By clicking the “I Accept” button, or by accessing, participating, or submitting any information, or using the Jabil Global Intelligence Portal or any of its associated software, you warrant that you are duly authorized to accept the Global Intelligence Portal Terms and Conditions on behalf of your Company, intending to be legally bound hereby, and your company shall be bound by the terms and provisions of the Global Intelligence Portal Terms and Conditions, accessible under the following link Portal T&Cs.
Sector Market Report
Medical Devices
Sector Market Report
Medical Devices
Get an in-depth analysis of the medical devices market's current state, trends, and future, including insights into key drivers, changing product lifecycles, and manufacturing challenges.
Medical Devices
Executive Summary
The medical device market is expected to continue its upward trajectory, fueled by continuous innovation, expanding healthcare access in emerging markets, and a growing focus on preventive healthcare. While traditional markets like North America and Europe remain strong, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to grow fastest due to rising healthcare expenditures, increasing disposable incomes, and a burgeoning medical tourism industry. However, stringent regulatory hurdles and pricing pressures could limit growth in certain segments.
The rise of personalized medicine and remote patient monitoring creates significant demand for connected and smart medical devices. Wearables for tracking health data, telehealth platforms for remote consultations, and devices capable of delivering therapies remotely are all experiencing strong growth. Demand for these technologies has been further accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic, highlighting the importance of remote healthcare delivery and the need for efficient and decentralized healthcare systems. Additionally, the increasing adoption of robotics in surgery, particularly in areas like orthopedics and urology, drives demand for advanced robotic surgical systems and associated instrumentation. According to a report published by Fortune Market Insights, the Medical Devices market is estimated at $518.46 Bn in 2024.
From a supplier standpoint, the medical device market is a complex mix of high growth potential and significant challenges. Companies face intense competition, stringent regulatory hurdles, and the need for continuous innovation to meet evolving healthcare needs. Pricing pressures and reimbursement complexities also impact profitability. Successful companies often focus on niche markets, strategic partnerships, and efficient supply chains. Companies increasingly use mergers and acquisitions to expand their portfolios and strengthen their market position. Johnson & Johnson MedTech, an American healthcare giant, has announced an exclusive U.S. commercial distribution agreement with Responsive Arthroscopy Inc., a medical device company specializing in soft tissue repair solutions. Fresenius Medical Care, a Germany-based medical device manufacturer, has received FDA 510(k) clearance for its 5008X Haemodialysis System, allowing for the start of U.S.-based clinical trials; in India, Philips introduced the new Azurion to specialist interventionalists across cardiology, neurology, vascular as well as surgery in India.
The medical device market has demonstrated resilience and adaptability throughout the last three to four years. While facing considerable challenges, the industry experienced accelerated innovation and a shift towards remote and digitally enabled healthcare solutions. The market is poised for continued growth, fueled by technological advancements, but companies must navigate economic uncertainties and shifting regulations to seize new opportunities.
Medical Devices
Market Definition & Overview
Market Definition: Medical Devices
Medical devices encompass a wide range of products used in healthcare for diagnosis, prevention, monitoring, treatment, or alleviation of disease or injury. Unlike drugs, which achieve their primary intended purpose through chemical or metabolic action within the body, medical devices primarily act through physical, mechanical, or thermal means.
By Intended Use/Application, Medical Devices can be categorized as follows:
| Diagnostic Devices: Used to identify diseases or conditions. Examples include X-ray machines, MRI scanners, ultrasound equipment, and blood glucose meters. | |
| Therapeutic Devices: Used to treat or alleviate diseases or injuries. Examples include surgical lasers, radiation therapy machines, and physical therapy equipment. | |
| Monitoring Devices: Used to track a patient's physiological parameters. Examples include electrocardiogram (ECG) monitors, pulse oximeters, and fetal monitors. | |
| Surgical Devices: Used during surgical procedures. Examples include scalpels, forceps, surgical robots, and endoscopes. | |
| Assistive Devices: Used to help individuals with disabilities. Examples include wheelchairs, hearing aids, and prosthetics. | |
| Implantable Devices: Devices placed inside the body. Examples include pacemakers, artificial joints, and cochlear implants. | |
| Vitro Diagnostic (IVD): Devices are used to perform tests on samples taken from the human body. Examples include blood glucose test strips, pregnancy tests, and laboratory reagents. |
Market Overview
Over the past three to four years, the medical device market has undergone significant transformation, largely shaped by the COVID-19 pandemic and its lasting effects. Initially, in 2020, the pandemic caused a surge in demand for specific devices like ventilators and PPE while disrupting supply chains and postponing elective procedures. This led to a mixed performance across different device segments. 2021 saw a gradual recovery, particularly in elective procedures, alongside sustained growth in remote monitoring and digital health technologies, spurred by the pandemic's influence on healthcare delivery.
However, 2022 brought new challenges, including inflationary pressures and geopolitical instability, which further impacted manufacturing costs and supply chains. This placed a greater emphasis on cost-effectiveness and value-based care within the industry. Despite these hurdles, the trend towards minimally invasive procedures and technological advancements in areas like robotics and AI-powered diagnostics continued. By 2023, the market had largely normalized, with a renewed focus on innovation, sustainability, and growth in emerging markets, particularly in the Asia-Pacific region.
The medical device industry in 2024 demonstrated resilience, building on its recovery from the inflationary pressures and supply chain disruptions experienced in 2022. While those challenges forced a greater emphasis on cost-effectiveness, they also accelerated trends like minimally invasive procedures and AI-powered diagnostics, which continued to drive growth in 2024. Coupled with the aging population and rising healthcare expenditures, these market changes fueled the adoption of digital health solutions and wearable devices. The industry is expected to maintain this growth trajectory, focusing on innovations in personalized medicine and remote patient monitoring, while expanding into emerging markets like the Asia-Pacific region.
According to Statista, the market for medical devices is estimated to be $539.1Bn in 2025 and to continue growing through 2029.
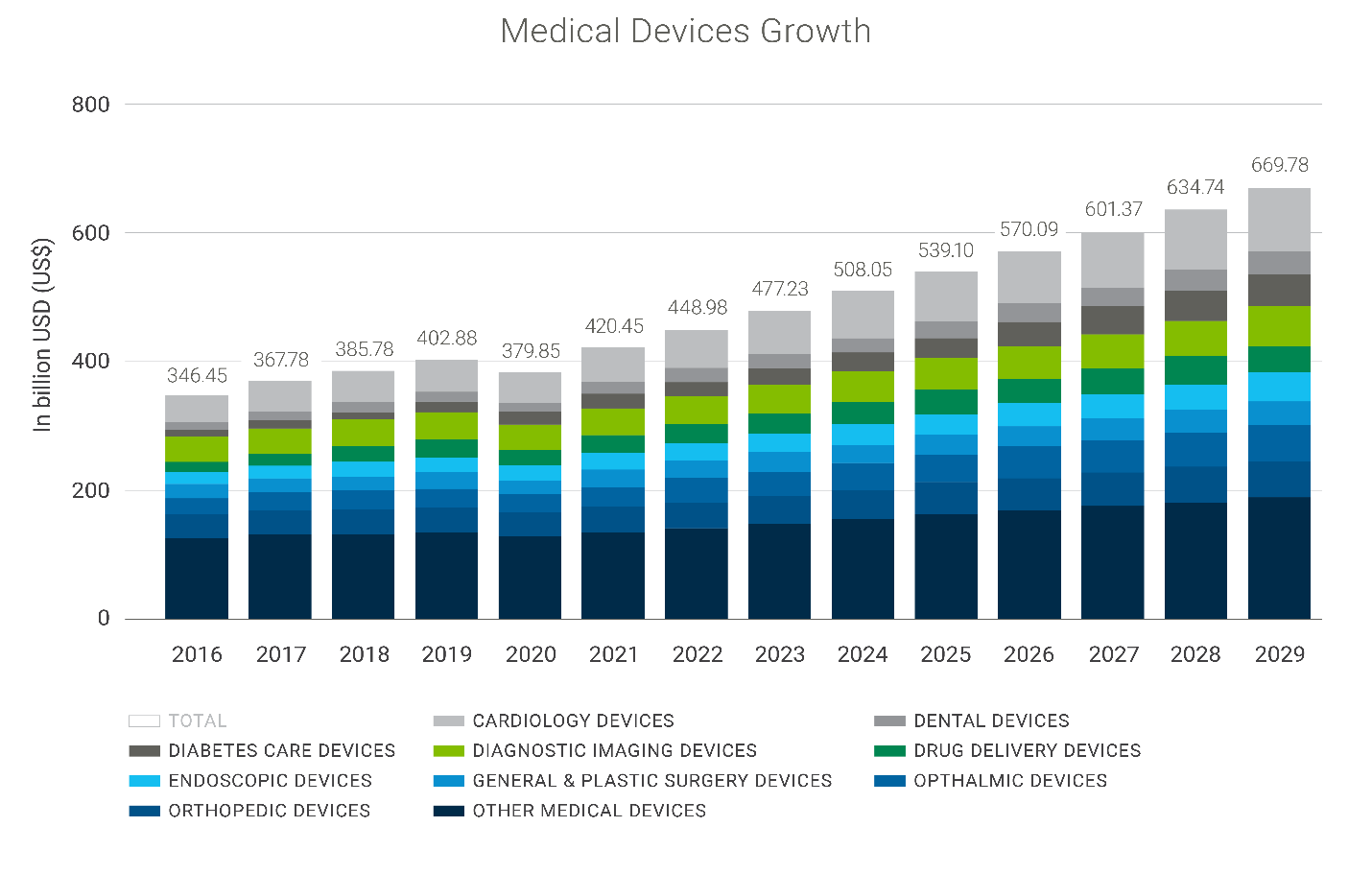
Market Growth Enablers
- Aging Global Population: The world's population is aging, and older individuals tend to have a higher incidence of chronic diseases. This demographic shift creates a significantly larger patient pool requiring medical interventions, consequently boosting demand for various medical devices, particularly those related to age-related conditions.
