By clicking the “I Accept” button, or by accessing, participating, or submitting any information, or using the Jabil Global Intelligence Portal or any of its associated software, you warrant that you are duly authorized to accept the Global Intelligence Portal Terms and Conditions on behalf of your Company, intending to be legally bound hereby, and your company shall be bound by the terms and provisions of the Global Intelligence Portal Terms and Conditions, accessible under the following link Portal T&Cs.
Sector Market Report
Retail & Payment Solutions
Sector Market Report
Retail & Payment Solutions
Get an in-depth analysis of the current state, trends, and future of the retail & payment industry, including insights into key drivers, changing lifecycles, and manufacturing challenges.
Retail Market
Introduction
The Retail & Payment industry is evolving rapidly. Historically, retailers have adhered to a fundamental model of providing products at competitive prices in convenient locations. However, digital technology has ushered in unprecedented shifts, with the recent global pandemic catalyzing accelerated change.
Traditionally, retailers operated through distinct channels, such as brick-and-mortar stores and online platforms, often functioning independently within organizational silos. Yet, the emergence of the omnichannel age, fueled by data analytics and artificial intelligence, has blurred the lines between channels. This convergence has given rise to seamless commerce, a paradigm where inspiration, exploration, choice, transaction, and receipt span both online and offline realms, integrating digital interactions into physical retail spaces.
Moreover, the pursuit of seamless commerce aligns with broader sustainability goals, allowing retailers to reduce waste and carbon emissions while offering consumers more sustainable options. By integrating sustainability into their operational framework, retailers can create value for customers and society, driving significant growth.
Alongside these transformative shifts in the retail landscape, the payments industry is evolving with the market, driven by consumer expectations and technological advances. Today's consumers demand personalized payment experiences that prioritize security, speed, and loyalty rewards. To remain competitive, organizations must not only cater to diverse payment preferences but also adapt to the unique dynamics of each market.
This Report provides insights into the dynamic landscape within the payment space, providing in-depth analysis at global, regional, and country levels. By examining technological trends, consumer behaviors, and market dynamics, the report provides organizations with the knowledge to navigate the evolving payment landscape and take advantage of significant technological advances.
As operators navigate shifting dynamics, they must monitor the trends that shape their strategies and investments. The e-commerce surge, the transformation of physical stores, and the omnichannel customer experiences are pivotal shifts driving innovation and reshaping industry dynamics.
Automation plays a central role in this transformation, revolutionizing various aspects of retail operations, from warehouse management to in-store customer experiences. Technologies such as Electronic Shelf Labels (ESLs) and autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) are transforming price management, order fulfillment, and inventory management, enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and customer satisfaction. Even for online retailers, automation touches many activities, from “pick, pack, ship” to warehouse automation and robotics.
While the benefits of automation are undeniable, challenges such as initial investment costs and job displacement concerns underscore the need for careful consideration and strategic implementation. However, the potential rewards in terms of operational efficiency, cost savings, and enhanced customer experiences justify the investment in these transformative technologies.
This report emphasizes that the convergence of digital technology, changing consumer expectations, and sustainability imperatives are reshaping the retail and payments industries. Embracing seamless commerce and leveraging automation technologies are essential for retailers and payment providers to thrive in this dynamic landscape. Businesses can position themselves for long-term success amidst market volatility and evolution by prioritizing customer-centricity, innovation, security, and sustainability.
Retail & Payment Solutions Market
Industry Overview
Market Outlook
The retail and payments industry in 2024 represents a story of resilience and growth. After a challenging 2020, the global payments industry rebounded strongly in 2021, exceeding pre-pandemic revenue expectations. This momentum is projected to continue, with the market reaching a staggering $3 trillion by 2026 (McKinsey). Several vital trends fuel this growth:
The rise of contactless payments is increasing as consumers embrace methods such as tap-to-pay and digital wallets. Juniper Research predicts contactless transactions will surpass $10 trillion by 2027, with tap-to-pay becoming the dominant method in the hospitality industry by 2024. Embedded finance, where financial services are integrated within non-financial platforms, is also growing exponentially. McKinsey estimates that the U.S. embedded finance market reached $20 billion in 2021 and could double in the next few years. Big Tech companies like X (formerly Twitter) are also entering the payments arena, offering super apps with integrated payment features. This intensifies competition and innovation in the space. The global retail market is projected to reach $22.6 trillion by 2024, driven by the surge of e-commerce and mobile shopping. The grocery and e-commerce sectors are robust, with both expected to experience significant growth.
These trends are driven by a confluence of factors, such as instant payment infrastructure, whose expansion and open banking frameworks are fostering the adoption of digital wallets and faster transactions. The volume of non-cash transactions is set to hit 1.3 trillion this year and then rise by 15% yearly to reach 2.3 trillion by 2027 as consumers and businesses adopt new digital payment schemes. The influence of emerging markets across Asia-Pacific, led by China's booming digital economy, is at the forefront of digital payment adoption.
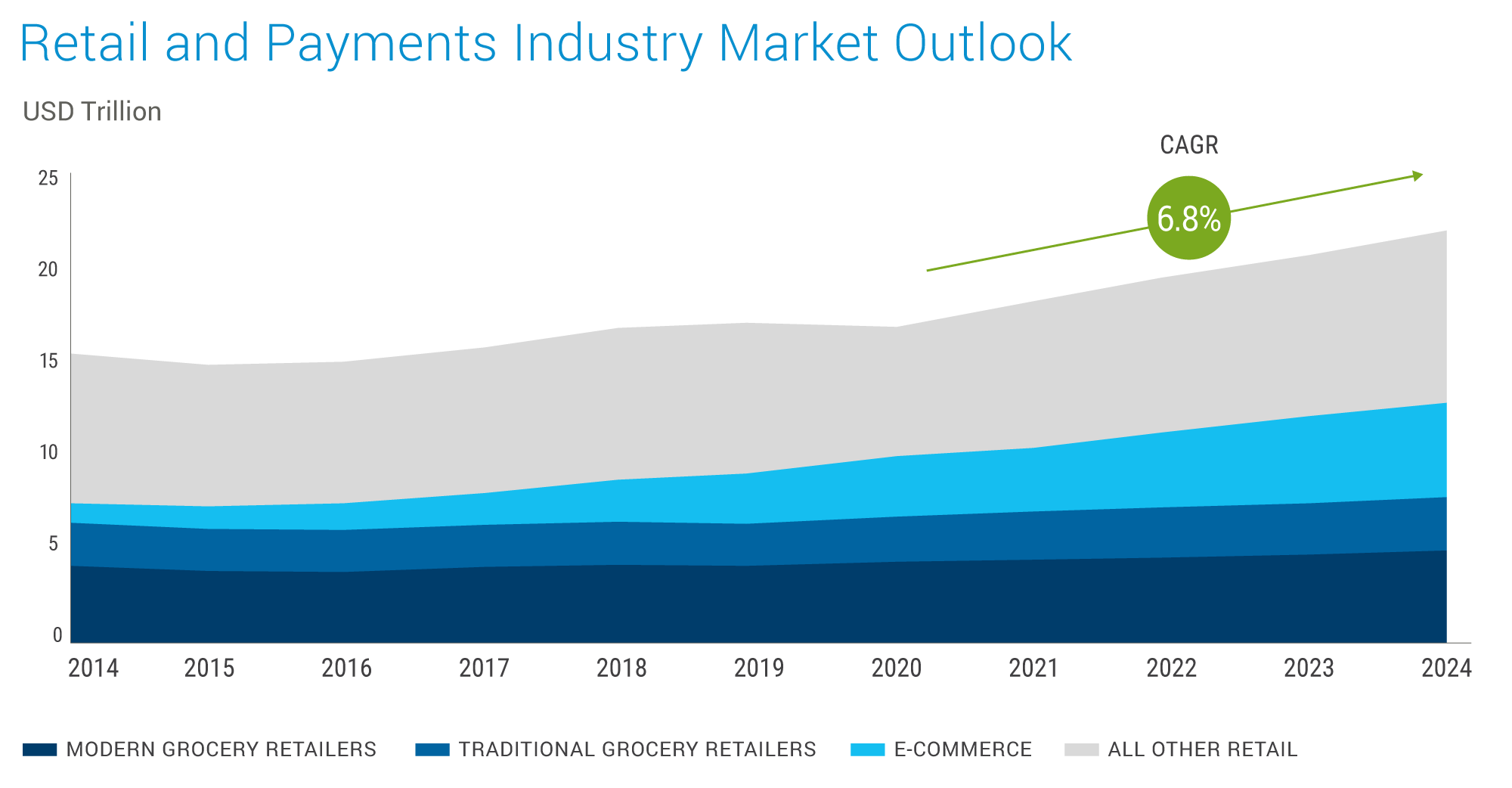 Data sourced from KPMG
Data sourced from KPMG
Key themes that are expected to shape the retail and payments industry in 2024 and early 2025:
- Customer-centricity in some companies with new payment instruments like instant payments and buy-now-pay-later options enhances customer experience. Additionally, the emergence of BigTech as a significant player in the market will intensify the competition for consumer loyalty.
