally, economic factors such as inflation and rising interest rates have contributed to the cautious investment approach by network operators. However, the focus has shifted towards optimizing existing networks for improved coverage, capacity, and performance. Despite the temporary slowdown, the long-term outlook remains positive, driven by increasing data consumption, emerging applications, and the need for denser networks to support the growing demands of advanced wireless services. While these factors are poised to drive substantial growth in the wireless infrastructure market over the upcoming years, the exact pace of recovery remains subject to some uncertainties. The ongoing economic fluctuations, potential supply chain disruptions, and the evolving regulatory landscape could influence the speed at which investments rebound. However, with increasing data consumption, the growing demand for advanced wireless services, and the ongoing efforts to optimize existing infrastructure, the wireless infrastructure market is expected to regain momentum and witness considerable expansion by the end of 2025.
The Open Radio Access Network (Open RAN) market is expected to grow exponentially. Open RAN promotes interoperability between network equipment from different vendors, offering greater flexibility and innovation. The rapid pace of technological advancements in areas like network infrastructure development and network optimization will continue to unlock new opportunities in the wireless infrastructure market. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) increasingly recognize the importance of robust wireless infrastructure. This segment is expected to be a significant driver of growth. The growth of new applications like the Internet of Things (IoT) and smart cities will create further demand for sophisticated wireless infrastructure solutions.
The wireless infrastructure market is a multifaceted sector driven by various user demands and technological advancements. Segmenting the market by connectivity type reveals distinct needs. Legacy technologies like 2G and Satellite cater to remote areas where basic communication infrastructure is a priority. 3G, 4G, and LTE fulfill users' needs, requiring progressively faster mobile internet and data transfer speeds. On the cutting edge, 5G ushers in an era of ultra-fast connectivity, laying the foundation for applications like virtual reality and the Internet of Things (IoT).
From a technological standpoint, the market offers a range of solutions. RANs form the backbone of wireless networks, providing broad coverage areas. Small cells and distributed antenna systems (DAS) complement microcells by densifying the network in high-traffic zones or indoors. Cloud RAN virtualizes network functions, offering greater flexibility and scalability. Mobile core and backhaul technologies ensure seamless data transmission within the network. Carrier Wi-Fi leverages existing Wi-Fi infrastructure to offload traffic from cellular networks. Finally, remote radio head (RRH) advancements enable flexible network deployments.
Understanding these segments and their growth dynamics is essential for market players to develop targeted strategies and capitalize on emerging opportunities. The wireless infrastructure market presents a compelling growth story fueled by the ever-increasing demand for high-speed connectivity and innovative applications.
Regional Outlook
The wireless infrastructure market is dynamic worldwide, with distinct regional trends and growth trajectories. This section delves into the key players and driving forces shaping the market in different geographic segments. The wireless infrastructure market is a tapestry woven from regional strengths and aspirations. While North America currently holds the top spot, driven by established infrastructure and high operator spending, other regions are poised for significant expansion. Let's delve deeper into the geographical outlook of this dynamic market.
Developed regions like North America, Europe, and East Asia are expected to be the early adopters of 5G technology and infrastructure investment. This advantage stems from their existing, robust infrastructure and higher disposable income, allowing for faster adoption and implementation of these advanced solutions. However, the story doesn't end there. Developing regions, while experiencing a slower initial uptake, might witness a steeper growth trajectory. They can use older technologies and invest directly in cutting-edge infrastructure, potentially surpassing developed regions' growth rates. For instance, semiconductors use RISC-V-based AI-enhanced DSP(digital signal processor) for wireless infrastructure. This innovation addresses significant challenges in deploying the Open RAN system, particularly for high traffic and low latency, such as massive MIMO.
The United States, with its well-established infrastructure, high operator spending on 5G deployment, and huge demand for high-speed data, is expected to maintain its strong position in the market. Similarly, Europe is anticipated to witness significant growth fueled by government initiatives promoting 5G rollout and network upgrades.
Shifting our focus to Asia-Pacific, a region brimming with potential, we see India as a rising star. Factors like increasing internet penetration, a surge in data usage, and government initiatives promoting digital connectivity fuel significant growth and development in India's wireless network infrastructure market. Revenue is projected to reach a staggering US$5.20 billion by 2024.
Another noteworthy trend is the rapid adoption of 5G technology in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea. Government backing and high smartphone penetration in these regions drive this rapid uptake. These countries have the potential to achieve exceptional growth rates as they bypass older technologies and invest in next-generation infrastructure.
While North America reigns supreme, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to become a significant global wireless infrastructure market player. This growth is attributed to several factors. India, for instance, boasts the world's largest Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) sector, which relies heavily on robust wireless infrastructure. Additionally, the expanding global economy and businesses venturing into new markets necessitate high-speed data solutions to manage ever-increasing data volumes and seamless transfer across borders. Furthermore, the rise of workplace mobility, where employees work remotely using their preferred wireless devices, has significantly increased the demand for reliable and efficient wireless communication.
The global wireless infrastructure market presents a diverse landscape with distinct growth patterns across regions. Developed regions are expected to lead the initial 5G adoption wave while developing areas hold immense potential for future growth as they embrace new technologies. With government initiatives, increasing internet penetration, and a growing demand for high-speed data, the future of the wireless infrastructure market looks bright across the globe.
North America
North America’s wireless infrastructure market is fueled by a robust foundation. The region boasts a high penetration of LTE and 4G services, driven by the presence of major players like the United States and Canada. This established infrastructure allows seamless upgrades to 5G technology, further solidifying North America's position. Strong government and private sector investments in infrastructure development and high disposable incomes also translate to a constant demand for high-speed data and advanced wireless solutions. Sectors like healthcare are embracing high-speed connections for critical applications like remote surgeries, further propelling market growth.
Although, The US Federal Reserve's aggressive interest rate hikes to combat inflation have made borrowing more expensive for businesses, including mobile operators. This higher cost of capital, combined with economic uncertainties like recession fears, has prompted some carriers to be more cautious with their investment plans.
Asia Pacific
The Asia Pacific region presents a compelling story of rapid expansion. This region is poised to become a significant global wireless infrastructure market player. Factors like rising internet penetration, surging data usage, and government initiatives promoting digital connectivity fuel this growth. Countries like India, with its vast Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) sector, need robust wireless infrastructure. As economies expand and businesses explore new markets, the demand for high-speed data solutions to manage large data volumes across borders is accelerating. Furthermore, the rise of workplace mobility, where employees can work remotely with wireless devices, necessitates reliable and secure wireless networks.
Europe
The European wireless infrastructure market in 2024 presents a complex landscape with regional variations. Western Europe, a mature market, is experiencing slower growth due to high penetration rates. However, densification for 5G and fiber-optic backhaul upgrades are driving demand. Eastern Europe, on the other hand, is witnessing significant growth fueled by government initiatives, network expansion plans of mobile operators, and rising internet consumption. The region is catching up with Western Europe regarding technology adoption, creating opportunities for infrastructure vendors. Northern Europe boasts robust infrastructure focusing on innovation and early adoption of technologies like 5G. Governments here are actively supporting infrastructure development through grants and subsidies. Southern Europe faces challenges due to economic disparity and regulatory hurdles. However, increasing demand for mobile data and government investments in underserved regions are creating pockets of growth.
Segment Outlook
5G
5G deployment will be a significant focus, with operators investing heavily in network upgrades and infrastructure expansion. Advancements in 5G Stand-Alone (SA) architecture are expected to enable network slicing for diverse applications like ultra-reliable low-latency communication (uRLLC) and massive machine-type communication (MTC).