- Rising Prevalence of Chronic Diseases: Due to lifestyle changes and increased life expectancy, chronic diseases like heart disease, diabetes, and cancer are becoming increasingly common worldwide. Management of these conditions often necessitates long-term care and medical devices for monitoring, treatment, and improving quality of life, thereby driving market growth.
- Technological Advancements: Continuous innovation in miniaturization, robotics, and AI leads to more sophisticated and effective medical devices. These advancements enable less invasive procedures, improve diagnostic accuracy, personalize treatments, and ultimately enhance patient outcomes, all of which contribute to increased adoption and market expansion.
- Improved Sterilization technology: Modern sterilization techniques transform medical device safety and innovation. These techniques enable the sterilization of complex devices, provide point-of-care sterilization, and support personalized medicine. While challenges like cost and validation remain, modern sterilization is key to the future of medical devices.
- Increasing Healthcare Expenditure and Access: Governments, especially in emerging markets, are investing more in healthcare and expanding access to medical services. This and rising disposable incomes make medical devices more accessible and affordable to a larger population, driving demand and fueling market growth.
- Growing Preference for Minimally Invasive Procedures: Minimally invasive surgeries offer advantages like reduced pain, faster recovery, and shorter hospital stays, making them increasingly popular among patients and surgeons. This trend fuels demand for specialized instruments, such as endoscopes and robotic surgical systems, specifically designed for these less invasive techniques.
- Rise of Personalized Medicine: Personalized medicine tailors treatment to individual patient characteristics, relying on advanced diagnostics and targeted therapies. This approach necessitates devices like companion diagnostics to identify suitable patients for specific treatments and customized drug delivery systems, boosting the demand for these specialized devices.
- Focus on Home Healthcare: There's a growing shift towards providing healthcare services at home, driven by cost pressures and patient preference. This necessitates using portable and user-friendly medical devices, such as home dialysis machines and remote monitoring devices, leading to increased demand in this segment.
Market Inhibitors
- Global Supply Chain Uncertainty: Global supply chain uncertainty disrupts the medical device market by causing shortages of crucial components, raw materials, and finished products. This increases costs, production delays, and difficulty meeting patient demand.
- Stringent Regulatory Requirements: Medical devices face rigorous safety and effectiveness regulations, requiring lengthy and expensive approval processes, which are different for all countries. This can delay product launches, increase development costs, and create significant hurdles, especially for smaller companies with limited resources.
- Pricing Pressures and Cost Containment: Healthcare systems are pushing for lower costs, putting pressure on medical device manufacturers to reduce prices. This can shrink profit margins, limit investment in research and development, and hinder the introduction of innovative, potentially life-saving, but higher-priced, products.
- Cybersecurity Threats: Connected medical devices are increasingly susceptible to cyberattacks, which can compromise patient safety and data privacy. These attacks can lead to device malfunctions, data breaches, product recalls, reputational damage, and legal liabilities for manufacturers.
- Counterfeit Medical Devices: Fake medical devices pose a significant threat to patient safety and undermine the reputation of legitimate manufacturers. These counterfeit products can be ineffective or harmful, leading to adverse health outcomes and eroding trust in the industry.
- Data Privacy and Security Concerns: Medical devices often collect sensitive patient data, raising concerns about privacy and security breaches. Compliance with data privacy regulations is complex and costly, and data breaches can result in substantial fines, reputational damage, and loss of patient trust.
- Ethical Considerations in Innovation: Advancements in AI, gene editing, and 3D printing raise ethical questions about their use in healthcare. Navigating these considerations requires careful consideration of societal values, patient autonomy, and equitable access to these new technologies, which can be complex and time-consuming.
- Shortage of Skilled Workforce: The industry needs highly skilled professionals, including engineers, scientists, doctors, and regulatory experts. A shortage of qualified workers can hinder innovation, slow production processes, and increase labor costs, ultimately impacting the industry's ability to grow and meet evolving healthcare needs.
Medical Devices
Technology Overview
Medical Devices Technologies
Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Medical Devices
- AI-powered diagnostic tools: Algorithms that analyze medical images (X-rays, CT scans, MRIs) to detect diseases like cancer, diabetic retinopathy, and heart conditions earlier and more accurately.
- Predictive analytics for patient monitoring: AI analyzes patient data from wearables and other monitoring devices to predict potential health risks and enable proactive interventions.
- Personalized treatment recommendations: AI systems that help clinicians tailor treatment plans based on individual patient characteristics and medical history.