- Payments industry innovations like composable architecture and automation are streamlining businesses' back-end operations. This includes faster cross-border payments and solutions for accounts payable and receivable.
- Payment providers leverage cutting-edge technologies like AI and tokenization for enhanced security, data processing using ISO 20022 standards, and Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDC) for interoperability.
- The rise of new technologies, innovative solutions, and a focus on customer experience have implied that retailers are adopting a new transacting method. Among these mobile payment solutions, Apple Pay® has emerged as a frontrunner; consumer behavior has changed significantly with the rise of mobile payment technologies. Consumers are more likely to pay for goods and services using mobile phones rather than cash or cards. Apple Pay® topped the chart of the ‘most used mobile payments by brand in the UK,’ capturing a staggering 70% market share. This remarkable uptake underscores the critical need for businesses to adapt to the changing tides of consumer preferences.
- Utilizing near-field communication (NFC) technology, Apple Pay® offers a secure and convenient way to conduct transactions without using credit or debit cards. Users hold their device near a payment terminal when paying in person and confirm the purchase through Touch ID, Face ID, or passcode. Online can be selected as a payment option, streamlining the checkout process by manually eliminating the need to enter payment and shipping details. This seamless integration of what Apple Pay® does and how it works offers an enhanced shopping experience, making it an attractive payment method for consumers and businesses. The rapid adoption of mobile payments, spearheaded by solutions like Apple Pay®, signifies a transformation in how transactions are conducted. For companies aiming to thrive in this digital era, embracing such technologies is imperative. Apple Pay’s® advantages — from enhanced security and speed to improved customer satisfaction and sales—are too significant to overlook.
- The sector is poised for continued growth and transformation in the future. The integration of digital payments across retail platforms, the growing power of BigTech, and the rise of emerging markets like India with its burgeoning consumer class all paint a picture of an industry brimming with potential.
Regional Outlook
The last few years have witnessed a remarkable rebound for the payments industry, exceeding pre-pandemic expectations. Global payments revenue surged by a robust 11%, reaching a record high of $2.1 trillion (McKinsey). This growth story was consistent across all regions, with APAC, Europe, and EMEA experiencing double-digit gains. Fee-based revenue continues to dominate, outpacing net interest income and comprising more than half of the total industry revenue. However, this trend might see a reverse soon due to rising interest rates implemented by central banks in response to above-target inflation.
The payment landscape is undergoing a significant transformation driven by a confluence of factors, including:
- Shifting Monetary Policy In response to record inflationary pressures, central banks globally are tightening the money flow, leading to rapid interest rate hikes, particularly in Europe and North America.
- Geopolitical tensions and capital market resets are impacting global economic dynamics, influencing the payments sector on a regional level.
- Evolving Consumer Preferences and changing commerce expectations, driven by factors like convenience and security, are shaping how people want to pay.
- Continuous technological advancements, such as artificial intelligence (AI) and tokenization, are pushing the boundaries of payment security and efficiency.
- Sustainability and ethical considerations are increasingly important, prompting payment providers to adopt responsible practices.
This rapidly evolving landscape presents opportunities for established players and new entrants in the market. Companies can thrive in this dynamic environment by developing innovative solutions and taking advantage of significant opportunities while mitigating risk.
However, despite an optimistic global ecosystem, regional variations must be observed.
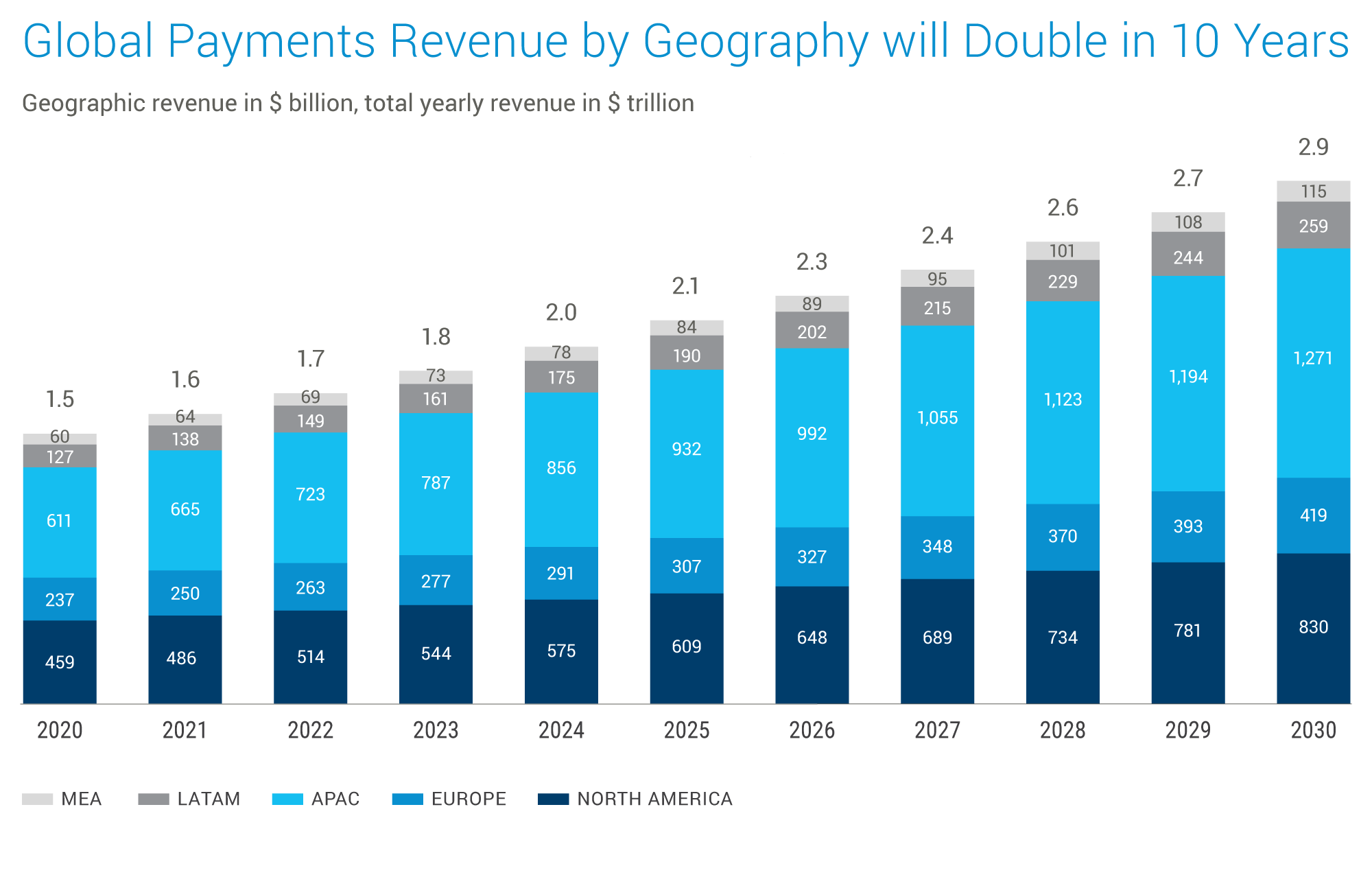 Data sourced from Cognizant Analysis of BCG Data
Data sourced from Cognizant Analysis of BCG Data
North America & Europe
The region is experiencing steady growth, projected to be around 5% annually. While these regions have well-developed payment infrastructure with cards as the dominant payment method, the focus is shifting towards contactless and mobile wallet transactions.
Technological advancements fuel the retail sector in North America, enabling personalized shopping experiences and streamlined supply chains. The U.S. holds a dominant position due to its sizeable tech-savvy consumer base, i.e., people aged 17-28, wherein eCommerce has been experiencing robust growth, with omnichannel strategies becoming increasingly popular. Sustainability and ethical concerns are gaining prominence in the US, prompting retailers to adopt more eco-friendly practices and offer sustainable products. Furthermore, emerging technologies like AI, AR, and blockchain are being integrated into the retail ecosystem to enhance efficiency and customer engagement.
Asia-Pacific (APAC)
The APAC region leads with an annual growth rate surpassing 8%, driven by increasing transaction volumes, tech-savvy populations, and a booming e-commerce sector. India and Southeast Asia are expected to see the highest e-commerce growth by 2026. Additionally, retail sales growth is forecasted to surge due to rising disposable income in China, policy changes promoting competition in India, and growing regional tourism.
The APAC region is a global leader in the adoption of digital payments. This dominance can be attributed to several factors, including booming economies fueling demand for convenient and secure digital payment solutions. A tech-savvy population with high smartphone penetration creates a fertile ground for mobile payment solutions. The surge in e-commerce activity necessitates secure and efficient digital payment methods. Supportive government policies promoting cashless transactions and financial inclusion are accelerating digital adoption.