Research and development (R&D) efforts in 6G technologies will pick up pace in 2024. areas will likely include even higher data rates, lower latency, and support for many connected devices. Initial
standardization discussions and pilot projects might emerge, but large-scale deployments are not expected in 2024.
O-RAN
O-RAN Adoption is expected to gain traction in 2024 as operators seek greater network flexibility and interoperability. This allows operators to mix and match equipment from different vendors, potentially leading to lower costs and faster innovation. It might see initial deployments of O-RAN-compliant infrastructure, particularly in greenfield sites (new network builds).
Hyperscalers
Hyperscalers (large cloud providers like Google, Amazon, and Microsoft) will play an increasingly prominent role in the wireless infrastructure market. They are expected to invest in network infrastructure, particularly for edge computing deployments closer to users for low-latency applications. Partnerships between hyper scalers and telecom operators will likely become more common for infrastructure development and service delivery.
Market Dynamics
Growth Enablers
Rising Demand for 5G
The rollout of 5G networks is a significant catalyst for growth in the wireless infrastructure market. 5G promises a revolution in mobile connectivity, offering ultra-fast speeds, significantly lower latency, and vastly enhanced capacity. This translates to a surge in demand for improved wireless infrastructure to ensure users can fully experience these benefits.
At the core of this enhanced infrastructure lies the deployment of small cells. These are low-powered cellular base stations with a smaller coverage area than traditional macro towers. They are strategically placed to densify the network, particularly in urban areas with high user concentration. This densification ensures consistent and robust signal reception, maximizing the potential of 5G technology.
Distributed Antenna Systems (DAS) are another critical component of the upgraded infrastructure. DAS distributes signals throughout buildings and campuses using a network of antennas and cables. This is crucial for overcoming signal penetration challenges within structures, ensuring seamless 5G connectivity indoors. Similarly, indoor repeaters are deployed to amplify existing signals within buildings, eliminating dead zones and providing consistent coverage.
Adopting the mmWave spectrum for 5G transmission adds another layer of complexity. Millimeter waves offer incredibly high bandwidth but have shorter propagation distances and are susceptible to blockages. This necessitates innovative solutions to overcome these challenges. In response, the in-building wireless solutions market is thriving, developing technologies like beamforming antennas that can precisely focus and direct signals. The rise of 5G drives significant investments in wireless infrastructure, encompassing small cells, DAS, indoor repeaters, and innovative solutions tailored for the mmWave spectrum.
Increasing Data Usage
The proliferation of data-hungry devices puts immense pressure on existing wireless networks. From smartphones and tablets to defense electronics and rugged desktops, the number of devices demanding high-speed and reliable connectivity is growing exponentially. This trend is particularly evident with smartphones, where user base and mobile data traffic have witnessed astronomical growth. A similar explosion is expected for Internet of Things (IoT) devices, further straining network capacity.
This surge in connected devices translates to a massive demand for robust network infrastructure components. Sensors play a crucial role in collecting and transmitting data from devices. Transmitters and receivers facilitate data transfer across the network, while powerful processors are needed to handle the ever-increasing volume of information. To meet this growing demand, manufacturers of network infrastructure components are constantly innovating and developing solutions that are more efficient, scalable, and capable of handling the ever-increasing data traffic.
The challenge of rising data usage presents a significant opportunity for the wireless infrastructure market. As network operators strive to meet user demands, investments in network infrastructure are expected to climb steadily. This translates to growth for companies manufacturing and deploying network equipment, creating a dynamic and lucrative market space.
Technological Advancements
Continuous advancements in wireless technologies propel the wireless infrastructure market forward in several ways. One key area of progress is expanding mobile network coverage to remote and underserved areas. This is being achieved through the development of innovative technologies like low-power wide-area networks (LPWAN) and satellite-based connectivity solutions. LPWANs enable long-range communication with low power consumption, making them ideal for connecting devices in remote locations. Satellite-based solutions offer connectivity in geographically challenging areas where traditional terrestrial infrastructure is impractical.
Another significant advancement is the reduction in data usage charges. Increased competition among network operators drives down prices, making mobile data more affordable. This incentivizes users to consume more data, highlighting the need for robust network infrastructure.
Network infrastructure improvements are also crucial in handling rising network traffic. This involves advancements in network architecture, protocols, and equipment. Software-defined networking (SDN) and network function virtualization (NFV) enable flexible and efficient network management, allowing operators to adapt to changing traffic patterns and user demands.
These continuous technological advancements are essential for handling the ever-growing data demands and contribute to a more efficient and cost-effective wireless infrastructure landscape.
Government Initiatives
Government initiatives worldwide constitute a significant catalyst for growth in the wireless infrastructure market. A prime example is the US government's launch of 5G services in 2019. This triggered substantial investments by key players like AT&T and Verizon in building their 5G networks, creating a domino effect that spurred the market. Similar initiatives are underway in Europe and China. European operators are aggressively building their 5G networks, while Chinese giants like China Mobile are leading the way in 5G infrastructure development. These government-backed initiatives create a favorable environment for market growth, encouraging investments in network infrastructure and accelerating the adoption of next-generation technologies.
Growth Inhibitors
While the wireless infrastructure market is experiencing significant growth, several key challenges remain. These challenges can hinder the adoption and optimal performance of next-generation technologies like 5G.
High Costs
Building and maintaining a robust wireless infrastructure is expensive, especially for cutting-edge technologies like 5G. The financial burden starts with securing spectrum licenses. These licenses grant operators the exclusive right to use specific radio frequencies within a designated area. However, obtaining these licenses can be competitive and costly, particularly in densely populated urban areas with high demand for bandwidth. Additionally, the equipment necessary for 5G networks is more complex and expensive than previous generations. This includes cell towers, antennas, and backhaul infrastructure – the high-capacity connections that carry data between cell sites and the core network. The cost equation becomes even more complex in remote rural locations. Deploying and maintaining infrastructure in these areas with lower population density can be challenging. The potential revenue generated from such deployments might not justify the initial investment, creating a financial disincentive for operators. Furthermore, the limited spectrum availability, particularly in the licensed bands preferred by mobile network operators, can exacerbate these challenges. When a limited amount of spectrum is shared by multiple operators, congestion and interference can occur. This ultimately hinders the ability of the network to deliver sufficient capacity and coverage, impacting user experience.
Technical Challenges
Deploying and managing a modern wireless infrastructure is no small feat. Several technical hurdles need to be overcome to ensure seamless and reliable connectivity. One such challenge is interoperability. Different vendors may use proprietary equipment and protocols, making their infrastructure unable to interact and share resources seamlessly. This lack of interoperability can increase complexity and cost during deployment and limit flexibility in network management.
Another significant technical challenge is signal propagation. Radio waves, the lifeblood of wireless communication, can be weakened or distorted by various factors. Buildings, trees, and weather conditions can affect signal strength, leading to patchy coverage or dropped connections. Radiofrequency (RF) interference can occur when multiple wireless signals compete for the same airspace. This interference can significantly degrade signal quality and network performance. Finally, optimizing a complex wireless network requires ongoing monitoring and adjustments. Factors like traffic patterns, user demand, and interference levels must be constantly analyzed to ensure efficient network resource allocation and optimal user experience. This network optimization process can be a complex and resource-intensive undertaking.
In-Building Wireless Challenges
While 5G promises to revolutionize connectivity with its ultra-fast speeds and low latency, it faces unique challenges within buildings. Unlike outdoor environments, indoor spaces introduce obstacles that can significantly impact signal quality. Building materials like concrete, metal, and low-emissivity glass can attenuate signals, leading to weak coverage and dropped calls. Structural features like pillars, elevators, and ventilation ducts can further disrupt signal propagation. These challenges are compounded by multipath propagation, a phenomenon where radio waves take multiple paths to reach the receiver, causing signal distortion and interference.