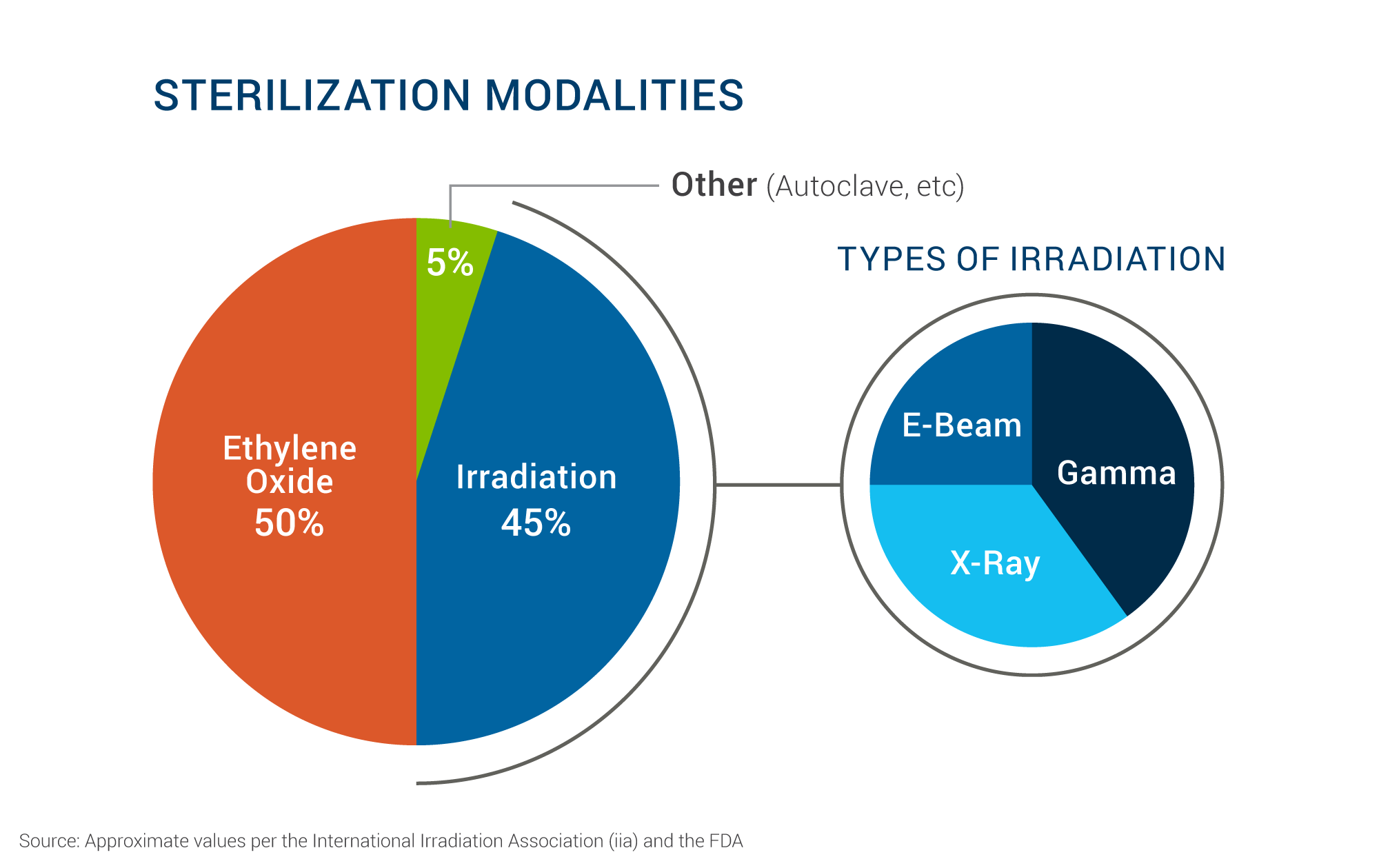
Sterilization
- Vaporized Hydrogen Peroxide (VHP): This method uses hydrogen peroxide vapor to kill microorganisms at low temperatures. It's fast, environmentally friendly, and compatible with many materials, making it ideal for heat-sensitive devices.
- Ozone Sterilization: This method uses ozone gas to destroy microorganisms by oxidation. It's effective at low temperatures, leaves no toxic residue, and is suitable for heat-sensitive medical devices and endoscopes.
- Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2) Sterilization: NO2 gas disrupts the DNA of microorganisms, offering rapid and low-temperature sterilization. It's effective for heat-sensitive devices and complex instruments.
- Supercritical Carbon Dioxide (scCO2) Sterilization: This method uses carbon dioxide in a supercritical state to inactivate microorganisms. It's non-toxic, environmentally friendly, and ideal for delicate instruments and bioabsorbable implants.
- Ultraviolet (UV) Sterilization: UV light damages microorganisms' DNA, preventing their replication. It's chemical-free, fast, and commonly used for surface disinfection in healthcare settings and water sterilization.
- Cold Sterilization Techniques (Gamma & X-Ray Sterilization): Both Gamma and X-ray sterilization methods are considered cold sterilization techniques, as they don't significantly raise the temperature of the treated items, making them suitable for heat-sensitive materials. They are widely used in the medical device industry to ensure sterility without compromising product integrity.
Gamma sterilization uses gamma rays emitted from radioactive isotopes like Cobalt-60 to kill microorganisms. It's known for its high penetration power, making it suitable for sterilizing dense products and packaged items.
X-ray sterilization uses X-rays produced by electron beam accelerators to achieve the same goal. It offers even greater penetration depth than gamma rays and provides excellent dose uniformity, making it ideal for complex or sensitive products.
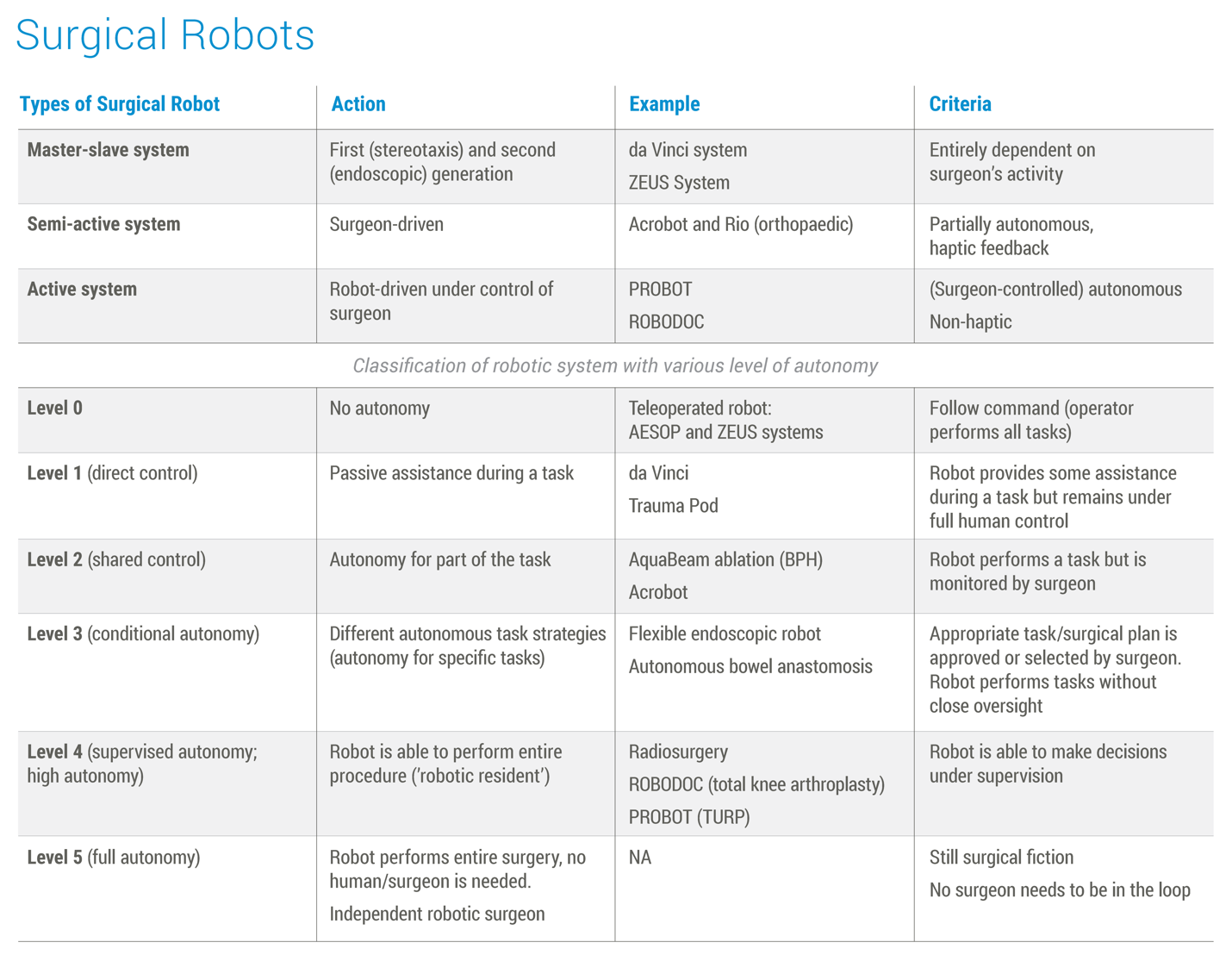
Robotics in Surgery
- Robot-assisted surgical systems: Advanced robotic platforms that enhance surgeon precision, dexterity, and control during minimally invasive procedures, leading to smaller incisions, less pain, and faster recovery.
- Microsurgical robots: Robots designed for delicate procedures like eye surgery or neurosurgery, offering unparalleled precision and stability.
- Autonomous surgical robots: The next frontier, still under development, these robots would be able to perform certain surgical tasks with minimal human intervention.