Reviewing the retail segment, according to a recent analysis by Euromonitor International, GoTo Gojek Tokopedia PT, based in Indonesia, has emerged as the most rapidly expanding retailer in the Asia Pacific region, achieving an impressive 44.4% growth in retail sales. Coming in second is the e-commerce powerhouse Sea Limited, owner of Shopee, which saw a 42.5% growth in sales, reaching $42.58b.
Discussing the Payment industry, Chinese multinational tech company Alibaba, formerly known as Ant Financial and Alipay, Ant Group is a prominent player in the cross-border payment landscape in APAC. Shein, a major player in the Chinese e-commerce landscape, has emerged as a significant force in the APAC cross-border payment landscape and was newly introduced to the list this year as part of FXC’s inclusion of e-commerce platforms. Singapore-based financial services group DBS has established itself as a critical player in the APAC cross-border payment landscape, being named one of the world's Top 100 cross-border payment companies for six consecutive years.
Latin America
Latin America follows closely behind APAC, with an annual growth rate surpassing 8%, according to cognizant analysis. Here, the growth story is driven by improvements in real-time payment (RTP) infrastructure, which makes digital transactions faster and more convenient.
A growing middle class and increasing urbanization drive retail growth in Latin America. However, the region faces economic instability and infrastructure limitations that hinder logistics and distribution. Despite these obstacles, opportunities exist in digital transformation, omnichannel strategies, and innovative payment solutions.
Middle East and Africa (MEA)
The MEA region is experiencing steady retail expansion, driven by a growing population, rising disposable incomes, and a shift towards modern retail formats like malls and shopping centers. E-commerce is also gaining traction due to increasing internet and smartphone penetration.
Segments Outlook
The retail and payments landscape is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by technological advancements, regulatory changes, and evolving consumer preferences. This transformation presents both challenges and opportunities for industry businesses. Several key trends that are shaping the future of retail and payments, including:
Cloud Migration
Cloud migration revolutionizes how financial institutions and retailers operate. The cloud migration services market is projected to reach a staggering $515.83 billion by 2027 (Allied Market Research), reflecting its growing importance. Cloud adoption offers several benefits, including Improved Interoperability, where cloud platforms allow institutions to access data and transfer information seamlessly between various IT systems, head offices, and third-party vendors. This fosters collaboration and streamlines operations. Cloud services make it easier for institutions to adopt ISO 20022, the new global standard for sending payment instructions. This facilitates smoother and more efficient international transactions. Cloud providers offer robust security features, including automatic updates and sophisticated monitoring systems. This reduces the burden on businesses of maintaining their cybersecurity infrastructure. Cloud environments also enable rapid development and testing of new online services, allowing companies to respond quickly to changing market demands. Cloud-based open banking infrastructure will enable businesses to collaborate with partners and offer personalized experiences to customers by integrating a more comprehensive range of services.
For instance, in January 2021, Mastercard partnered with NMI and Global Payments to launch its first cloud-based point-of-sale acceptance technology. This exemplifies the potential of cloud solutions to improve security and streamline payments for merchants.
Riskified is an AI-powered fraud management and risk intelligence platform that helps eliminate risks and block threats, enabling merchants to maximize revenue and profit securely. It helps reduce and shift fraud chargeback liability and leverages machine learning, automation, and e-commerce expertise to grow approval rates. It also uses precise decisions and data attributes to detect and block ATOs. Riskified strives to ensure customers can enjoy a positive customer experience while at the same time preventing refund, promo, and reseller abuse. The software’s ability to scale with a business makes it viable for growing e-commerce stores’ fraud protection.
Payments as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS is becoming increasingly popular for businesses to develop innovative payment solutions. It can provide the building blocks for companies to create customized payment functionalities without extensive in-house development. Some real-world examples of PaaS include:
- Goldman Sachs and AmEx debuted a cloud-based payments service for large corporate clients. The platform’s multiple payment options provide a more accessible and streamlined B2B payment process, eliminating redundancies and reducing bank fees incurred by multi-file initiation.
- Astra, in collaboration with Visa Direct®, brought instant account funding to US neo-banks, marketplaces, and exchanges. The Astra Platform is integrated via APIs and allows builders to add payment functionality to applications without the need to handle additional compliance, capital commitments, or operational costs. Astra partners with Visa Direct® to accelerate transfers for peer-to-peer payments, cross-border remittances, account-to-account transfers, and disbursements.
- Lloyds Bank partnered with Form3 to build a cloud-native PaaS platform to streamline their payment processes. This platform promises to improve efficiency and reduce processing time. This strategic partnership will enable the investigation and development of a cloud-native Payments-as-a-Service platform that has the potential to improve the overall payment processes significantly. The collaboration with Form3 will simplify payment capabilities, creating the basis for overall response to the industry NPA initiative and providing support for enhanced data and new overlay services.
- JPMorgan's collaboration with Paymentus, a provider of cloud-based bill payment technology and solutions. The service’s single platform for customer engagement, bill presentation, and payments is expected to help clients digitize their receivables journey through innovations like request to pay (RTP). The strategic collaboration between Visa Inc. and JPMorgan Payments is set to empower many businesses with enhanced domestic payment solutions. Central to this initiative is the integration of Visa Direct®’s Push to Card payment rail, facilitating the rapid and secure transfer of funds directly to recipients’ bank accounts. The partnership is poised to significantly improve the efficiency and security of financial transactions for diverse client segments. This integration represents a significant leap forward in pursuing a seamless and secure economic environment for all stakeholders.
Cybersecurity
In the digital era, safeguarding cybersecurity is paramount, especially in the payments sector, which remains a prime target. The global payments security market is projected to rise to $60.56 billion by 2030 (Allied Market Research), underscoring the increasing recognition of cybersecurity risks. Among the notable trends in payment security is tokenization, a method replacing magnetic strips. Tokenization provides heightened security for transactions by generating unique tokens for each card and merchant, making it exceedingly challenging to pilfer card information. Visa and Google's partnership to add virtual cards to autofill features on Android devices and Chrome browsers is a concrete example of this trend. Contactless payments using near-field communication (NFC) technology offer increased security compared to traditional swipe methods. Additionally, dynamic PINs generated for every transaction add another layer of protection. Banks like ING are piloting P2P payment apps that use ultra-wideband technology for even more secure money transfers. MFA is a powerful tool that requires users to provide multiple verification methods, such as passwords, device recognition, and biometric authentication, when making payments. This significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized transactions.
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)
DLT, with its foundational blockchain technology, is effecting significant transformations across various sectors, and the payments industry is no exception. Noteworthy applications of DLT in payments include the exploration by central banks worldwide of the development of Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) as a strategic response to the diminishing use of cash and the ascendancy of cryptocurrencies. CBDCs hold the promise of advancing the digitalization of economies while providing central banks with heightened oversight of monetary policy. Furthermore, payments within the metaverse are emerging as a prevalent phenomenon concurrent with the increasing adoption of virtual environments such as the metaverse.
JPMorgan became the first bank to enter the metaverse, opening a lounge in Decentral and the Onyx lounge, which allowed institutions and businesses to enter the metaverse. The bank expects $54 billion will be spent yearly on virtual goods. Meta has rolled out payment tools for creators of virtual mini-worlds and communities in its Horizon Worlds metaverse platform. Visa, Mastercard, and Amex are all making moves in the metaverse. Mastercard’s patent and trademark filings have also revealed that they plan to move into metaverse commerce, although they have not publicly shared plans.
Market Dynamics
Growth Enablers
Below are the growth enablers revolutionizing the future of payments.