The dynamic nature of the RF environment within buildings adds another layer of complexity. Occupancy levels, furniture placement, and even the presence of electronic devices can all influence signal propagation. To overcome these challenges, 5G networks within buildings require adaptive systems that dynamically adjust signal strength and direction based on real-time conditions. Additionally, careful spectrum management is crucial to minimize interference and ensure optimal performance.
Finally, the cost of deploying and maintaining in-building 5G infrastructure can be significant. The initial investment in equipment, installation, and integration with existing infrastructure can be high. Ongoing maintenance further adds to the operational expenditure. This can negatively impact building owners' return on investment (ROI) and potentially hinder the adoption of 5G within buildings. Regulatory compliance adds another complexity and cost, as building owners must adhere to specific safety and health standards for radio frequency emissions. Overcoming these challenges will be critical to ensure users enjoy the full potential of 5G connectivity indoors.
Absence of “Killer app” for 5G
Although 5G offers significant improvements over 4G in speed, latency, and capacity, its adoption has been slower than anticipated. This is largely due to the lack of a "killer app" that showcases 5G's revolutionary potential. Current applications, like faster downloads and improved video streaming, are nice enhancements but haven't fundamentally changed user experiences. Factors such as limited device availability, spotty network coverage, and high data costs have also contributed to this slower uptake.
However, the 5G landscape is set to evolve rapidly. As the technology matures, we can expect a wave of transformative applications to emerge. These could include immersive AR/VR experiences in various fields, widespread adoption of IoT devices in industries like manufacturing and logistics, safer and more reliable autonomous vehicles, and even revolutionary telemedicine capabilities.
With the advent of these game-changing applications and increased accessibility, 5G adoption is poised to accelerate significantly, reshaping how we interact with technology and the world around us.
After-effects of Semiconductor Allocation Crisis
Initially sparked by the pandemic's impact on demand and supply chains, the global chip shortage, caused significant disruptions in various industries, including the mobile sector. Manufacturers faced challenges securing enough chips to meet the surging demand for electronics, leading to production delays and limited availability of new devices.
However, as the global supply chain gradually recovered and consumer spending patterns shifted, the chip shortage transformed into an oversupply in certain categories. This was particularly evident in older phone models, as consumers held onto their devices longer and demand for upgrades slowed down.
This unexpected turn of events left mobile operators with excess inventory, tying up capital and potentially impacting profits. The situation serves as a reminder of the semiconductor industry's cyclical nature and the importance of adapting to changing market dynamics to mitigate the risks of oversupply.
Wireless Infrastructure Market
Supply Chain
Sustainability
The telecommunications industry is actively seeking solutions to minimize its environmental footprint. A 2022 report by GSMA, the mobile industry trade body, revealed a significant increase in operator commitment to sustainability. The number of operators pledging to reduce their carbon footprint over the next decade has more than doubled since 2021. Furthermore, nearly half of all operators, representing 44% of global telecom revenue, have committed to achieving net-zero emissions by 2050. The environmental impact of mobile technology is undeniable. As per the TechTarget sustainability report, A typical mobile connection generates roughly 59 kilograms of carbon dioxide annually, a significant amount compared to other activities. However, this pales compared to the emissions associated with air travel, highlighting the potential for positive change within the mobile sector.
Data sourced from TechTarget
Understanding the energy consumption within mobile networks is crucial for effective sustainability initiatives. Studies by TechTarget sustainability indicate that radio access networks (RAN) are the primary culprit, responsible for a staggering 73% of energy consumption. The remaining energy is divided among core networks (13%), data centers (9%), and operations (5%). The encouraging news is that progress is being made. While data traffic has surged by 31%, corresponding increases in electricity consumption and carbon emissions have been modest at 5% and 2%, respectively. These figures indicate that operator-led sustainability efforts are yielding positive results.
Mobile operators are deploying several key strategies to achieve sustainability goals. A primary focus is on reducing carbon emissions and optimizing energy consumption. To measure energy efficiency, operators utilize various metrics, including energy consumption per data transfer unit, energy used per base station, and energy required per connection. Additionally, they track energy consumption relative to revenue generation.
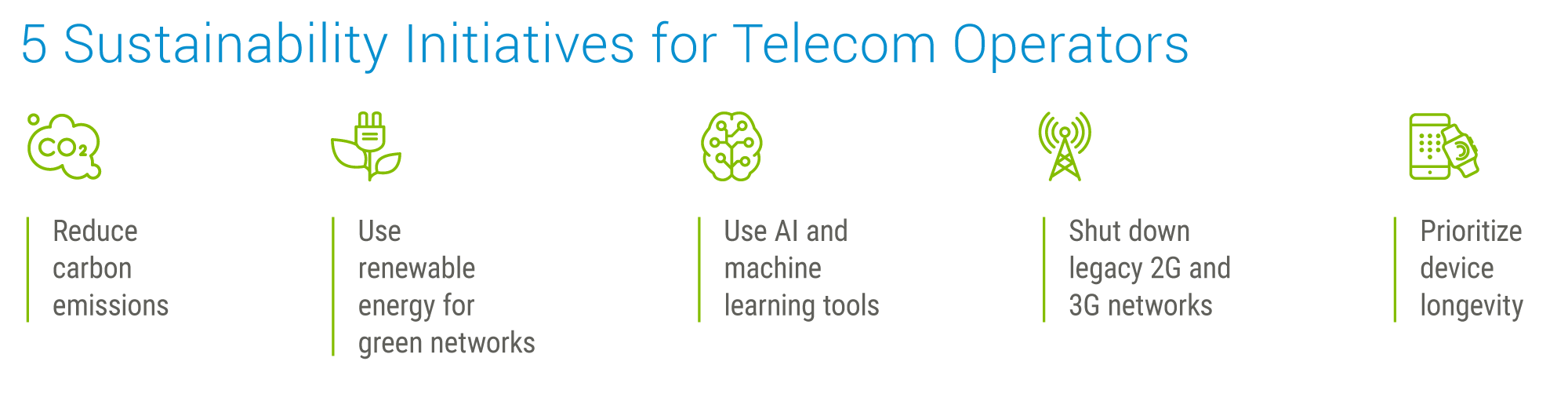
Here's a closer look at some of the significant sustainability initiatives being undertaken:
Reducing Carbon Emissions
Most of an operator's carbon footprint (over 90%) stems from the electricity powering their networks. Operators can accurately assess their environmental impact by evaluating greenhouse gas emissions across three scopes:
Direct emissions from operator activities (e.g., diesel-powered base stations). Indirect emissions associated with purchased energy (e.g., heating or cooling buildings). Indirect emissions from customer use of operator services (most challenging to calculate but represents the most significant share)
Transparency and accountability are critical aspects of sustainability efforts. Operators can disclose their carbon footprint data to the Carbon Disclosure Project. In 2021, over 60 operators opted for this level of transparency, with connections serving 2.7 billion users, achieving top scores for implementing best practices.
Embracing Renewable Energy and Green Networks
Transitioning to renewable energy sources for powering networks is a critical strategy for reducing carbon emissions and optimizing energy use. Solar power, wind power, lithium-ion batteries, and renewable electricity from the grid are all viable alternatives to traditional diesel generators. Additionally, operators are investing in energy-efficient wireless technologies and equipment. However, challenges exist in implementing renewable energy solutions. Factors such as local climate, regulatory environments, grid availability, and the cost of renewable energy can significantly impact feasibility.