Telehealth and Remote Patient Monitoring
- Connected medical devices: Devices that transmit data to healthcare providers, enabling remote monitoring and managing chronic conditions.
- Telemedicine platforms: Video consultations and remote diagnostic tools allow patients to access care from anywhere.
- Digital therapeutics: Software-based interventions that can treat or manage diseases, often delivered through mobile apps.
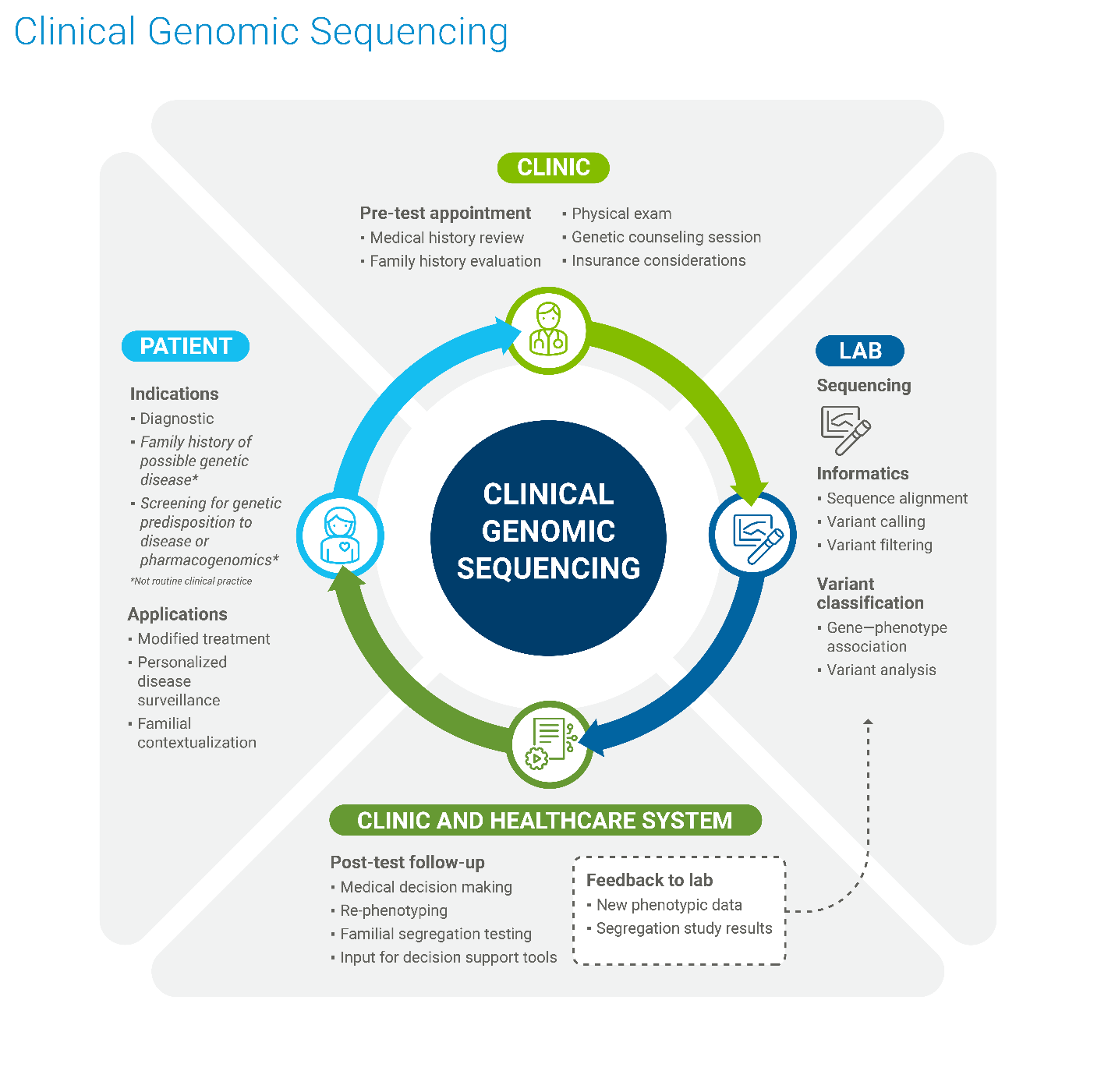
Genomic Diagnostics
Genomic diagnostics involves using an individual's genetic information to diagnose diseases, predict disease risk, and guide treatment decisions. It goes beyond simply looking at single genes and analyzes the entire genome, providing a more comprehensive picture of a person's genetic makeup and its potential impact on their health. Below are the steps involved in the Genomic diagnostics process:
- Analyzing DNA: It examines an individual's DNA sequence, looking for variations or mutations that may be associated with diseases.
- Identifying disease risks: It can reveal a person's predisposition to certain conditions, such as cancer, cardiovascular disease, or rare genetic disorders.
- Guiding treatment decisions: Genomic diagnostics can help determine which therapies are most likely to be effective for a particular patient based on their genetic profile. This is particularly important in cancer treatment, where targeted therapies are often selected based on the specific genetic mutations present in a tumor.
- Early detection and prevention: By identifying genetic risks, genomic diagnostics can enable early detection and preventive measures, leading to better health outcomes.
Supporting Technologies
Advanced Sensor Technologies
- Wearable biosensors: Continuous monitoring of vital signs (heart rate, blood pressure, glucose levels) through wearable devices, enabling early detection of health problems.
- Ingestible sensors: Tiny sensors that can be swallowed to monitor conditions within the digestive tract or to deliver drugs in a targeted manner.
- Implantable sensors: Long-term monitoring of physiological parameters through implanted devices, providing valuable data for managing chronic conditions.
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) in Healthcare
- Surgical planning and training: VR and AR can be used to create 3D models of patient anatomy for pre-operative planning and to train surgeons in a simulated environment.
- Pain management and rehabilitation: VR can be used to distract patients from pain during procedures or to create immersive environments for physical therapy and rehabilitation.
- Telemedicine and remote diagnostics: AR can overlay digital information onto the real world, allowing physicians to remotely examine patients and guide procedures.
Advancements in Sensor Technology
- Biosensors: These sensors detect and measure biological molecules like glucose, enzymes, and antibodies. They are crucial for continuous glucose monitoring systems for diabetic patients, rapid disease diagnostics, and personalized medicine.
- Wearable sensors: Integrated into smartwatches, fitness trackers, and clothing, these sensors track physiological parameters such as heart rate, activity levels, and sleep patterns. They enable remote patient monitoring, early detection of health issues, and promote proactive health management.
- Implantable sensors: These sensors are placed inside the body to monitor various parameters like blood pressure, temperature, and even brain activity. They are vital for managing chronic conditions like hypertension and epilepsy, and for providing real-time feedback during surgical procedures.
- Image sensors: These sensors capture visual data and are used in medical imaging technologies like endoscopes, X-rays, and MRI machines. They provide high-resolution images for accurate diagnostics and minimally invasive procedures.
- Microfluidic sensors: These sensors analyze small volumes of fluids like blood or saliva for rapid diagnostics and point-of-care testing. They are revolutionizing disease detection and monitoring, particularly in resource-limited settings.
- Pressure sensors: These sensors measure pressure changes and are used in various medical applications, such as monitoring blood pressure, intracranial pressure, and respiratory function. They are essential for critical care and managing patients with respiratory illnesses.
- Acoustic sensors: These sensors detect and measure sound waves and are used in ultrasound imaging and for monitoring heart and lung sounds. They provide valuable diagnostic information and aid in non-invasive monitoring.
- Environmental sensors: These sensors monitor environmental parameters like temperature, humidity, and air quality. They are crucial for maintaining optimal conditions in hospitals and operating rooms, and for monitoring patients with respiratory sensitivities.
- Motion sensors: These sensors detect movement and are used in rehabilitation devices, prosthetics, and for monitoring patients with mobility impairments. They provide valuable data for assessing and improving movement patterns.