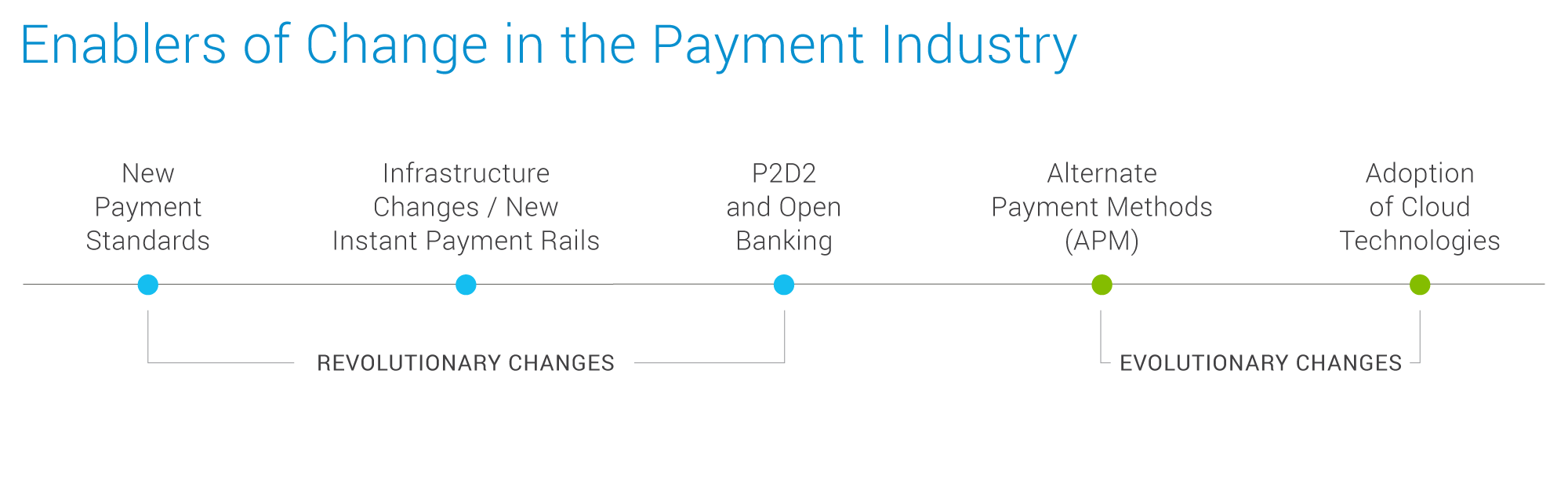 Data sourced from GlobalLogic Payment Report
Data sourced from GlobalLogic Payment Report
The Emergence of the E-commerce Boom
The retail and digital payments industry is experiencing an extraordinary phase of growth driven by a combination of factors. This report delves into the primary drivers facilitating this transformation and explores the emerging trends shaping the industry's future. The thriving e-commerce sector represents a pivotal growth driver in the digital payments market. As online shopping experiences a surge in popularity, consumers are increasingly reliant on secure and convenient payment methods. This has prompted the development of innovative solutions tailored specifically to meet the needs of e-commerce transactions.
As an example, in September 2023, HDFC Bank unveiled the introduction of three novel digital payment products tailored for the Unified Payments Interface (UPI). These offerings are anticipated to enhance the efficiency of the payment process for both merchants and customers, thereby catalyzing further expansion in the realm of e-commerce.
Government Support Fosters Innovation in the Adoption of Digital Payments
Supportive government policies play a crucial role in promoting the adoption of digital payments. Initiatives that encourage contactless transactions, such as demonetization efforts in some countries, contribute significantly to the growth of the market. Additionally, government support for fintech companies fosters innovation in developing new and secure payment solutions. The emergence of a burgeoning fintech sector has significantly altered the landscape of the digital payments industry. Fintech companies are introducing cutting-edge payment processing solutions that offer greater efficiency, security, and convenience compared to traditional methods. This not only benefits consumers but also creates a more competitive environment within the industry.
COVID-19 Catalyst for Cashless Transactions
The COVID-19 pandemic significantly impacted the retail payment industry, accelerating the shift towards digital transactions by roughly a decade. While the initial economic disruption caused a decline in overall payment volumes, particularly in sectors like travel and hospitality that rely heavily on physical interactions, the lockdown measures pushed consumers towards online alternatives. This led to a surge in digital payments for essential services like online grocery shopping, bill payments, and online education.
Even after the reopening of physical stores, the predicted rebound in cash usage failed to materialize. Having familiarized themselves with the convenience and safety of digital payments during the pandemic, consumers continued to utilize electronic channels for a significant portion of their transactions. This trend highlights the pandemic's lasting impact on consumer behavior, permanently altering payment preferences.
Furthermore, the pandemic acted as a catalyst for the adoption of embedded payments, a technology allowing purchases directly within websites, apps, and social media platforms. This seamless payment experience proved particularly attractive to consumers and is expected to experience significant growth in the coming years.
The pandemic's impact wasn't limited to consumer behavior. It also pushed the retail industry to rapidly adapt and prioritize online commerce. The decline in foot traffic due to lockdowns forced retailers to invest in omnichannel capabilities, offering a blend of physical and digital shopping experiences. This shift towards online retail further fueled the growth of digital payments, creating a mutually reinforcing cycle.
In conclusion, the COVID-19 pandemic served as a turning point for the retail payment industry, accelerating the digital transformation by an estimated ten years. The pandemic has permanently altered consumer preferences and pushed the retail industry toward a more digital future by fostering the adoption of digital wallets, contactless payments, and embedded payment solutions.
Looking at 2024, it's clear that the pandemic acted as a catalyst, propelling the digital payments industry forward by a decade. Consumers, now accustomed to the ease and security of digital transactions, are unlikely to revert to pre-pandemic habits. This shift presents both challenges and opportunities for retailers and financial institutions alike. As the industry continues to evolve, focusing on innovation, security, and a seamless user experience will be paramount for success in the new normal.
Advancement in Digital Payment Systems
The introduction of new contactless payment systems, like radio frequency identification (RFID), near-field communication (NFC), and host card emulation (HCE), is revolutionizing the way we pay. These technologies offer a faster, more secure, and more convenient alternative to traditional swipe methods.
For instance, The National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) recently unveiled a range of innovative products, including BillPay Connect, Credit Line on UPI, UPI LITE X, and Tap & Pay. These solutions leverage contactless technology to create a more efficient and inclusive digital payment ecosystem.
New Payment Standards & Payment Rails
Over the past few decades, the payments industry has been hampered by a multitude of standards, often proprietary to specific regions or financial institutions. This has led to inefficiencies and inconsistencies that hinder smooth transactions. New standards like ISO 20022 are emerging to mitigate the challenge by establishing a universal language for payment messaging, paving the way for more streamlined and efficient communication. Payment rails act as the invisible highways through which funds flow, both domestically and internationally. Recognizing the changing needs of consumers and businesses, central banks are actively transforming national payment rails to accommodate advancements in payment technology and data formats. These upgrades aim to ensure a robust and future-proof infrastructure for digital transactions.
Open banking, coupled with regulations like PSD2 (Payment Services Directive 2)
Open banking with PSD2 is fundamentally reshaping the way financial institutions interact with consumers. Open banking fosters competition and innovation in the payments landscape by allowing third-party providers access to customer data with explicit consent. This gives consumers more choices and control over their financial data, enabling fintech companies to develop new and exciting payment solutions. The increasing shift towards digital wallets, contactless payments, and mobile banking is a defining characteristic of the current digital payments landscape. Consumers are drawn to the unmatched convenience, security, and speed offered by these methods, leading to a significant rise in cashless transactions.
Inhibitors
While the digital payments industry is flourishing, several key inhibitors threaten to impede its growth. Here, we explore three major challenges that need to be addressed to ensure the continued success of this sector:
Security Woes like Cyberattacks and Data BreachesThe increasing number of cyberattacks and data breaches remains a significant concern for consumers. These incidents erode trust in digital payments and deter some individuals from embracing cashless transactions. More robust security measures and responsible data handling are crucial to combating these threats and building trust among consumers. The rise in online fraud, such as identity theft and unauthorized transactions, creates a sense of vulnerability for users. Businesses in the industry must invest in robust fraud detection systems and implement stringent authentication protocols to mitigate these risks. For instance, in 2021, a major US-based fintech company suffered a data breach via a third party, exposing the personal information of millions of customers. This incident highlighted the vulnerabilities within the digital payments ecosystem and underscored the need for more robust security measures.
Limited Infrastructure and Digital Divide
Limited internet connectivity and a lack of access to compatible devices, such as smartphones, restrict the growth of digital payments in some regions. This creates a digital divide that excludes a significant segment of the population from participating in the cashless economy. The lack of robust digital infrastructure, particularly in emerging economies, poses a challenge to the widespread adoption of digital payments. This includes limited access to reliable internet and the absence of a well-developed network of point-of-sale terminals. For instance, in rural areas of many developing countries, internet access remains unreliable or unavailable altogether. This significantly hinders the adoption of digital wallets and other mobile payment solutions.
Digital wallets and mobile payment solutions rely on applications. In a remote village like Kibera, on the outskirts of Nairobi, Kenya, residents might face issues downloading these apps due to unreliable internet. This becomes a primary barrier to even starting to use these services.
Even if someone manages to download the app, transactions require internet connectivity for processing. Imagine a farmer at a market in Kibera trying to sell his produce through a mobile payment app. An internet outage would prevent the transaction, potentially causing a missed sale or frustration for both the farmer and the buyer.
Reliable internet access opens doors to information and educational resources. Without it, villagers in Kibera might have limited knowledge about digital wallets and their functionalities. This lack of awareness can lead to hesitancy and a preference for sticking with traditional cash transactions.
These limitations create a cycle that hinders the adoption of digital financial technologies in rural areas. Without reliable internet and widespread access to smartphones and electricity, digital wallets and mobile payment solutions struggle to gain traction. This can exclude these communities from the potential benefits these technologies offer, such as increased financial inclusion, security against theft, and easier access to financial services.