Leveraging AI and Machine Learning
As artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) evolve, operators deploy these tools to gain insights into energy use and network performance. For instance, AI can provide key performance indicators (KPIs) related to RAN performance and 5G degradation, enabling operators to identify areas for improvement. Furthermore, AI can be used for root cause analysis, helping to optimize field operations, performance, cost savings, energy consumption, and carbon reduction.
Circular Economy
The current global economic model, heavily reliant on a "take-make-dispose" approach, is unsustainable. This linear economy generates massive waste and puts immense strain on resources. To address these challenges, industries worldwide are embracing the circular economy, a more sustainable model focused on minimizing waste and maximizing resource efficiency. The circular economy prioritizes reducing, reusing, and recycling materials. It also promotes practices like repair, sharing, refurbishment, and remanufacturing. Compared to the traditional linear approach, this model minimizes waste and optimizes resource use. Waste generation is a significant concern in the telecommunications sector, with its rapid technological advancements and ever-shorter product lifecycles. The circular economy offers a promising path towards a more sustainable future for wireless infrastructure.
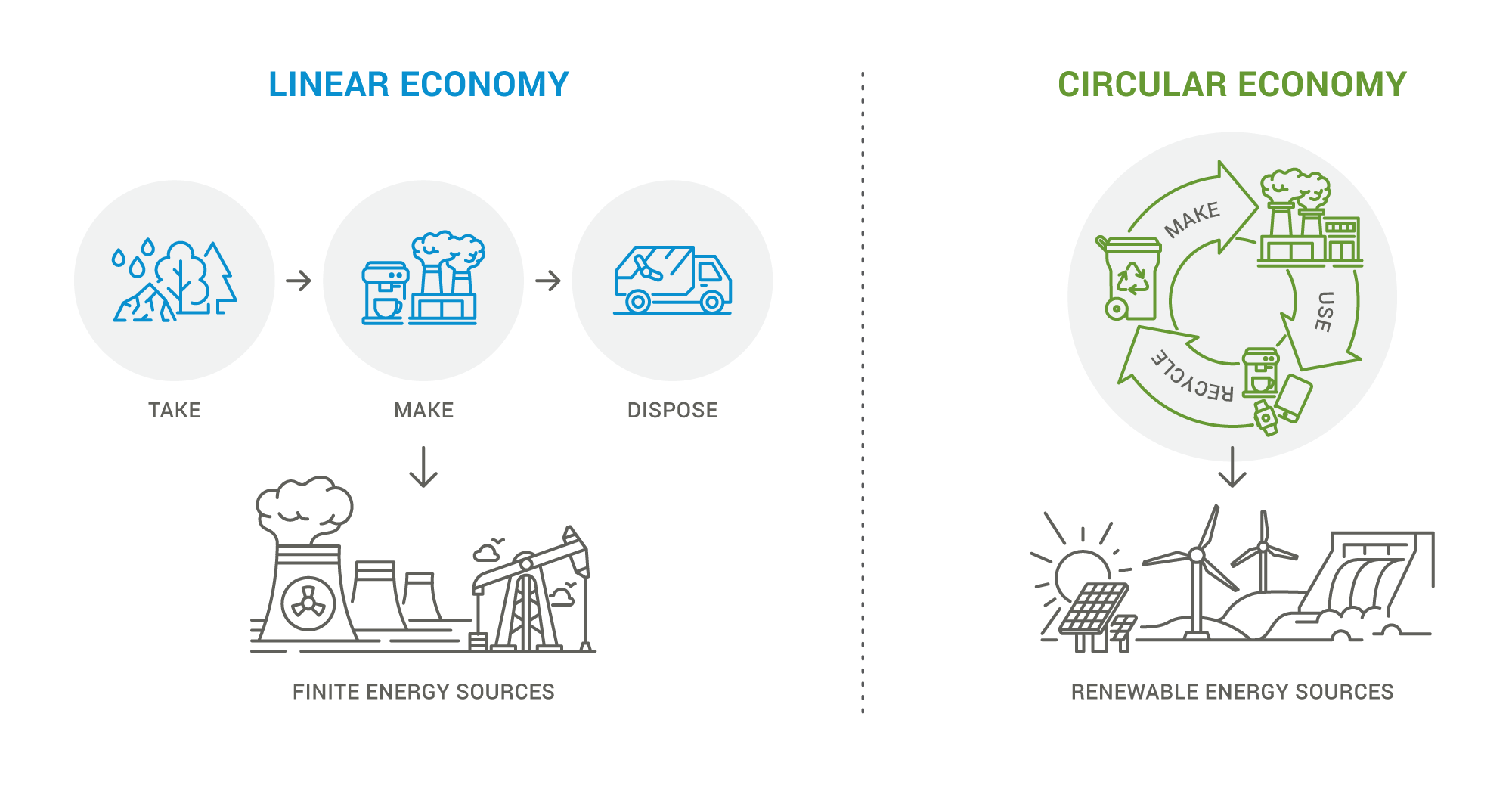
Circular supply chains prioritize reusing and repurposing raw materials, eliminating waste, and minimizing the environmental footprint.
Circular practices promote energy efficiency, sustainable packaging, use of alternative fuels, optimized shipping routes, and responsible returns management. These practices contribute significantly to overall sustainability goals. By efficiently utilizing recycled materials, businesses can manage budgets and control costs associated with volatile raw material prices. Governments are increasingly mandating circular supply chain practices, including material recycling and responsible waste disposal. Additionally, they offer incentives for companies implementing green initiatives, further driving sustainability efforts. Consumers are becoming increasingly environmentally conscious. Many are willing to pay a premium for sustainable products, pressuring companies to adopt environmentally responsible practices throughout their supply chains.
Telecom businesses need to embrace sustainability education. This includes learning about circular economy principles and their applications within the industry. Companies should evaluate their current business models to identify areas where they deviate from circular practices. This allows for the targeted implementation of circular strategies. Successful transformation requires industry-wide collaboration, including partnerships with suppliers, NGOs, investors, and consumers. Stakeholders can establish a circular model throughout the entire value chain. Ambitious environmental objectives should focus on reuse, recycling, and waste reduction. Progress needs to be tracked and measured regularly to ensure goals are met and adjustments can be made as required. Companies should communicate their circularity efforts openly and transparently to consumers. Sharing success stories and inspiring others to implement similar initiatives fosters awareness and drives positive change.
For instance, Ericsson and IoT Squared signed a memorandum of understanding at the Mobile World Congress Barcelona 2024, Spain, to offer the Ericsson Connected Recycling platform in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Ericsson Connected Recycling digitalizes waste flows to enable traceability, optimization, and monetization of waste and recycled raw materials. The platform eliminates unnecessary waste by enabling circularity, turning waste into new products through connectivity and IoT.
Reshoring and Nearshoring
The wireless industry is undergoing a significant transformation in its supply chain strategies. Companies increasingly embrace reshoring and nearshoring practices as the sector experiences rapid global growth. This shift is driven by various factors, including the desire to mitigate financial risks, enhance responsiveness to consumer demands, and adapt to a rapidly evolving technological landscape.