Medical Devices
Recent Developments
|
Date |
Equipment Supplier/ Manufacturer |
End User (Company 2) |
Development Type |
Description |
|
Nov 2024 |
Johnson & Johnson (US) |
Responsive Arthroscopy Inc. (US) |
Agreement |
Johnson & Johnson MedTech and Responsive Arthroscopy Inc. have partnered in an exclusive distribution agreement. This collaboration will bring Responsive Arthroscopy's sports soft tissue repair solutions to the US market through Johnson & Johnson MedTech's established network. The move strengthens Johnson & Johnson MedTech's sports medicine offerings and allows them to capitalize on the growing demand for advanced soft tissue repair technologies. |
|
Nov |
Phillips Healthcare |
- |
Product Development & Launch |
Philips India has launched its latest interventional system, the Azurion. This new technology is aimed at specialists in cardiology, neurology, vascular, and surgery. The Azurion system is designed to improve neurovascular procedure efficiency, enabling faster decision-making, increased patient throughput, and improved patient outcomes through features like enhanced C-arm movement. |
|
Oct |
Johnson & Johnson (US) |
V-Wave (US) |
Acquisition |
Johnson & Johnson has finalized its acquisition of V-Wave Ltd. V-Wave is a privately held company specializing in innovative treatments for heart failure. This acquisition expands Johnson & Johnson's portfolio in the cardiovascular space and provides access to V-Wave's promising technologies. |
|
Apr 2024 |
Philips |
- |
Business Expansion |
Philips has inaugurated its new research and development center in Pune, Maharashtra. This expansion of its Healthcare Innovation Centre (HIC) in India underscores the country's increasing importance in Philips' global healthcare innovation strategy. The new center will focus on developing cutting-edge healthcare solutions. |
|
Feb |
Fresenius |
- |
Product Deployment |
Fresenius Medical Care has obtained FDA 510(k) clearance for its 5008X Hemodialysis System. This regulatory approval paves the way for clinical trials in the United States. The 5008X system is designed for adults with kidney disease and uses hemodiafiltration, combining diffusion and convection, for blood purification and fluid management. It is designed to be used with the FX CorAL dialyzer, incorporating advanced engineering and membrane technology. |
|
February 2024 |
Phillips Healthcare (Netherlands) |
- |
Product Development & Launch |
Philips has released the Philips Image Guided Therapy Mobile C-arm System 9000 – Zenition 90 Motorized. This new mobile C-arm system is intended to support surgeons in providing high-quality care to a greater number of patients by offering advanced imaging capabilities and motorized movement. |
Source: Company Website & Press Releases
Medical Devices
Use Case Analysis
Diagnostics
Freestyle Libre 3: This system utilizes advanced sensor technology. Its tiny sensor measures glucose levels in interstitial fluid and transmits the data wirelessly to a reader or smartphone. The sensor also incorporates miniaturized electronics to create a smaller and more comfortable sensor.
Aidoc: This platform leverages artificial intelligence (AI) and deep learning algorithms to analyze medical images and identify abnormalities, assisting radiologists in faster and more efficient diagnoses.
Monitoring
Biobeat: This sensor patch utilizes reflective photoplethysmography (PPG) and bio-impedance to measure vital signs. It also incorporates advanced algorithms to analyze the data and provide accurate readings.
Eversense: This system uses a fluorescent biosensor implanted under the skin that measures glucose levels. It also incorporates a transmitter that sends the data wirelessly to a smart device.
Treatment
da Vinci Surgical System: This system uses robotic arms with endowrist instruments that provide greater dexterity and range of motion. It also incorporates 3D high-definition visualization to enhance surgical precision.
Stryker Mako: This system uses 3D modeling and haptic feedback technology to create a personalized surgical plan and guide the robotic arm during surgery, ensuring precise implant positioning and alignment.
Therapeutics
Philips Trilogy Evo: This ventilator utilizes adaptive support ventilation (ASV) to automatically adjust to the patient's breathing needs, providing personalized respiratory support. It also incorporates remote monitoring capabilities for enhanced patient care.
Abbott FreeStyle Libre 2: This system utilizes advanced sensor technology with a small sensor that measures glucose levels in interstitial fluid and transmits the data wirelessly to a reader or smartphone.
Medical Devices
Supply Chain Overview
Demand Overview
The demand for medical devices is experiencing robust growth across numerous applications, driven by factors such as an aging global population, increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, and technological advancements leading to more sophisticated and effective treatments.
Areas experiencing exceptionally high demand include cardiovascular devices (like stents and pacemakers) for managing the rising incidence of heart disease, orthopedic devices (implants, prosthetics) for addressing age-related joint problems and injuries, and diagnostic imaging equipment (MRI, CT, ultrasound) essential for accurate and early disease detection.
Minimally invasive surgical devices are also seeing significant uptake due to their benefits in reducing patient trauma, recovery times, and hospital stays. Furthermore, the demand for diabetes care devices, such as insulin pumps and continuous glucose monitoring systems, is escalating due to the global surge in diabetes prevalence.
Supply Analysis
The global medical device supply and manufacturing landscape has transformed from traditionally concentrated hubs to a more diversified model. Historically, countries like the US, Germany, and Japan dominated, but Asia, particularly China, emerged as a significant manufacturing center due to lower costs and improved infrastructure. However, recent events like the pandemic and geopolitical tensions have highlighted the vulnerabilities of this concentrated approach. Consequently, companies are increasingly exploring nearshoring and reshoring to enhance supply chain resilience.
Due to the critical nature of medical devices, supply chains are inherently complex, involving numerous global suppliers and stringent quality requirements. Many devices require specialized manufacturing processes, often produced in low volumes but with high value. Currently, the industry faces challenges such as supply chain disruptions, geopolitical risks, and increasing pressure for sustainable practices. Digitalization is being adopted to improve visibility and efficiency, while talent acquisition and retention remain crucial issues.
Medical device companies worldwide are particularly attracted to the Dominican Republic as a manufacturing base due to its exceptional access to the world’s largest consumer healthcare market, the United States. Medical and pharmaceutical product manufacturing began in the Dominican Republic over 40 years ago. By 2022, exports of these healthcare market products amounted to $2.25 billion, accounting for nearly one-third of total exports from the country.
Medical Devices
Jabil Insights
Jabil Insights
Digital technologies are playing an increasingly pivotal role in today’s rapidly evolving healthcare landscape. From diagnostic tests to remote patient monitoring, digital solutions are transforming the way healthcare is delivered — and likewise transforming how OEMs approach the development of new products and integrations of tech innovations into legacy devices.
Digital healthcare has been on a steady rise, with product development and lifecycle management strategies evolving over the last six years. Integrating technology into medical devices must consider healthcare’s strict regulatory and quality requirements as well as the market’s pressures for lowering costs. Resetting their goals post-pandemic, many OEMs have shifted their approach to product development, manufacturing, and outsourcing.