Standardization and Regulatory Hurdles
The existence of numerous payment systems, each tailored to specific use cases, can create interoperability challenges. This makes it difficult for businesses and consumers to seamlessly transact across different platforms, hindering efficiency and convenience. Stringent regulations aimed at combating identity theft and money laundering can create an administrative burden for businesses in the digital payments industry. Finding the right balance between security and ease of use is crucial for fostering growth in this sector. For instance, the lack of standardized protocols for cross-border transactions can lead to delays and additional business charges. This can be a significant barrier to international trade and commerce.
Retail & Payment Solutions Market
Supply Chain
Traditional stores are transforming into smart stores, where online inventory is updated in real-time, offering enhanced customer experience. Moreover, new dynamic supply chain models allow stakeholders to exchange goods with data and information.
A fully-fledged sustainable supply chain ecosystem should enable suppliers and buyers to interact seamlessly, provide a robust sustainability rating methodology, and offer preferable rates to organizations that meet sustainability thresholds. The key strategic distinction of this wave is the use of advanced analytics to assess and manage ESG risk across the entire base of suppliers and buyers. For example, banks can help corporations assess the amount and types of GHG emissions each supplier adds to total supply chain emissions and set policies for minimum standards and bidder exclusion criteria. The rating capability (typically provided by a third party focused on sustainability assessment) is integrated within a technology platform that is usually supported by a trade fintech company.
Technological advancement often plays a role in optimizing the supply chain, enhancing customer engagement, and improving inventory and restocking processes. An example includes smart shelves, which automatically detect when products have been purchased. Advancements in technology, enabling personalized shopping experiences and streamlined supply chains, are key growth drivers for the retail sector in North America. The U.S. has led the market because of its tech-savvy population and large consumer base. Canada has also experienced steady growth with a focus on sustainable practices and expanding online sales.
 Data sourced from Dimensional Scanner
Data sourced from Dimensional Scanner
Semiconductor Scarcity and Current Concerns
The semiconductor shortage began in 2020 and continues to disrupt supply chains across numerous industries, including consumer goods, in 2024. This crisis stems from a surge in demand for electronics during COVID-19 lockdowns, coupled with limited chip production capacity.
The bottleneck lies in several areas. First, there's a lack of raw materials needed for chip production. Second, existing fabrication facilities operate at maximum capacity and can't be easily expanded due to the complex and time-consuming process. This inability to meet rising demand has led to extended lead times, meaning it takes longer for new chip-based products to reach the market.
The impact on consumer goods is significant. Delayed deliveries and production shortfalls frustrate consumers, who might cancel orders or face price hikes due to potential scarcity. Industries like mobile phones, laptops, and gaming consoles are particularly affected.
Looking ahead, experts predict the shortage will likely ease further by late 2024. However, navigating this period requires proactive measures from both manufacturers and governments.
Expanding fabrication capacity and diversifying production locations are crucial steps for manufacturers. Modernizing existing facilities and exploring alternative sourcing options can also help alleviate the pressure.
Governments can play a role by investing in domestic chip production and fostering international collaboration to strengthen the global semiconductor value chain. Additionally, promoting self-reliance through subsidies and strategic partnerships can help countries become less vulnerable to future supply chain disruptions.
Ultimately, overcoming this challenge requires a multi-pronged approach. By improving supply chain visibility, implementing real-time monitoring, and fostering collaboration, companies can navigate the current crisis and avoid similar situations in the future. As the industry recovers, continuous adaptation, strategic planning, and a focus on long-term sustainability will be essential for ensuring uninterrupted growth.
China+1 and Nearshoring
The globalized manufacturing landscape is shifting as companies in various sectors, including payments and retail, grapple with supply chain disruptions and changing economic realities. A key trend is the rise of "reshoring" and "nearshoring," where businesses bring production closer to home or nearby regions. This strategy aims to shorten supply chains, reduce transportation costs, and increase resilience against disruptions like pandemics or geopolitical tensions.
However, challenges exist, such as limited capacity in nearshoring hubs like Mexico, requiring careful planning and investment. This shift from purely cost-driven "just-in-time" models towards "just-in-case" approaches focusing on flexibility and redundancy is evident in every industry, where government incentives like the US Inflation Reduction Act encourage domestic battery production to reduce reliance on China. Similarly, the retail and retail technology sectors are adopting "China+1" strategies, diversifying production across Southeast Asia to mitigate risk. Despite the potential benefits, challenges remain in these new production hubs, such as ensuring adequate after-sales support, efficient logistics, and readily available equipment. Overall, these trends highlight the need for companies to adapt their sourcing strategies to balance cost, efficiency, and resilience in a dynamic global market.
Sustainability
The retail payments industry faces a complex challenge: the chips powering its technological advancements pose a significant environmental threat. These chips, crucial for enabling contactless payments and secure transactions, are made using a process that consumes vast quantities of water and energy, generating hazardous waste in the bargain.
The fight against climate change is pushing businesses to adopt sustainable practices. The retail and payment industry is no exception, with "net zero" becoming a key goal. This means achieving a balance between the amount of carbon dioxide released and removed from the atmosphere. International agreements like the Paris Agreement call for significant reductions in greenhouse gas emissions. For companies, net zero isn't just a good idea, it can be a legal requirement in some regions.
The payments industry has a unique opportunity to promote sustainability. Using renewable energy for data centers and processing can significantly reduce the industry's carbon footprint. Financial institutions can invest in eco-friendly projects and businesses, directing capital away from high-polluting industries.
For Instance, Visa, a leading payment network, has pledged to achieve net zero emissions by 2040. They're investing in renewable energy and working with partners to create sustainable payment solutions for low-carbon transportation. A key strategy is transitioning to 100% renewable energy sources to power their operations. This could involve investing in solar, wind, or geothermal energy. Visa is likely exploring and developing new payment solutions that promote sustainable behaviors. This could include supporting electric vehicle charging infrastructure or contactless payment systems for public transport. By achieving net zero emissions, Visa aims to set an example for the industry and contribute to a more sustainable financial system. Their commitment goes beyond simply reducing their footprint and involves influencing positive change throughout the financial ecosystem.
To address these sustainability concerns, the industry is exploring alternative materials like silicon carbide and gallium nitride. These potentially hold promise for reduced environmental impact during chip production. While the chip shortage that plagued the industry for several years has shown signs of improvement, it's not entirely over. This ongoing challenge continues to hinder the widespread adoption of sustainable technologies, making the development of eco-friendly chip solutions even more critical.
Sustainability in Retail Payments
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors are playing an increasingly prominent role in consumer and stakeholder expectations. This shift requires the retail payments industry to take responsibility for the environmental impact of its supply chain, including chip manufacturers. A key concern lies in Scope 3 emissions – those generated by a company's activities but outside its direct control, such as emissions from chip suppliers. Retailers are actively collaborating with chip manufacturers to find ways to reduce these emissions throughout the supply chain. For instance, Companies like PayU are setting a positive example by launching ESG initiatives that prioritize responsible sourcing and environmentally conscious practices within the payments sector. This leadership encourages industry-wide collaboration towards sustainable chip production.
The retail payments industry needs to navigate a delicate balance. It must continue to embrace technological innovation for secure and efficient transactions, while prioritizing environmental responsibility. By actively engaging with chip manufacturers, exploring sustainable alternatives, and implementing responsible sourcing practices, the industry can create a future where innovation in payments contributes to a greener tomorrow.
Retail & Payment Solutions Market
Technology Evolution
The year 2024 paints a dynamic picture for the retail and payment industry, where cutting-edge technologies are redefining the landscape. This report explores four key trends shaping the future of how we shop and pay:
Self-Service Checkouts
Self-service checkouts (SSOs) have become a ubiquitous feature in the retail landscape, transforming the checkout experience for both customers and retailers.
SSOs can significantly reduce wait times, particularly during peak shopping hours. This translates to customer satisfaction and a smoother shopping experience. SSOs require fewer cashiers, leading to reduced labor costs. Additionally, faster checkout times free up space for displaying merchandise or customer service areas. Customers who prefer a quicker checkout or a more independent shopping experience appreciate the control SSOs offer. They can scan items and pay at their own pace. SSOs can be integrated with inventory management systems, allowing real-time stock updates while streamlining the stocking process.
Considerations: Self-checkout environments require robust security measures to deter theft. This may involve security cameras, weight verification systems, and age verification for age-restricted products. Seamless integration of SSOs with existing point-of-sale systems and inventory management software is crucial. Although SSOs aim for ease of use, some customers may require assistance. Retailers must provide readily available support staff for troubleshooting technical issues. SSOs need to be accessible to customers with disabilities. This may involve incorporating features like voice commands, lowered scanners, or larger screens.