By shortening supply chains, reshoring and nearshoring aim to achieve several key objectives. Firstly, they seek to reduce logistics costs during heightened economic uncertainty. Secondly, they aim to bolster supply chain resilience against potential disruptions, a critical lesson learned from recent global events like the COVID-19 pandemic and its associated supply chain bottlenecks. This trend toward bringing manufacturing closer to consumer markets directly responds to the recent logistical challenges and economic uncertainties. However, the path towards reshoring and nearshoring is not without its hurdles. Establishing robust supply bases and securing skilled labor for the sophisticated needs of the wireless technology sector presents a significant challenge. Regions like Mexico or the U.S. face hurdles related to capacity constraints and the need for highly specialized technical expertise. This industry-wide pivot from prioritizing cost minimization to emphasizing supply chain resilience and flexibility marks a significant strategic realignment.
The wireless sector's specific needs and priorities underscore the importance of this transformation. With the dual objectives of boosting performance and facilitating process enhancements, the industry is ripe for operational innovations and digital transformations. A prime example is the U.S. government's policy initiatives, like the CHIPS Act, which incentivizes domestic production of critical wireless components, such as semiconductor chips. This initiative aims to bridge the gap in domestic production and stimulate significant investments in semiconductor manufacturing, a vital element for wireless devices.
Furthermore, the global transition towards sustainable and energy-efficient homes drives investments in domestic manufacturing of green technology components, including smart thermostats, energy management systems, and advanced lighting solutions. As companies increasingly consider the environmental impact of their supply chains, this move aligns with consumer expectations for sustainable products.
The shift towards reshoring and nearshoring in the wireless industry is a multifaceted strategy. It aims to secure supply chains against future disruptions, optimize costs, and swiftly adapt to new technological advancements and consumer demands. As companies in this sector navigate these changes, balancing cost, efficiency, and resilience will likely remain a key focus. This focus is critical for maintaining a competitive edge in an industry characterized by rapid innovation and evolving consumer demands.
The global landscape of globalization is shifting. While cost reduction was once a primary driver, factors like reduced dependence on China, post-pandemic supply chain fragility, geopolitical shifts, and declining domestic demand due to inflation are now more significant. Recent trends show a decline in demand for electronic components sold in China, indicating a potential plateau of globalization. However, this shift presents an opportunity. New product designs requiring electronic components are no longer limited to one or two countries. This trend and nearshoring and reshoring empower manufacturers to innovate their manufacturing processes and talent development strategies. This shift can potentially drive better outcomes for businesses and their communities.
One significant challenge lies in converting existing manufacturing plants, particularly older facilities in China designed for labor-intensive processes. On the other hand, Greenfield factory builds offer a more favorable environment for leveraging automation, data, the Internet of Things (IoT), and new forms of intelligence within the manufacturing process. Automation is critical to reducing waste, increasing reliability, and driving better return on investment (ROI) in manufacturing plants. Technologies like Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines enable manufacturers to control factory machinery and tools with pre-programmed software. This technology offers accuracy, consistency, and efficiency that is impossible with manual processes.
Raw material costs are another primary concern for global companies. Since a significant portion of a product's value comes from its materials, manufacturers must control their processes and materials to optimize profits. Automated materials management systems help companies track and access raw materials while implementing just-in-time dispatching to avoid production stoppages. Additionally, new forms of intelligence can provide visibility across the electronics supply chain, preventing disruptions by ensuring manufacturers have the necessary semiconductors and other components to meet their production needs.
Mexico has become a favorite nearshoring manufacturing location for companies in North America. Europe is looking toward countries like the Czech Republic, Hungary, and Poland. In Asia, India, where companies like Apple and Samsung are expanding their electronics production, has the highest growth potential for attracting new investments and creating new manufacturing sources. However, many of these newer markets face a significant skills gap. The global factory automation market is expected to experience considerable growth, but the limited availability of skilled professionals is a crucial factor hindering its expansion.
COVID-19 and Semiconductor Scarcity
Although it’s the past, the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on wireless infrastructure extends beyond initial disruptions. Misinformation campaigns around 5G safety led to vandalism and highlighted the vulnerability of information networks in a globally connected world. The pandemic also exposed the fragility of supply chains, with lockdowns and production slowdowns affecting chip availability. New variants or wider lockdowns could further disrupt production, hindering market growth. Geopolitical tensions add another layer of complexity. The war in Ukraine threatens chip production due to its reliance on neon gas, a crucial element. The ongoing tensions between the US and China also strain the already stressed supply chain. While initiatives like the CHIPS Act aim to bolster domestic chip production in the US, their effectiveness remains uncertain. This heavy dependence on a single source pushes companies to diversify their supply chains, potentially leading to a geographical shift in the market.
The chip shortage primarily affects smaller players. While larger wireless companies can secure enough chips to maintain production, Internet of Things (IoT) companies with lower production volumes are more susceptible. However, there are signs of improvement. According to Strategy Analytics, the worst shortage for the cellular infrastructure segment might be over. Increased foundry capacity and production expansion will alleviate shortages in cellular equipment, Wi-Fi hotspots, and cell phones over the coming year. This aligns with predictions from Strategy Analytics' director of RF & Wireless Component Services, who anticipates gradually easing tight semiconductor supply as new production capacities come online throughout 2022 and 2023. the wireless infrastructure market in 2024 faces challenges from misinformation campaigns, supply chain disruptions, and geopolitical tensions. While the chip shortage may be easing for some segments, the long-term impact of these factors remains to be seen. Moving forward, diversification of chip production and a focus on combating misinformation will be crucial for the market's stability and continued growth.
Wireless Infrastructure Market
Technology Evolution
Evolution of 1G to 5G
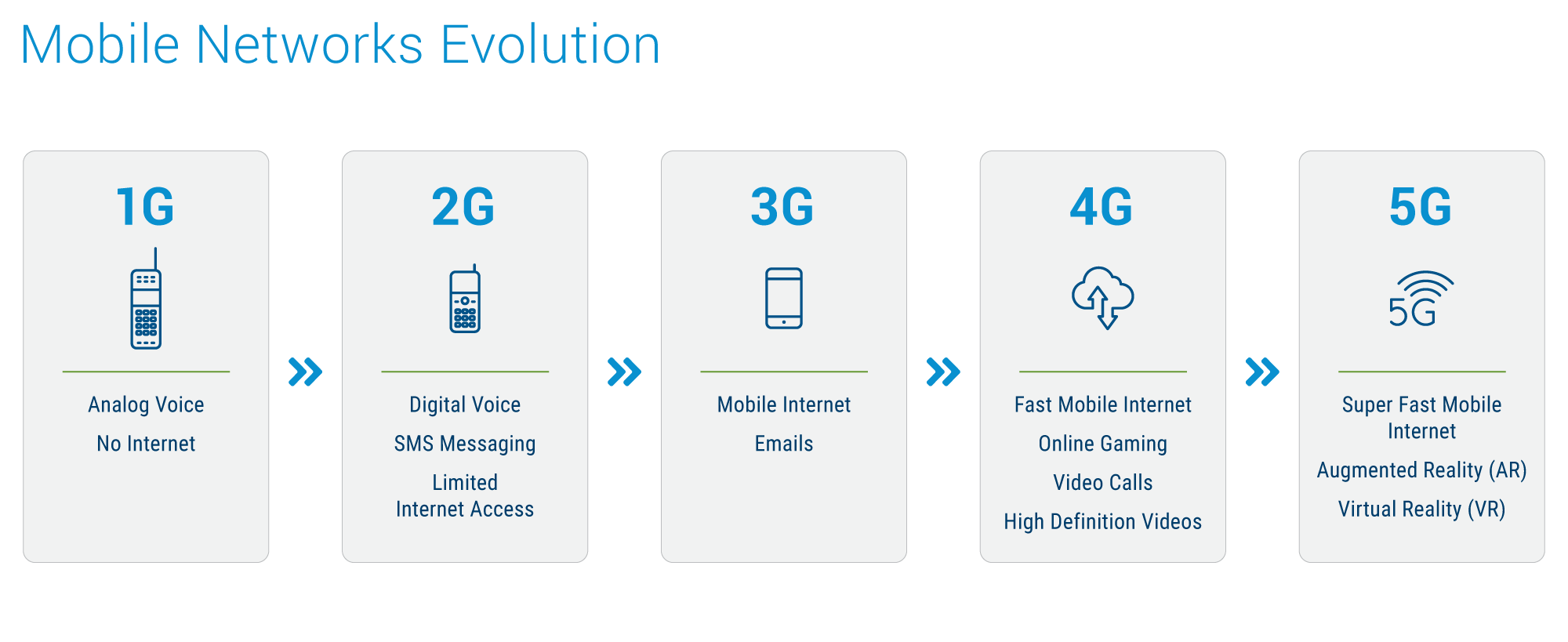
Since its inception, wireless technology has undergone a remarkable transformation. This journey, marked by five distinct generations (1G to 5G), has revolutionized how we connect and interact with the world.