At Jabil, our insights into the medical devices market reveal a trajectory of growth and diversification that we find both promising and pivotal for future developments. Our market analysis draws from a solid established performance baseline, laying the groundwork for a strategic forecast and an actionable roadmap. Here are the key takeaways for top commodities that are utilized in the medical devices market:
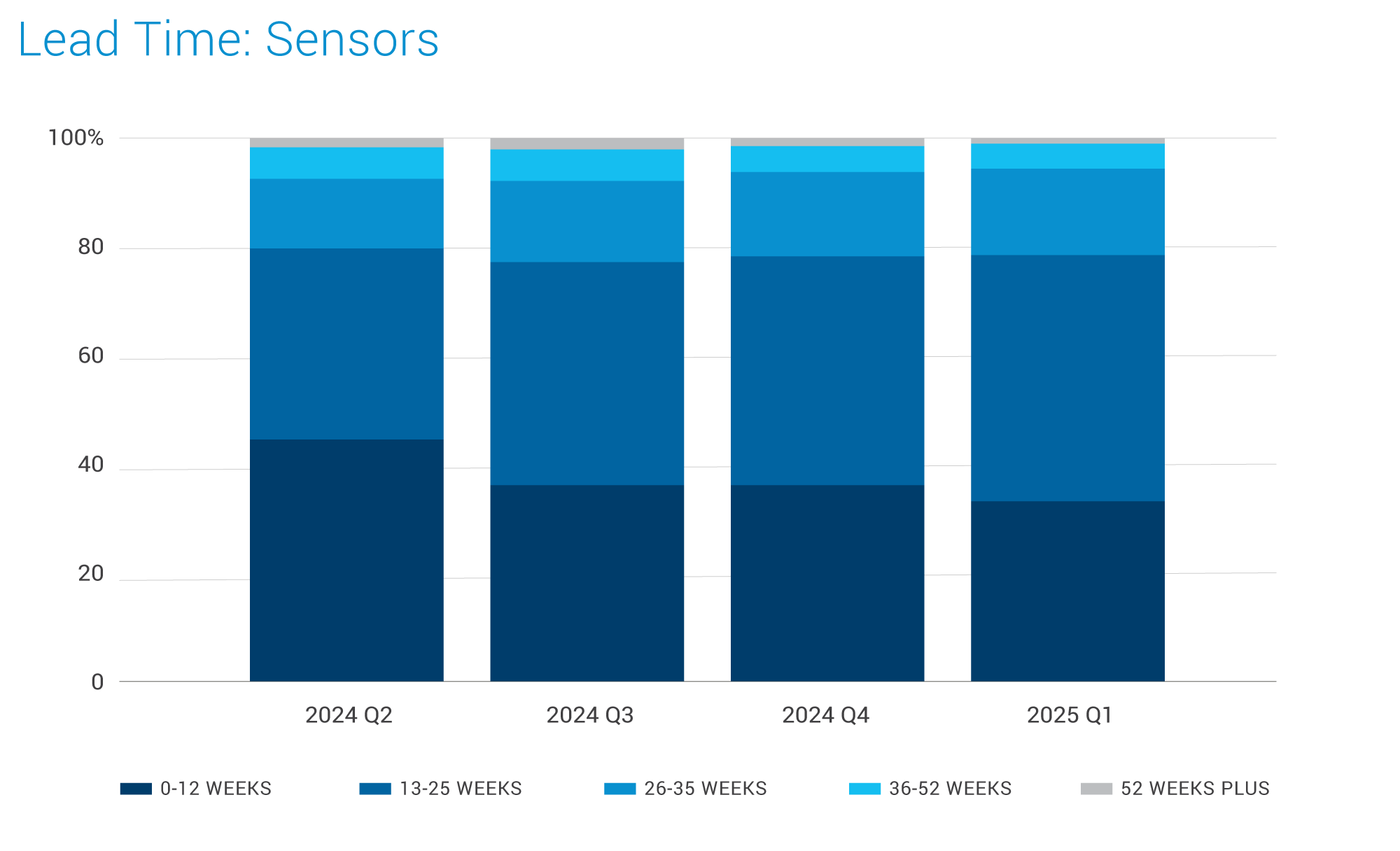
Sensors:
- In general, supply is stable as recent investments in wafer capacity over the past few years are beginning to yield results.
- Global brands are actively reviewing their product portfolios to align with growing markets and new applications driven by AI advancements. Key AI driven healthcare applications include remote patient monitoring (RPM), smart wearables, biosensors, and AI-powered diagnostics.
- Key drivers for new product and technology innovation include Healthcare, automotive electrification, and industrial applications.
- Rising demand across all sectors is expected to encourage new suppliers to enter the market however stringent regulatory approvals will be a crucial barrier.
- Sensor prices across sectors have slightly decreased due to the market slowdown and intense competition but high-precision medical-grade sensors maintain relatively stable pricing.
- Prices may increase in the second half of 2025 due to sustained cost pressures and uncertain market trends.
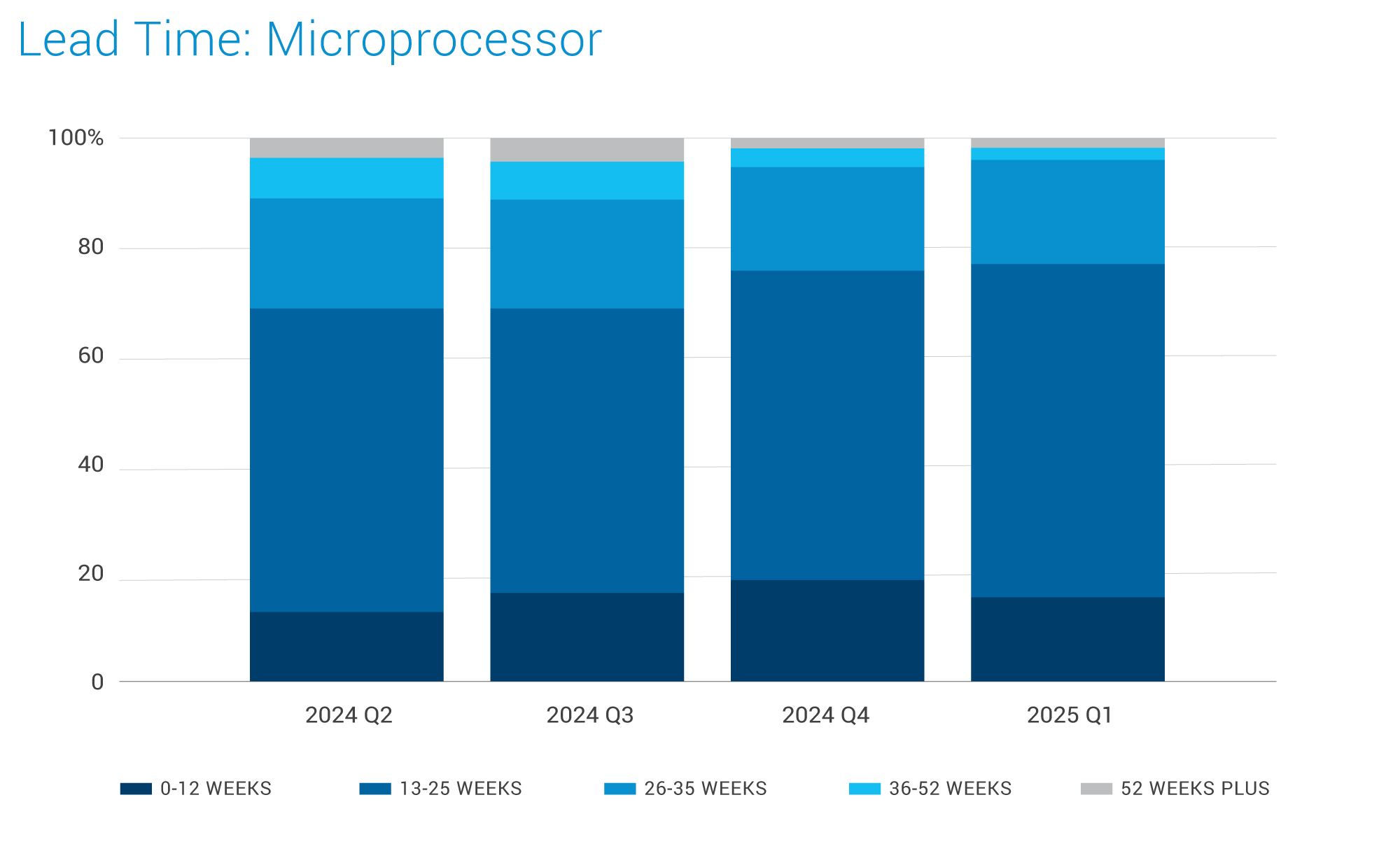
Microprocessors:
- Supply is healthy for most product lines, with slight lead time improvements
- Capacity utilization of high-end semiconductors for broad-range manufacturers is at low levels, averaging around 70% for most internal factories.
- In general, pricing for products built on mainstream process nodes is expected to remain stable, but manufacturers may deploy strategies similar to AMD and Altera.