Future of SSOs: AI-powered systems automatically recognize items placed in the checkout bag, eliminating the need for scanning. Technologies like Amazon Go, where cashierless stores utilize sensors and cameras for automatic billing, are paving the way for a grab-and-go shopping experience. Intuitive touchscreens and voice-activated commands will further simplify the self-checkout process for customers. Self-service checkouts offer significant benefits for both retailers and customers. As technology evolves and addresses existing challenges, SSOs are poised to become an even more dominant force in the future of retail.
AR, AI, and ML
The retail industry is undergoing a radical transformation driven by advancements in Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and Augmented Reality (AR)
Artificial Intelligence (AI) & Machine Learning (ML)
AI helps retailers understand customer preferences and buying habits, allowing for targeted recommendations, promotions, and marketing campaigns tailored to individual customers. AI-powered analytics can anticipate demand fluctuations and optimize inventory levels, reducing stockouts and overstocking. AI-powered chatbots can provide 24/7 customer support, answer questions, and resolve issues. This frees up human customer service representatives for more complex inquiries. AI can automate tasks like in-store logistics and robotic warehouse management, improving efficiency and reducing operational costs.
AI algorithms can analyze purchase patterns and identify suspicious transactions, helping to prevent fraud. For instance, Amazon Go is a convenience shop business that operates in the United States and the United Kingdom. Customers can make purchases without being checked out by a cashier or via a self-checkout station because the stores are cashierless and mostly automated. It started when a team of Amazon executives designed and tested Amazon Go stores. Amazon revolutionizes the traditional shopping experience through the integration of advanced technology. By leveraging sensor fusion, computer vision, and deep learning algorithms, Amazon Go stores provide a seamless and frictionless shopping experience. Customers can simply walk in, grab the items they need, and leave the store without the need for checkout lines or cashiers. The company’s first store opened to employees on December 5, 2016, and to the public on January 22, 2018. Prepared foods, meal kits, groceries, and booze are available in the flagship location. Amazon Go Grocery, a larger version, debuted on February 25, 2020, in Seattle’s Capitol Hill area. Amazon began offering its technology to other merchants the next month, allowing their consumers to make purchases without the need for cashiers or Amazon accounts.
KEY FEATURES OF AMAZON GO:
Just Walk Out technology
One of the key features that sets Amazon Go apart is its "Just Walk Out" technology. This innovative system enables customers to enter the store, grab the items they need, and simply walk out without the need for traditional checkouts. The technology uses computer vision, sensor fusion, and machine learning algorithms to track customers and the items they pick up, automatically charging their Amazon accounts upon exit.
Store layout and design
Amazon Go stores are designed to optimize the customer experience and facilitate a seamless shopping journey. The layout is carefully planned to ensure easy navigation and efficient product placement. Additionally, the store design incorporates a combination of modern aesthetics and practicality, creating a visually appealing and functional environment for shoppers.
Product selection and offerings
Amazon Go offers a diverse range of products catering to various customer needs. While initially focused on convenience store-style offerings like snacks, beverages, and ready-to-eat meals, Amazon Go has expanded its product selection to include a more comprehensive array of grocery items, fresh produce, and even meal kits. The goal is to provide customers with an extensive shopping experience that meets their everyday needs.
Mobile application and digital integration
The Amazon Go mobile application serves as a vital component of the shopping experience. Customers use the app to gain entry into the store by scanning a QR code upon arrival. The app also provides real-time information, such as product availability and pricing, enabling shoppers to make informed decisions. Furthermore, the app leverages digital integration to offer personalized recommendations based on customers' shopping history and preferences, enhancing the overall shopping experience.
TECHNOLOGY BEHIND AMAZON-GO
Sensor fusion
Sensor fusion is a key technology employed in Amazon Go stores. The stores are equipped with a network of sensors, including cameras and weight sensors embedded in shelves. These sensors collect real-time data, capturing information about customer movements, product interactions, and inventory changes. By combining and analyzing data from multiple sensors, the system gains a comprehensive understanding of the store environment and customer behavior.
Computer vision
Computer vision plays a vital role in Amazon Go's operations. Advanced computer vision algorithms process the data captured by cameras in real-time, enabling the system to identify and track customers, detect items picked up or returned to shelves, and monitor overall store activity. Computer vision algorithms enable accurate item recognition and tracking, forming the Just Walk Out technology's basis and eliminating the need for traditional checkouts.
Deep learning algorithms
Deep learning algorithms are utilized in Amazon Go to enhance item recognition and optimize the shopping experience. These algorithms learn from vast amounts of data, enabling the system to identify products based on visual cues accurately. Deep learning models are trained to recognize various packaging, shapes, and sizes, ensuring accurate item detection and reducing errors in the automated checkout process. The algorithms continually improve their performance over time as they are exposed to more data.
Data analytics and machine learning
Data analytics and machine learning techniques are integral to the functioning of Amazon Go. The vast amount of data collected from sensors, cameras, and customer interactions is analyzed to gain insights into shopping patterns, customer preferences, and store operations. Machine learning algorithms are used to extract valuable information from the data, such as identifying popular products, optimizing inventory management, and providing personalized recommendations to customers. These insights and machine learning models help Amazon Go continually enhance its operations and deliver a better customer experience.
Machine Learning
ML can analyze vast amounts of data to predict upcoming consumer behavior and product demand trends. This allows retailers to adjust their strategies and product offerings proactively. ML algorithms can analyze real-time data to determine optimal pricing strategies based on factors like demand, competition, and customer behavior. ML can personalize search results based on a customer's previous purchases and browsing history, making it easier for them to find what they're looking for.
ML can help retailers segment customers into distinct groups based on demographics and buying patterns. This allows for targeted marketing campaigns and personalized promotions. For instance, BNYM’s clients receive payments to review and authenticate through BNYM’s Digital Authentication tool. After final review and approval by BNYM, the platform generates a SWIFT instruction to affect the money movement.
Augmented Reality
AR allows customers to try on clothes, makeup, or even glasses virtually before purchasing them, which can increase customer confidence and satisfaction. AR can overlay product information onto physical items, providing customers with detailed specifications and reviews before purchasing. AR apps can guide customers around the store, locate specific products, and provide real-time information on promotions.
AR Payments seem bound to set a new standard for customer expectations in the retail sector. As consumers become accustomed to immersive and interactive experiences, there will be an increased demand for innovative payment solutions beyond traditional methods. This could prompt a shift in industry norms, with other sectors exploring ways to incorporate augmented reality into their payment processes.
Some concerns exist regarding security and convenience. Those elements remain paramount in the realm of payments, and AR technology can certainly rise to the challenge. With secure authentication methods embedded in AR payment systems, shoppers can confidently complete transactions using a combination of biometrics and visual recognition. This streamlines the checkout process and ensures the utmost security for financial transactions.
Augmented Reality in retail is revolutionizing the shopping experience. With AR in retail, customers can better interact, customize, and engage with products to make the right purchase decisions. Nike's Virtual View is one top example of how WebAR boosts customer engagement and trust in retail. The virtual view experience lets shoppers preview clothing on 3D holograms of models in WebAR. Nike partnered with volumetric video agency Omnivor to create ‘Nike Virtual View,' a feature that lets shoppers preview clothing on 3D holograms of models in WebAR while browsing the Finish Line website. Another instance is Nike Fit, the foot measuring feature is something that Nike has been able to successfully implement both in-store and on its app, making e-commerce and retail shopping a much easier experience for its customers. In-store employees are equipped with an iPod Touch with the app installed, so they're always ready to help you find the right shoe size for your feet. You are also able to measure your feet at home, using the app to accurately attain your size and order shoes, knowing you are ordering exactly the right product. Nike has also combined the app and shopping in-store, with the app producing a barcode. This means you don't have to measure your feet more than once. This barcode can then be scanned by an employee, instantly giving them the exact measurements of your feet.
This feature has made shopping a much easier and more enjoyable activity. You're almost certain to get the right shoe size for your feet, regardless of the style of footwear you want. By providing this feature through their app, Nike is transforming the entire shopping industry and transforming how we view e-commerce and retail. This function is likely to mean fewer shoes will be returned due to customers ordering the wrong size online. Nike's incorporation of AR into its shopping applications and in-store environment means it can market products in a much more personalized way. Surely, this will lead to more customers being happy and satisfied with the items they receive.
AR is transforming the shopping industry, and Nike is just one company using these technological advancements to help its customers and eliminate the guesswork of online shopping.
Millennials are the core shoppers today and need services at their fingertips. Standing in long queues to grab that limited offer is off the trend. Now shoppers love to book it first online. With AR in retail, online shopping experiences take a new turn. Customers can try on items virtually while customizing and interacting with the products better to make more efficient purchasing decisions. Getting complete satisfaction with online shopping increases brand trust and drives revenue growth.