The first generation (1G), introduced in the early 1980s, offered an essential step towards mobile communication. It enabled voice calls through analog cellular service, albeit with limited data speeds. While groundbreaking, 1G paved the way for more advanced technologies. The 1990s ushered in the era of 2G with its digital revolution. This generation introduced features like text messaging and faster data transfer speeds compared to 1G. 2G relied on GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications), enabling digital encryption and network roaming. It played a pivotal role in shaping the modern mobile phone, although it has primarily been surpassed by 3G and 4G advancements.
Data sourced from Visermark
The late 1990s saw the arrival of 3G technology, significantly enhancing data transmission speeds and multimedia capabilities. This generation shifted the focus towards internet access, multimedia streaming, and video calls. 3G offered improved coverage compared to 2G and provided higher data transfer speeds, making it ideal for web browsing, downloading files, and enjoying multimedia content. Additionally, 3G boasted better energy efficiency, leading to longer battery life for mobile devices.
4G, the successor to 3G, arrived with a focus on drastically improved data rates and bandwidth. This generation offered significantly faster speeds, allowing users to download movies in seconds. 4G brought a more reliable connection with improved signal strength, enabling faster browsing and streaming experiences. Furthermore, it enhanced voice call quality and supported data-intensive activities like online gaming, video streaming, and sending large files. 4G's capabilities extend to location-based services, mobile TV, and Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP).
The current frontier of wireless technology is 5G, boasting speeds that are 100 times faster than 4G. This revolutionary technology promises data transmission speeds of up to 10 Gbps, enabling users to access the internet at lightning speed, stream ultra-high definition videos, and experience virtual and augmented reality applications seamlessly. 5G's key features include fast speeds, low latency, massive capacity, and improved reliability. With speeds exceeding the average home broadband connection, 5G allows for buffer-free streaming of high-quality content. Additionally, its low latency caters to applications like gaming and virtual reality, where even slight delays can significantly impact the user experience. 5G's most significant advantage lies in its ability to support many devices and users simultaneously, paving the way for a truly connected future.
The evolution of wireless communication from 1G to 5G is a testament to human ingenuity and its relentless pursuit of a more connected world. Each generation has built upon the foundation laid by its predecessor, pushing the boundaries of speed, capacity, and reliability. As we move forward with 5G and beyond, we can expect even more transformative applications to redefine how we live, work, and interact with the world around us.
6G Technology
The cellular network industry has witnessed significant advancements every decade, with the first mobile phone call in 1973 using 1G technology. This trend is expected to continue, with 6G research beginning around 2012 and standardization anticipated to start in 2025, targeting deployment by 2030. While consumers may not have been using 6G devices for several years, researchers are actively exploring the core technologies defining this next generation of wireless infrastructure.
Faster and more reliable connections are a common thread across the various potential applications of 6G. Consumers can expect significantly faster data transfer speeds, enabling activities like sharing high-resolution videos and photos, streaming media, playing games, and browsing the internet on mobile devices with greater ease. These improvements will also support the development of smart devices and connected homes.
The self-driving car revolution is heavily reliant on 6G. Faster vehicle-to-vehicle communication and near-instantaneous updates on road conditions, traffic, and weather would significantly enhance the capabilities of on-board sensors, cameras, and computers. Current limitations in latency and data speeds are inadequate for autonomous vehicle technology, where even a slight delay can have catastrophic consequences. Many experts believe 6G is a crucial prerequisite for the widespread adoption of self-driving cars.
Factories already utilize robots for various tasks, but 6G has the potential to usher in a new era of sophisticated automation. High-speed private networks would enable precise tracking of robots' location and status within a facility. Equipment could communicate directly with each other, coordinating movements and adjusting processes in real-time based on factors like an assembly line slowdown. Additionally, 6G could facilitate the creation of digital twins – virtual replicas of physical machine components that would provide an incredibly accurate, near real-time view of performance, allowing for proactive maintenance and preventing downtime.
Extended reality (XR) represents another exciting application domain for 6G, with potential benefits for both businesses and consumers. XR devices or headsets superimpose digital information onto the real world, blurring the lines between augmented and virtual reality. Imagine a mechanic seeing fault codes displayed for each car part while looking under the hood or a nurse being able to view a patient's vital signs with a simple glance. XR even has the potential to incorporate haptic feedback, further dissolving the boundaries between the physical and virtual worlds. To achieve its full potential, XR requires high data speeds and a reliable connection, making 6G a critical factor in bringing this technology to the mainstream.
Beyond specific applications, 6G is expected to deliver improvements across several key performance areas, including speed, throughput, reliability, coverage, latency, energy efficiency, and cost. These advancements will cater to three primary usage scenarios: enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB) for consumers, massive machine type communication (MTC) for the Internet of Things (IoT), and ultra-reliable low-latency communication (uRLLC) for applications requiring minimal delay. The impact of 6G will be felt across diverse industries.
Several vital technological advancements will be crucial for developing 6G networks. One area of exploration is joint communication and sensing, which combines communication and environmental sensing functionalities. Autonomous vehicles, for instance, rely on sophisticated sensing systems powered by machine learning algorithms that analyze data from cameras, lidar, and radar sensors. At the same time, these vehicles utilize cellular networks for data transmission and communication with other vehicles and infrastructure (V2X). Researchers are exploring how communication technologies can be leveraged to enhance sensing capabilities and vice versa. The extent to which these traditionally separate functions converge depends on regulatory and technical considerations. Still, this merging of communication and sensing has the potential to be a defining characteristic of 6G.
The ever-growing demand for data bandwidth pushes researchers to explore new frontiers in the sub-Terahertz (sub-THz) frequency range. Frequencies between 90 GHz and 300 GHz offer significantly more bandwidth than the spectrum currently used for cellular communication. While path loss, or signal weakening over distance, presents a significant challenge in these higher frequency bands, researchers are exploring ways to mitigate this issue. One approach involves matching the attenuation properties of specific frequency bands with appropriate applications. For instance, high-attenuation bands could be used for high-security applications where limiting the signal's reach is desirable. Another strategy leverages the inverse relationship between frequency and antenna size. As frequencies increase, antenna size can be reduced, allowing for more antenna elements within a smaller footprint, thereby improving signal gain. While widespread deployment of sub-THz bands may seem premature considering the ongoing rollout of 5G mm-wave technology, leading researchers are actively investigating this approach to expand network capacity significantly.