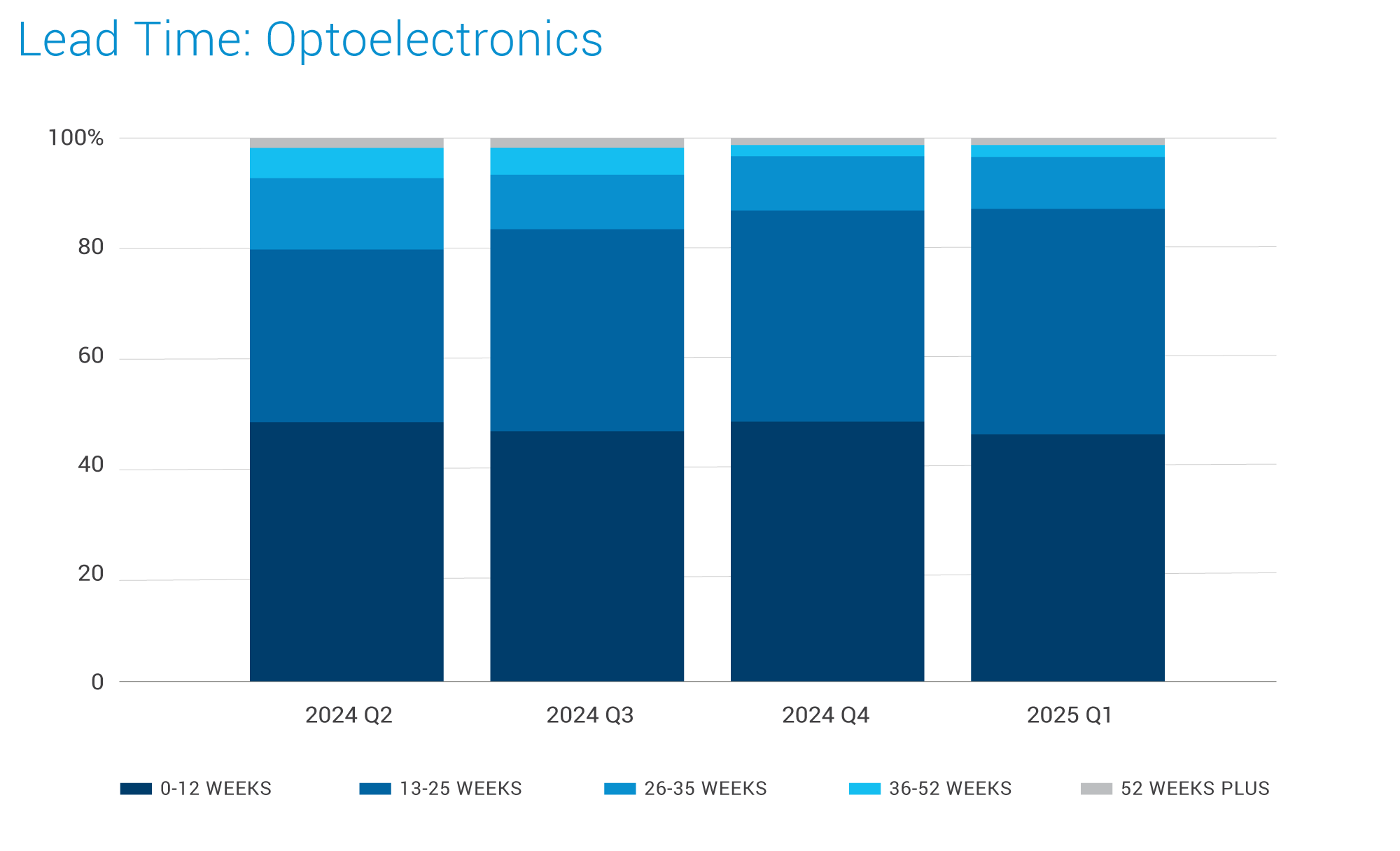
OptoElectronics:
- Supply remains healthy across Optoelectronics-related products, although inventory levels are depleting, which could impact the ability to meet sudden surges in demand or short lead-time requests.
- The business outlook for 2025 remains uncertain for most suppliers. Many do not have sufficient orders to utilize their full capacity, leading to hesitance in making significant investments. This could potentially cause lead times to increase.
- Demand in the Medical and Industrial segments remains stable.
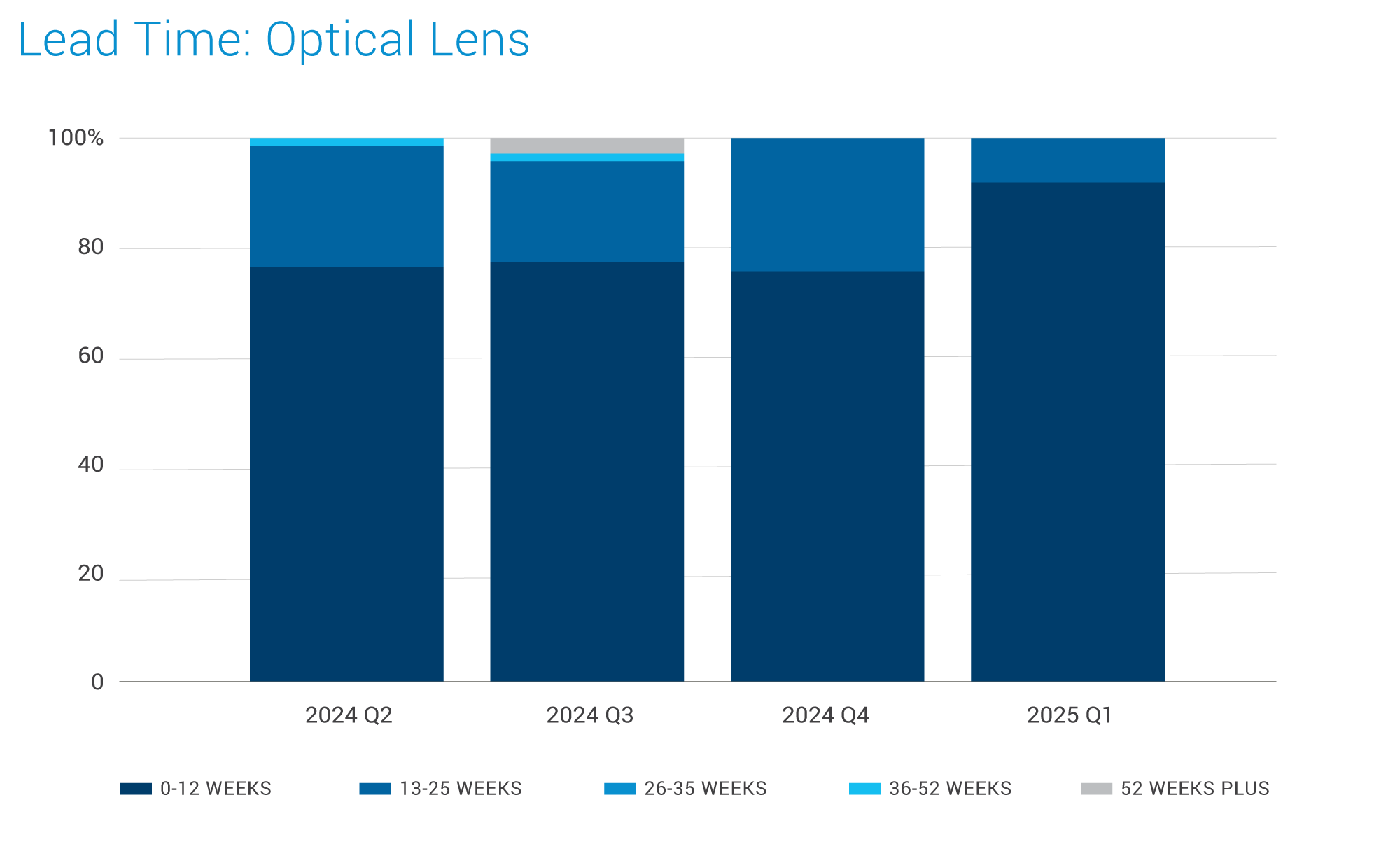
Optical Lens:
- The optical lens suppliers have surplus capacity, and the supply remains stable.
- The standard lead time is approximately 16 weeks, which includes around 12 weeks for raw materials and 4 weeks for processing.
- This stable supply of optical lenses and consistent lead times are positive indicators for medical device manufacturers who utilize lenses in their products, such as in imaging equipment and diagnostic tools.