Modern consumers value personalization and convenience over pricing and products. From the study by McKinsey and Company, it is stated that over three-quarters of consumers (76 percent) said that receiving personalized communications was a key factor in prompting their consideration of a brand, and 78 percent said such content made them more likely to repurchase. Personalization is especially effective at driving repeat engagement and loyalty over time. Augmented Reality allows brands to develop smart retail experiences that influence their customers' buying decisions. The technology makes online selling easier and more comfortable by creating virtual simulations for users to interact with a product, just like how they try a fashion outfit in a physical store. Using AR, retail customers can virtually visit their favorite brand stores, try products, and make comparisons without leaving the comfort of their homes.
By 2025, it is anticipated that nearly 75% of the global population and almost all people who use social or communication apps will be frequent AR users. AR adoption will see growth in these four key areas:
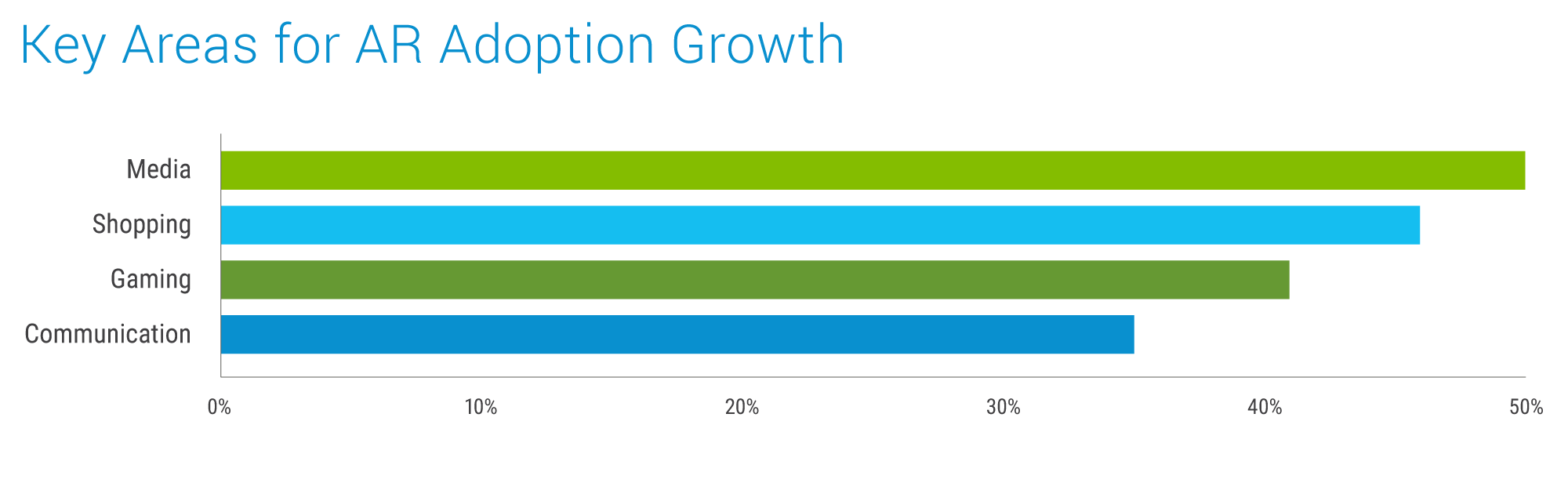 Data sourced from Secondary research
Data sourced from Secondary research
Using AR apps on mobile devices, customers can quickly access product details, try out varied colors of the desired products, and make purchase decisions more efficient. The popular brand Lacoste gained traction when implementing the AR feature to bring their sports shoe colors to life. Lacoste's utilization of Augmented Reality (AR) to enhance their sports shoe shopping experience marked a significant step in their marketing strategy. By integrating AR technology into their app or website, Lacoste allowed customers to virtually try on different shoe colors in real-time, offering an interactive and immersive shopping experience. This innovative approach not only differentiated Lacoste from competitors but also addressed common pain points in online shopping, such as uncertainty about how products will look in real life. By bringing their shoe colors to life through AR, Lacoste effectively engaged customers, encouraging them to spend more time interacting with the brand and ultimately increasing the likelihood of purchasing. Additionally, the buzz generated by this AR feature likely contributed to increased brand visibility and word-of-mouth marketing, further driving traction for Lacoste in the competitive sports shoe market. Overall, the implementation of AR technology by Lacoste demonstrated their commitment to innovation and customer-centricity, ultimately leading to greater brand recognition and customer loyalty.
Autonomous Retail and Warehouse Robotics
The retail landscape is undergoing a significant transformation driven by automation. Retail robotics are rapidly changing how stores operate, enhancing efficiency and improving the customer experience. This trend is fueled by a growing consumer demand for convenience and a need for retailers to compete effectively in the digital age.
One significant advantage of retail robots is their ability to automate manual tasks. Activities such as inventory management, warehouse operations, and order fulfillment exhibit characteristics that make them optimal candidates for automation through robotics due to their repetitive nature. These robots operate continuously, significantly improving processing speed and eliminating human error.
Beyond streamlining operations, retail robots can also play a crucial role in enhancing the customer experience. Social robots equipped with AI and speech recognition capabilities can greet customers, answer questions, recommend products, and even assist with wayfinding. This personalized approach fosters a more engaging shopping experience, allowing employees to focus on higher-value tasks and customer interactions.
Retail robots play a vital role in integrating online and offline retail experiences. For instance, pick-and-pack robots in warehouses can efficiently fulfill online orders, enabling click-and-collect options or faster home deliveries. Additionally, robots can streamline the in-store fulfillment of online orders, improving overall customer satisfaction.
As technology advances, we can expect even more sophisticated applications for retail robots. These may include robots capable of stocking shelves, assisting with price changes, and providing real-time product information. Furthermore, collaboration between robots and human employees will likely become increasingly common, leveraging the strengths to create a more efficient and customer-centric retail environment. The integration of retail robotics also presents significant challenges. The initial investment cost can be substantial, and there are concerns regarding job displacement for human workers. However, the potential benefits for efficiency, customer experience, and omnichannel integration are undeniable. As technology continues to evolve and costs fall, retail robotics are poised to become an indispensable part of the future of retail.
Amazon currently has more than 750,000 mobile drive units nicknamed Hercules, which were originally Kiva Robotics robots. Additionally, they have deployed more than 1,000 Robin robotic arms and recently added Proteus, an autonomous mobile drive unit designed to work safely alongside humans on the warehouse floor. Another instance is DHL, one of the world's largest logistics companies, which has invested in warehouse automation to improve efficiency and accuracy in its operations. The company uses robots for tasks such as picking and packing, as well as for sorting and moving goods.
Electronic Shelf Labels (ESLs)
Electronic Shelf Labels (ESLs) are transforming how retailers manage pricing in physical stores. These digital displays offer a multitude of advantages over traditional paper labels, enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and customer experience.
ESLs enable retailers to update prices electronically across the entire store in real-time. This eliminates the tedious and error-prone process of manually changing paper labels, saving time and labor costs. Furthermore, ESLs can be programmed to automatically adjust prices based on promotions, competitor pricing, or time of day, ensuring consistent and accurate pricing throughout the store.
ESLs can display more than just basic price information. These labels can be used to provide customers with additional product details, such as nutritional information, ingredients, or warranty details. This empowers customers to make more informed decisions and creates a more interactive shopping experience.
Improved inventory management: ESLs can be integrated with a store's inventory management system, allowing for real-time stock level tracking. This enables retailers to identify low-stock situations and replenish items more efficiently. Additionally, ESLs can be used to trigger alerts when items are out of stock, minimizing empty shelves and lost sales opportunities.
The ability to electronically update prices makes ESLs vulnerable to tampering. Therefore, robust security measures are crucial to prevent unauthorized access and ensure the integrity of pricing information.
Electronic Shelf Labels represent a significant advancement in in-store price management. Their ability to streamline processes, improve accuracy, and enhance customer experience positions them as a key technology for the future of retail.
Retail & Payment Solutions Market
Jabil Insights & Strategic Considerations
Jabil Insights
- Consumers are increasingly opting for digital payment methods over traditional plastic cards; this shows the strategic shift of technologies.
- Chinese dominance in the payments industry faces a challenge. Security concerns are prompting American and European customers to seek alternative solutions for payment processing and device manufacturing. Locations like Vietnam and Brazil are emerging as potential contenders, highlighting the desire for supply chain diversification while still maintaining some reliance on China.
- Opportunities are flourishing in-store digitization with the implementation of solutions like electronic shelf labels, evident in grocery stores and Walmart’s across the US and Europe
- Retailers are increasingly embracing digital solutions to minimize paper usage and staff reliance, paving the way for frictionless transactions and shopping experiences. Increased competition and the emergence of cost-effective options are driving down the cost of digitization.
- Post-pandemic trends indicate a significant rise in automation and robotics within warehousing and background store functions.
- Geopolitical tensions pose a continuing threat to supply chains, as evidenced by recent disruptions.