NVF
The wireless infrastructure landscape is undergoing a significant transformation driven by Network Function Virtualization (NFV). This approach sheds the traditional reliance on dedicated hardware devices and ushers in an era of software-defined networks. By virtualizing network functions, operators gain new flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness in managing their infrastructure.
At the heart of NFV lies virtual network functions (VNFs). These are software counterparts to physical hardware like routers, firewalls, and load balancers. Instead of being confined to specialized devices, VNFs run on standard servers, storage, and switches, offering greater agility in deployment and management. A virtualization layer acts as the conductor, enabling multiple VNFs to share the same physical infrastructure while maintaining isolation and ensuring efficient resource allocation.
This shift towards software-based functions brings a multitude of benefits. Firstly, NFV slashes costs. Replacing dedicated hardware with software on commodity infrastructure translates to significant capital and operational expenditure savings. Gone are the days of procuring, deploying, and maintaining specialized devices. Secondly, NFV empowers operators with unparalleled agility. Deploying and scaling network functions becomes a breeze. Gone are the lengthy processes of physical hardware installation and maintenance. Operators can now respond swiftly to changing network demands, swiftly deploying new services and applications.
Scalability is another key advantage. NFV allows operators to scale VNFs up or down seamlessly based on real-time traffic patterns. This ensures that the network can accommodate fluctuating demands without compromising performance. Security also benefits from NFV. Virtualized network security functions like firewalls and intrusion detection systems can be easily deployed and scaled, bolstering the overall network defense. NFV fosters innovation. The ease of deploying and scaling VNFs paves the way for introducing new network services and applications at an accelerated pace. This opens doors for creative solutions that cater to evolving business and user needs. The convergence of NFV and 5G marks a pivotal moment in wireless infrastructure. 5G promises to revolutionize connectivity, transforming mere "dumb pipes" into intelligent platforms that support various applications, from autonomous vehicles and smart grids to industrial robotics and beyond. NFV's agility and scalability are instrumental in meeting the stringent demands of 5G for high speed, low latency, and massive scalability. The journey towards a fully virtualized 5G network unfolds in distinct stages with gradual transitions. Undoubtedly, NFV will continue to be a driving force in shaping the future of wireless infrastructure, empowering operators with the tools to build agile, efficient, and future-proof networks.
Blockchain
The year 2024 is witnessing a significant transformation in wireless infrastructure, driven by the burgeoning demand for seamless, high-speed connectivity. Blockchain technology is at the forefront of this change, which offers a secure and decentralized approach to managing wireless networks.
Traditional wireless access has relied on centralized control by network providers. However, blockchain disrupts this model by creating a peer-to-peer network. Each participant possesses a copy of the entire blockchain, a tamper-proof record of transactions secured by cryptography. This eliminates the need for a central authority, fostering transparency and resilience. Imagine a future where individuals can share their local Wi-Fi networks with others through one-time blockchain contracts. This reduces reliance on public Wi-Fi hotspots and optimizes network resource allocation. Additionally, it presents a cost-effective solution for network providers, potentially minimizing infrastructure investments and energy consumption.
The ever-growing number of connected devices puts immense strain on existing wireless networks. Experts predict an 80-fold increase in wireless traffic by 2030 compared to 2020. This necessitates innovative solutions to tackle congestion and potential connection failures. While traditional approaches involve installing more base stations, which are expensive, blockchain offers a compelling alternative. Blockchain can significantly improve network capacity without hefty infrastructure upgrades by efficiently utilizing existing private wireless networks, including local 5G and Wi-Fi systems. However, legal frameworks and regulations must adapt to facilitate seamless wireless access sharing. The concept of smart homes, where appliances and devices seamlessly integrate with mobile applications, is gaining immense popularity. This technology offers convenience and control, allowing users to manage their homes remotely. However, security vulnerabilities associated with these interconnected devices pose a significant challenge. Hackers can exploit loopholes in security systems or human error to gain unauthorized access to smart devices. This raises concerns about data privacy and potential security breaches. Blockchain emerges as a promising solution due to its inherent security features. By leveraging the decentralized nature of blockchain, smart home devices can achieve end-to-end security. Data collected by these devices is encrypted and stored securely on the blockchain, accessible only to authorized users. This significantly reduces the risk of cyberattacks and unauthorized data access.
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the vast network of interconnected devices generating massive amounts of data. Integrating blockchain technology with IoT networks offers a powerful solution for overcoming limitations. Centralized IoT platforms often face scalability issues as the number of connected devices increases. Additionally, the lack of standardized data formats creates interoperability problems. Distributed ledger technology offered by blockchain eliminates these hurdles. Blockchain enables direct communication between devices on a secure, decentralized network, enabling secure data exchange within the IoT ecosystem. This enhances scalability and fosters interoperability, ensuring seamless communication between different devices.
The convergence of wireless infrastructure with blockchain technology presents a promising future for secure, efficient, and scalable connectivity. As the demand for bandwidth continues to surge, blockchain offers a transformative approach to network management, fostering innovation in smart homes and the broader IoT landscape. By harnessing the power of decentralization and robust security, blockchain paves the way for a future where wireless connectivity caters to our ever-evolving needs.
Wireless Infrastructure Market
Jabil Insights
Current Market Outlook – Analyst Perspective
The wireless infrastructure market 2024 is characterized by a growing interest in Open Radio Access Networks (Open RAN) alongside lingering cost concerns. While Open RAN offers the benefit of greater flexibility and interoperability between equipment from different vendors, its current reliance on Field-Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) makes it pricier compared to traditional radios built with Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs). FPGAs offer more functionality but come at a premium. Determining if ASICs can be developed to deliver the same functionality at a lower cost remains challenging. Despite these initial hurdles, analysts anticipate a large-scale adoption of Open RAN similar to the shift from 3G to 4G networks. However, lower-than-expected adoption rates could hinder cost reduction due to economies of scale not kicking in as anticipated.
The analyst perspective remains optimistic about Open RAN's long-term impact. Network operators are expected to see significant cost benefits in reduced Capital Expenditure (CAPEX) and Operating Expenditure (OPEX) as Open RAN technology matures. Additionally, China is predicted to retain its position as a significant player in the wireless infrastructure market despite efforts by Western Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) to diversify their manufacturing locations. This is primarily due to China's strong focus on innovation, ensuring a steady stream of new telecommunications technologies from the region.
Strategic Considerations
The current market landscape necessitates strategic adjustments from key players in the wireless infrastructure industry. OEMs, for instance, should explore strategies to reduce Open RAN costs. This could involve investigating the use of ASICs for specific functionalities within the Open RAN architecture and preparing for potential volume increases to unlock economies of scale.
Sustainability is also becoming a growing concern for telecom OEMs. Building solid relationships with suppliers committed to sustainable practices and minimizing carbon emissions throughout the supply chain will be crucial for success. Network operators and OEMs alike are prioritizing reduced energy consumption within their networks. Selecting suppliers and designing components with lower power requirements will contribute to environmental sustainability goals and operational cost savings.
In conclusion, the wireless infrastructure industry is experiencing significant transformation. Companies that adapt to new technologies, evolving component landscapes, geographical shifts in manufacturing, and innovative business models will be best positioned to thrive in this dynamic environment.