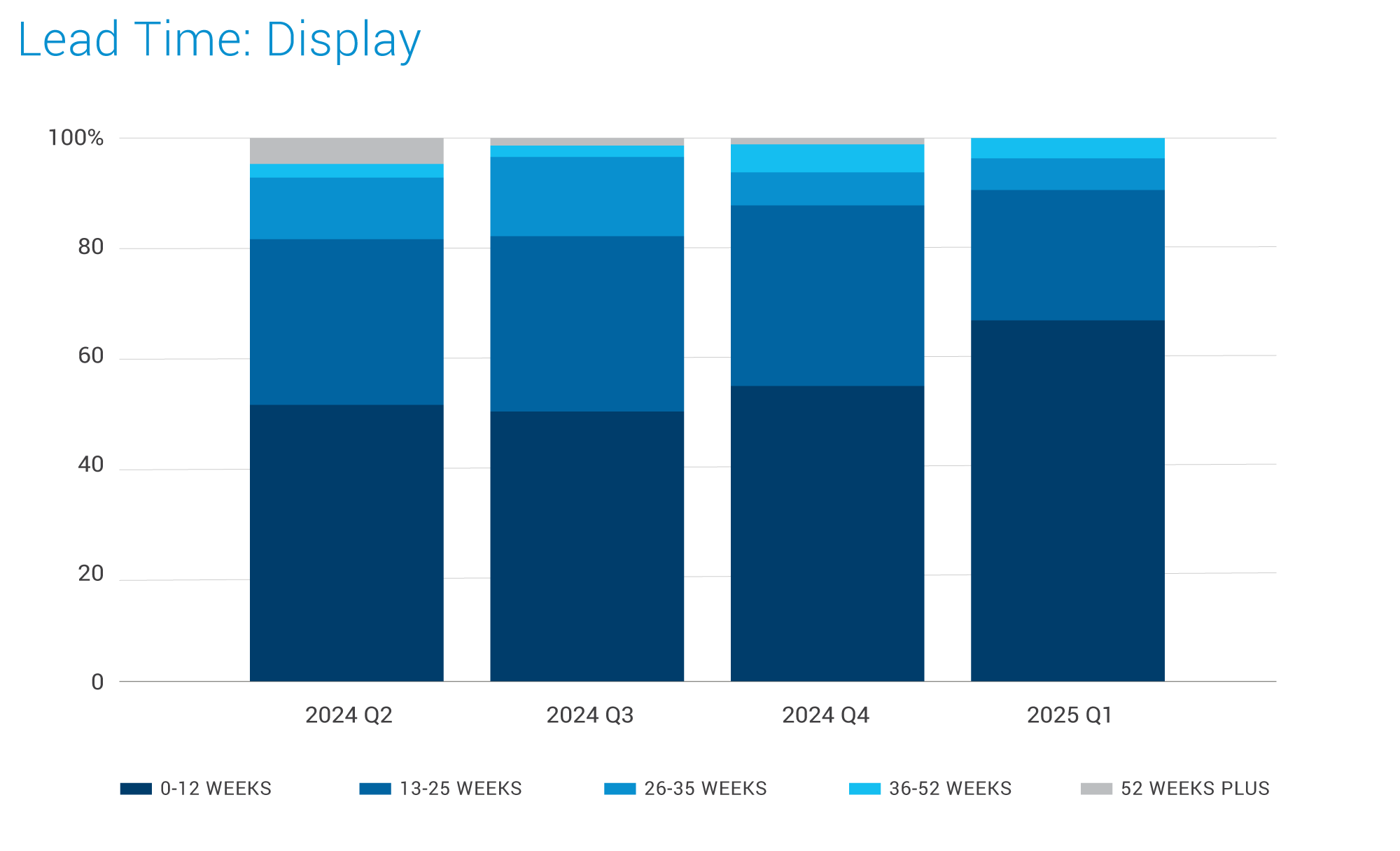
Displays:
- Panel makers' fab utilization forecasts were increased to 72% in October, driven primarily by the increased fab utilization plans of the top three Chinese panel makers: BOE, China Star, and HKC Display.
- These developments in the display panel market likely to have positive effects across various industries, including medical devices, which rely on high-quality displays for patient care and diagnostics.
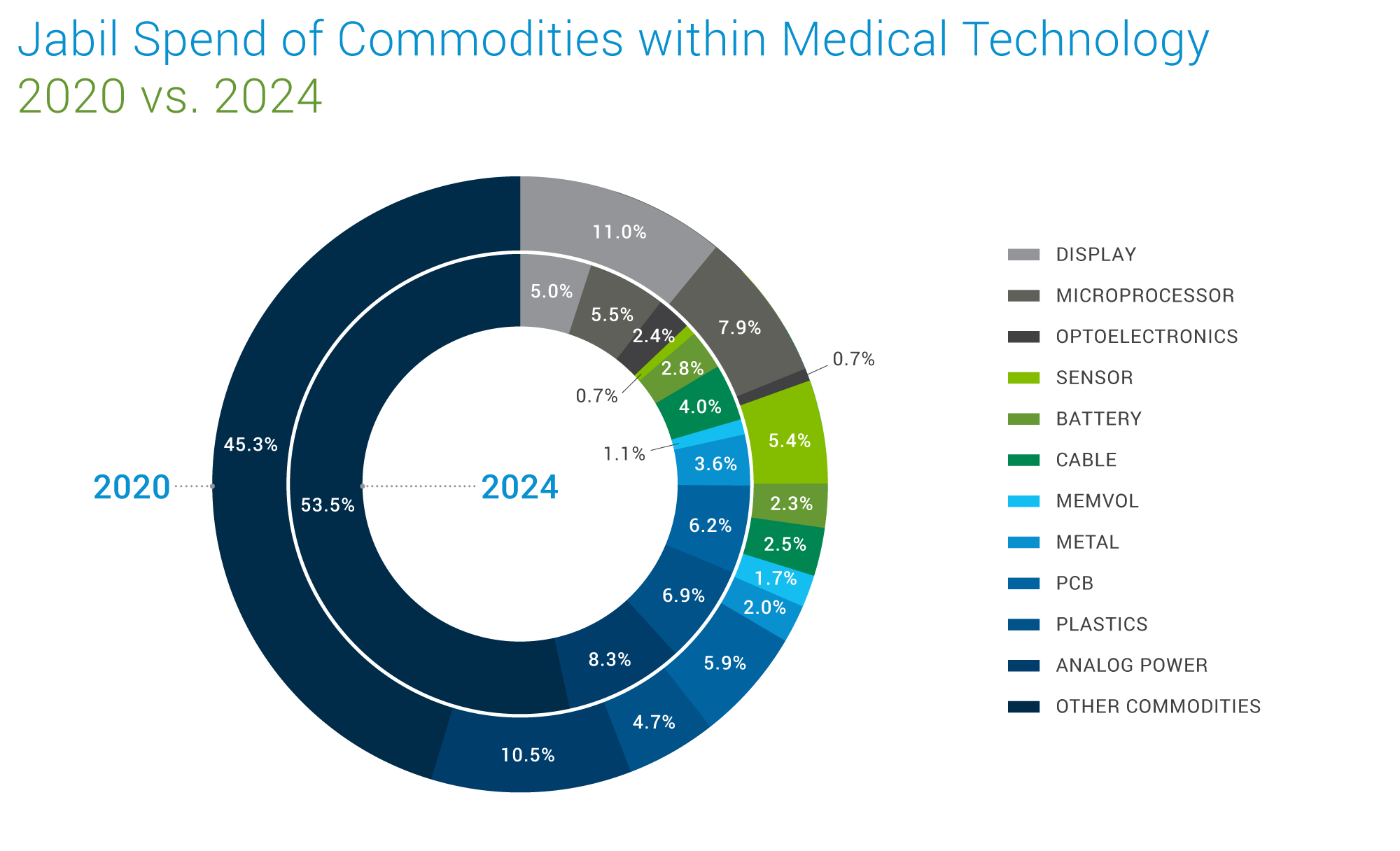
Jabil Spend Analysis
This chart illustrates the comparison between Jabil's 2020 & 2024 spend allocation across key commodities within the medical technology sector. Representing over 70 commodities, the analysis provides insight into Jabil's strategic sourcing trends in this sector, reflecting alignment with broader market dynamics.
Back to Top