Jabil Spend Analysis
JABIL SPEND IN THE RETAIL SECTOR, BY CATEGORY (2020 VS 2023)
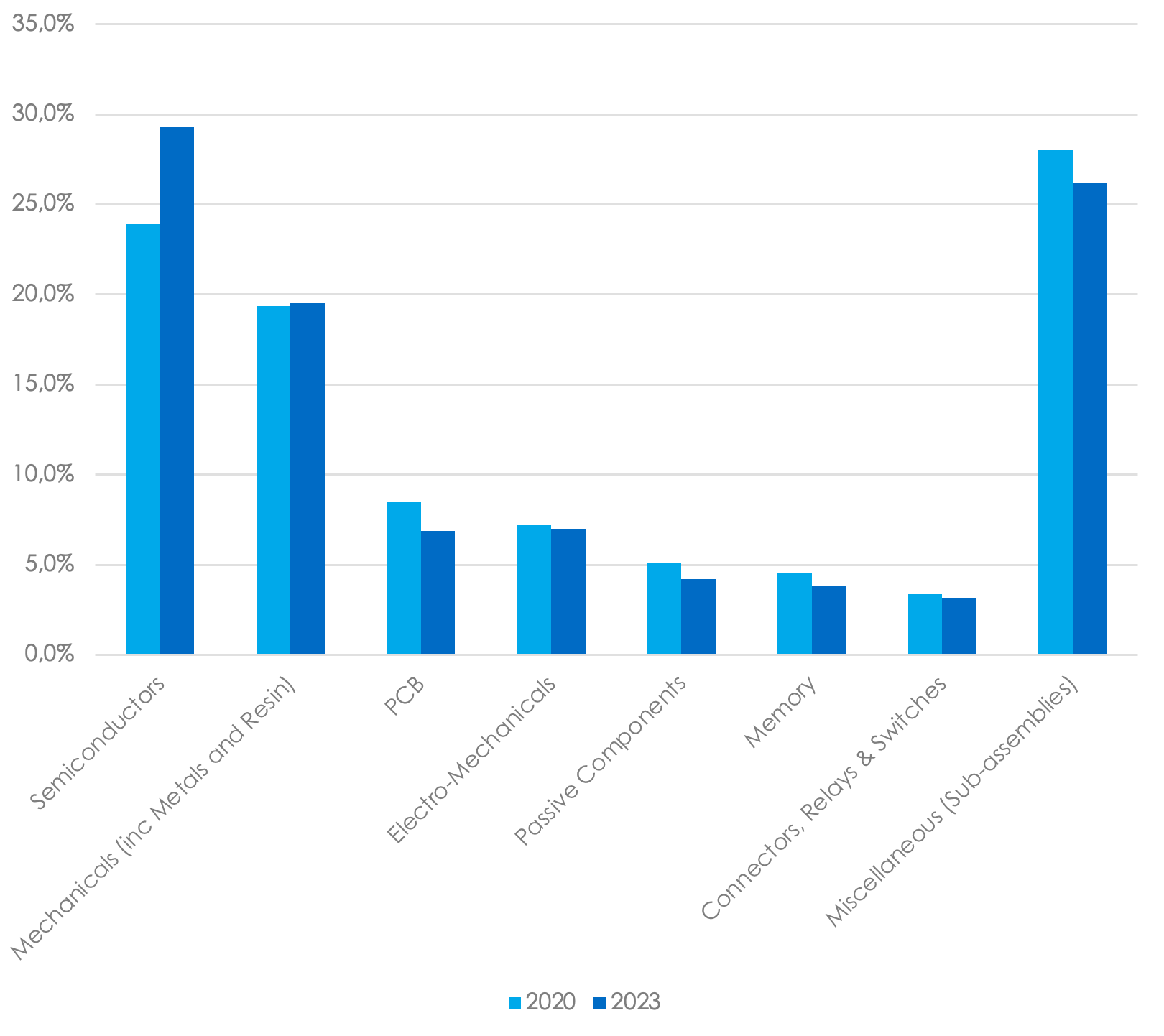
Data based on Jabil's historical spending data for the Retail Customer Segment
JABIL CATEGORY SPEND IN THE RETAIL SECTOR (2019-2023, YOY %)
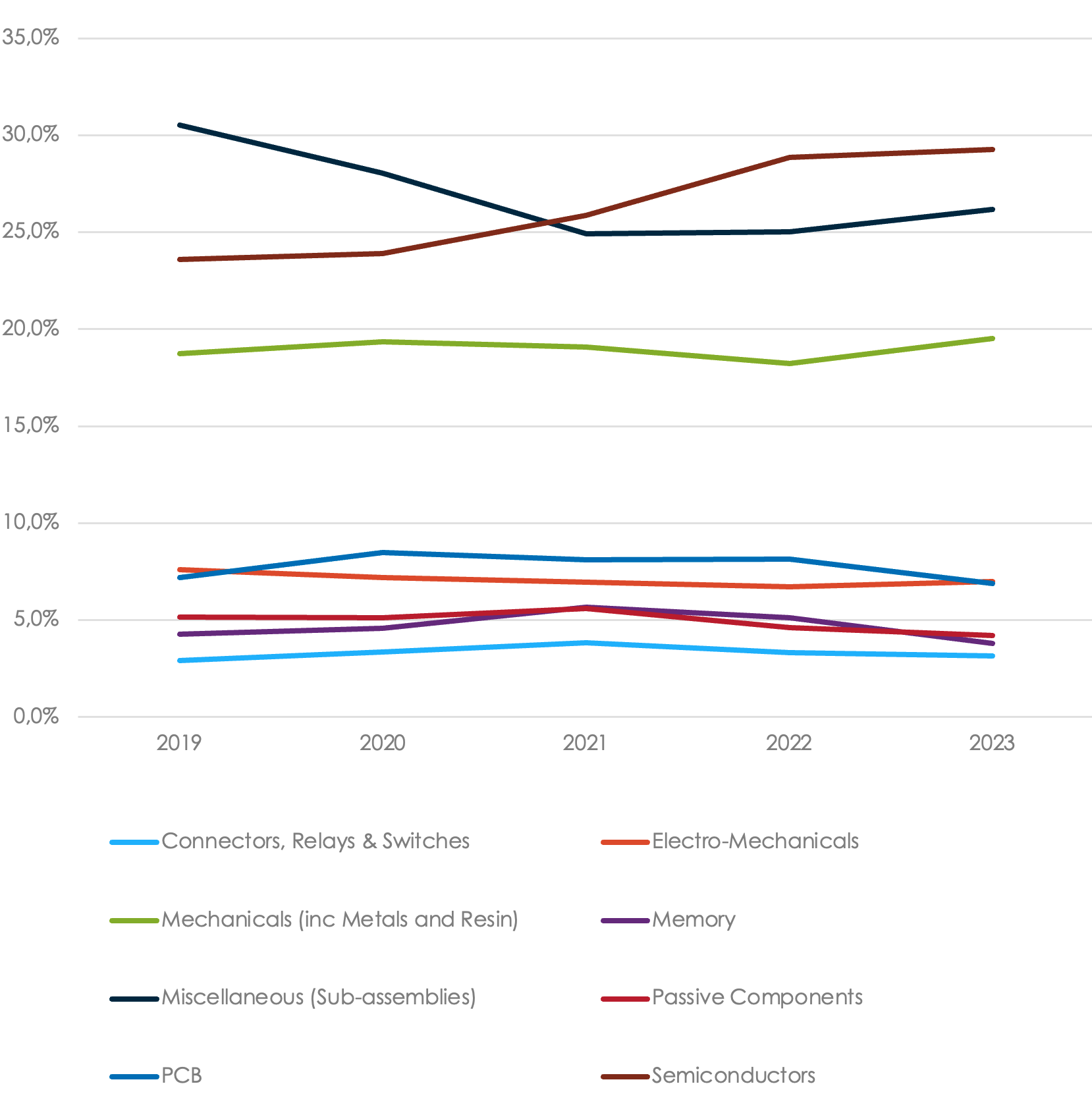
Data based on Jabil's historical spending data for the Retail Customer Segment
Strategic Considerations
- Businesses should prioritize offering a variety of secure digital payment options. To obtain customer preference for convenience and security.
- To mitigate security concerns and geopolitical risks, businesses should explore alternative sourcing options beyond China, fostering a more diversified supply chain.
- Enhanced operational efficiency and customer experience can be achieved by implementing digital solutions like electronic shelf labels.
- Addressing labor challenges and optimizing warehouse operations can be achieved through leveraging automation and robotics.
- Industry further needs to explore the potential of emerging technologies like artificial intelligence and machine learning for future competitive advantage. Focus on areas like personalized recommendations and demand forecasting.
- The growing demand for convenient payment methods necessitates investment in mobile point-of-sale systems and Android terminals.
Back to Top