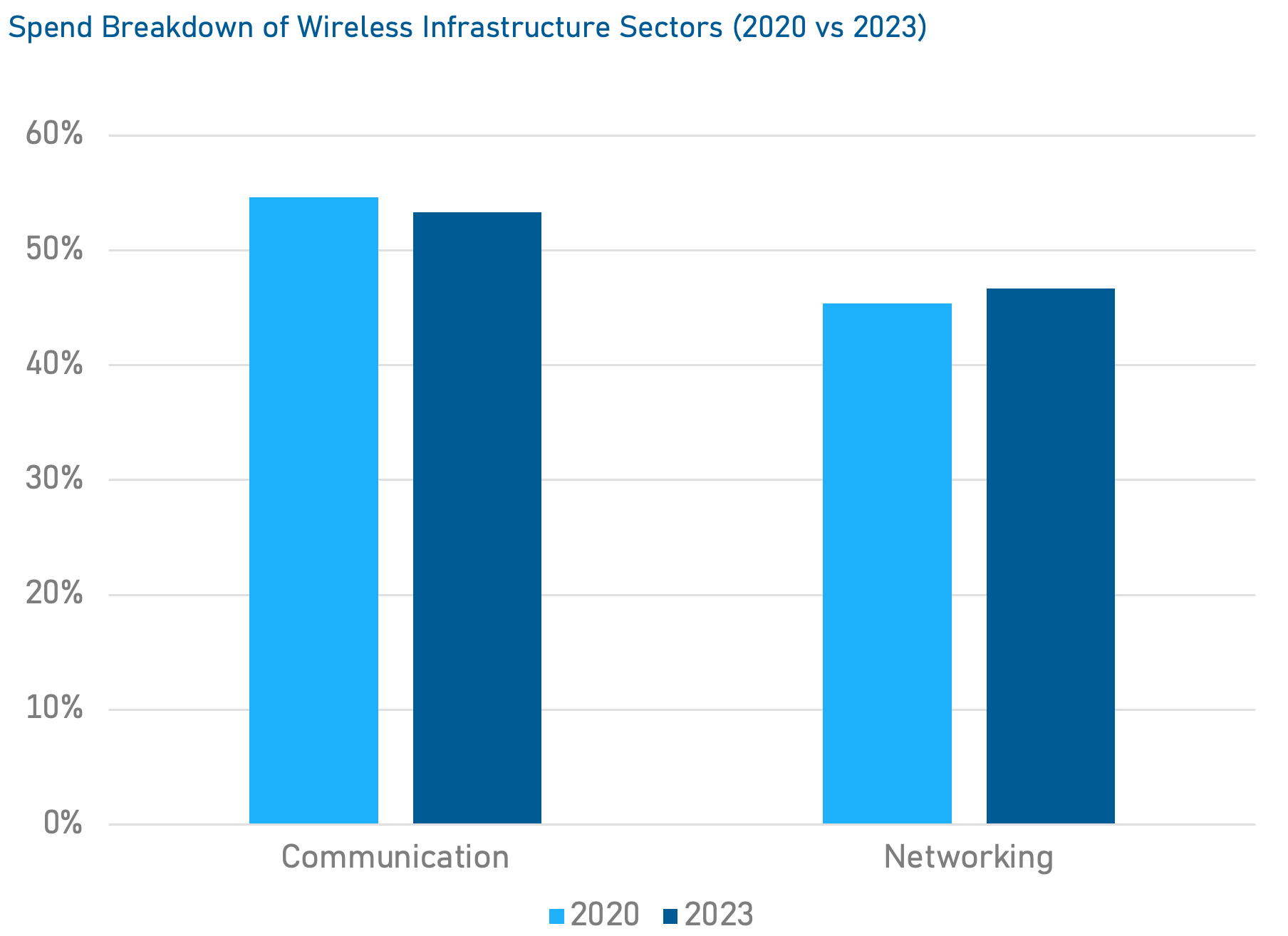
Jabil Spend Analysis
.2024-07-10-16-58-00.png)
Data based on Jabil's historical spending data for the Wireless Infrastructure Customer Segment
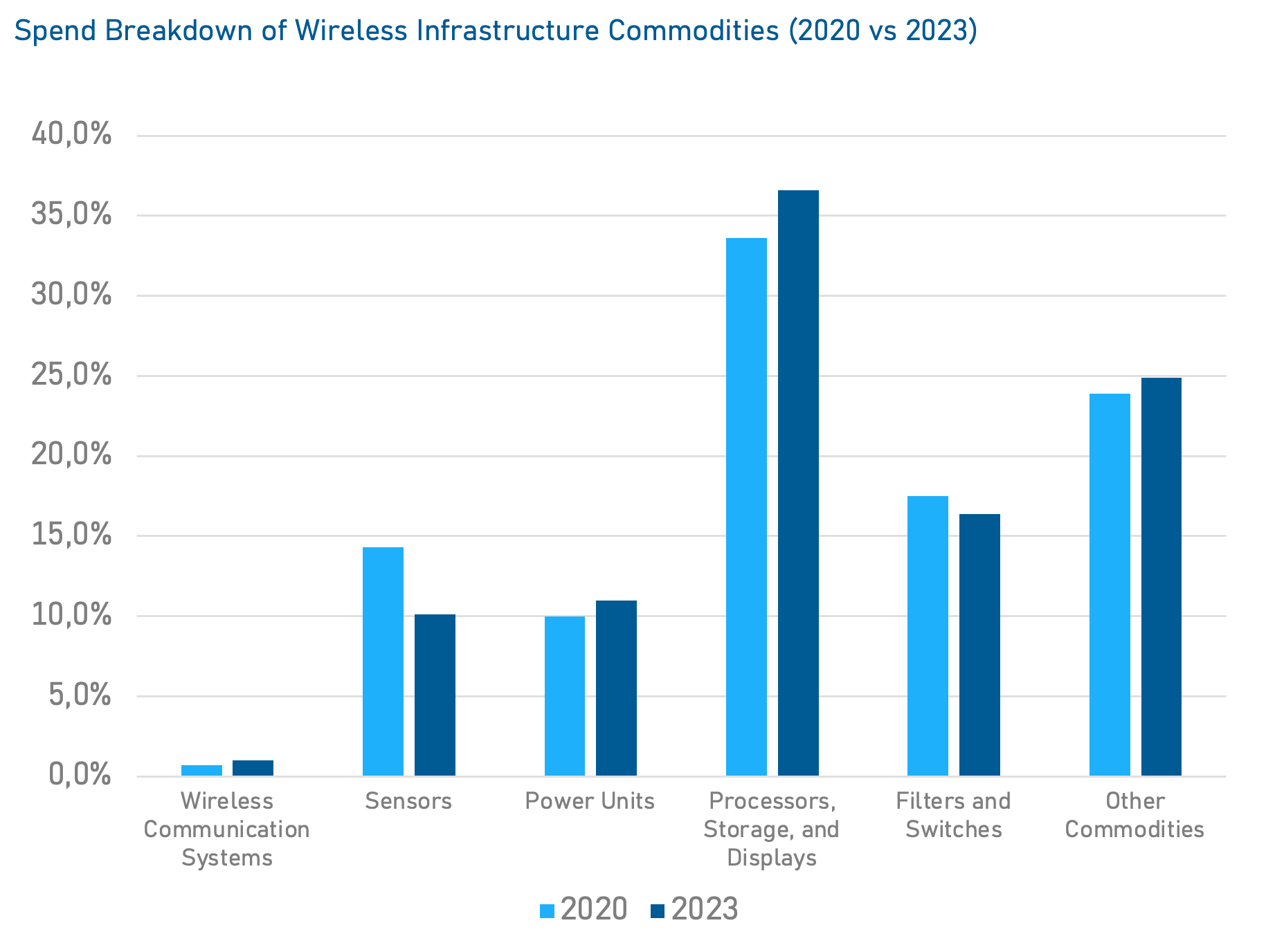
Data based on Jabil's historical spending data for the Wireless Infrastructure Customer Segment
Back to Top
