By clicking the “I Accept” button, or by accessing, participating, or submitting any information, or using the Jabil Global Intelligence Portal or any of its associated software, you warrant that you are duly authorized to accept the Global Intelligence Portal Terms and Conditions on behalf of your Company, intending to be legally bound hereby, and your company shall be bound by the terms and provisions of the Global Intelligence Portal Terms and Conditions, accessible under the following link Portal T&Cs.
Sector Market Report
Satellite Communication
Sector Market Report
Satellite Communication
Get an in-depth analysis of the satellite communication market's current state, trends, and future, including insights into key drivers, changing product lifecycles, and manufacturing challenges.
Satellite Communication Report
Executive Summary
The satellite communication (satcom) market is at a critical juncture as the residual effects of the COVID-19 pandemic gradually diminish, creating new opportunities for stakeholders. System enhancements, increasing adoption, and technology evolution bring significant opportunities to those operating in the industry. With the increasing adoption of satellite applications across several industries, including communications, defense, automotive (navigation), and aviation, satcom equipment manufacturers must refine their strategies to remain competitive.
The lower cost and increased frequency of launches drive the growth of the satellite communication equipment market by making it more affordable and accessible to deploy and maintain satellite networks. This allows for the development of larger constellations with more advanced equipment, leading to increased capacity, improved coverage, and lower latency for various applications. As launch costs decrease, investing in innovative satellite technologies and expanding services becomes more economically viable, further driving demand for satellite communication equipment.
The diverse sizes and functions of satellites enable a wider range of applications and services. Smaller, more affordable satellites cater to niche markets like IoT and remote sensing, while larger, more powerful satellites support broadband internet and navigation systems. This variety drives demand for specialized equipment, including antennas, transponders, and ground stations, tailored to the specific needs of each satellite type and application. This expanding ecosystem of diverse satellites and their corresponding equipment needs contributes significantly to the market's growth.
- In North America, Viasat recently won a five-year contract from the US Department of Defense to modernize its satellite communications infrastructure. Furthermore, SpaceX has launched 20 Starlink satellites into Earth's orbit, enabling direct-to-cellphone connectivity for subscribers.
- In Europe, the European Space Agency has awarded Thales Alenia Space a contract for the Italian earth observation satellite constellation.
- In Aisa, ST Engineering has been awarded a contract by PT Pasifik Satelit Nusantara (PSN), a company that operates Indonesia’s Satria-1 satellite network, to undertake the phase 2 expansion of the Satria-1 satellite network. In India, Starlink is set to launch its satellite internet service in January 2025, pending the finalization of government regulations.
Satellite Communication Market
Market Overview
Market Definition: Satellite Communications
Satellite communication is a mode of telecommunication that uses artificial satellites orbiting the Earth to relay signals between different locations on the ground. Essentially, it acts as a giant, space-based repeater system. A ground station transmits a signal (carrying data, voice, or video) to the satellite, a process known as the "uplink." The satellite, equipped with transponders, receives the signal, amplifies it, and then re-transmits it back down to Earth on a different frequency called the "downlink." This allows communication over vast distances, even to remote or geographically challenging areas where terrestrial infrastructure is impractical or unavailable.
The key advantage of satellite communication is its wide coverage area, as a single satellite can cover a large portion of the Earth's surface. This makes it ideal for broadcasting, long-distance telephony, and internet access, particularly in rural or underserved regions. Different orbits, such as geostationary, medium Earth orbit (MEO), and low Earth orbit (LEO), are used depending on the specific application and required coverage area. While satellite communication offers many benefits, it can also be affected by factors like latency (the delay caused by the signal's travel time), atmospheric interference, and the higher initial cost of deploying and maintaining the satellite infrastructure.
Market Overview
The satellite communication equipment market has grown exponentially over the past few years, driven by the increasing need for high-speed, uninterrupted, and reliable communications networks in remote areas. The commercial space industry has developed significantly in the last few years, mainly because of its increasing adoption in 5G terrestrial networks. The need for connectivity across critical platforms, such as Aircraft & Seafaring Vessels, has also boosted the market for satellite communications. According to a report published by MarketsandMarkets Research Pvt. Ltd., the market for satellite communication Equipment is estimated to be $24 Bn in 2024 and is expected to reach $41 Bn by 2029 at a CAGR of ~11%.
On the terrestrial network providers’ end, service providers are embracing satellite-to-cellular technology through partnerships with satellite providers like SpaceX and AST SpaceMobile to extend their network coverage. Network Providers are exploring new business models and pricing strategies to incorporate satellite services while addressing technical challenges like seamless handover and latency. These companies are actively navigating the regulatory landscape and ensuring compliance with relevant standards. Furthermore, they are evaluating their competitive strategies in this evolving market by differentiating their services and exploring potential collaborations to leverage this transformative technology effectively. For instance, Starlink aims to provide satellite internet connectivity to underserved and remote areas worldwide where internet access has traditionally been limited or nonexistent. SpaceX is looking for cell phone companies to work with on selling the services and is currently already working with T-Mobile (US), Rogers (Canada), KDDI (Japan), Optus (Australia), One NZ (New Zealand), and Salt (Switzerland).
Market Growth Enablers
- Lower Launch Costs: The emergence of reusable rockets and smaller satellites helps reduce satellite launch costs, making satellite deployments more economically feasible.
- Improved Ground Segment Technology: Advancements in ground station terminals, modems, and network management systems are making satellite communication more efficient and user-friendly.
- New Space Companies and Innovation: The rise of private space companies has brought innovation and competition to the satellite communication market, leading to new business models and service offerings.
- Government Initiatives: Governments worldwide recognize the strategic importance of satellite communication for national security, disaster relief, and economic development, leading to increased investments and supportive policies.
- Convergence with Terrestrial Networks: Satellite communication is being integrated with terrestrial networks (5G, fiber) to create hybrid solutions that offer enhanced coverage, resilience, and performance.
- In-Flight Connectivity (IFC): The growing demand for broadband internet access on aircraft is a major driver of the satellite communication market.
- Military and Defense Communications: Secure and reliable communication is critical for military operations, and satellites provide connectivity in challenging environments.
- Disaster Relief and Emergency Communications: Satellites can provide essential communication services in areas affected by natural disasters when terrestrial infrastructure is damaged.
- Maritime Connectivity: The maritime industry's demand for connectivity for vessel tracking, crew welfare, and operational efficiency is growing.
Market Inhibitors
- Infrastructure Costs: Establishing and maintaining satellite network infrastructure requires substantial investment. This can be a barrier to entry for new players and limit the deployment of new services.
- Spectrum Allocation and Licensing: Obtaining the necessary spectrum licenses and regulatory approvals can be complex and time-consuming, varying significantly across different countries.
- Orbital Slot Coordination: Securing orbital slots for satellites requires international coordination and can be challenging due to increasing space congestion.
- Data Security and Privacy Concerns: Ensuring the security and privacy of data transmitted via satellite is crucial, and regulations in this area are still evolving.
Space Debris: The increasing space debris threatens operational satellites and future missions. Sustainable practices in satellite deployment and disposal are becoming increasingly important.
Satellite Communication Market
Technology Overview
Satellite Communication Equipment Technologies
Software Defined Satellite
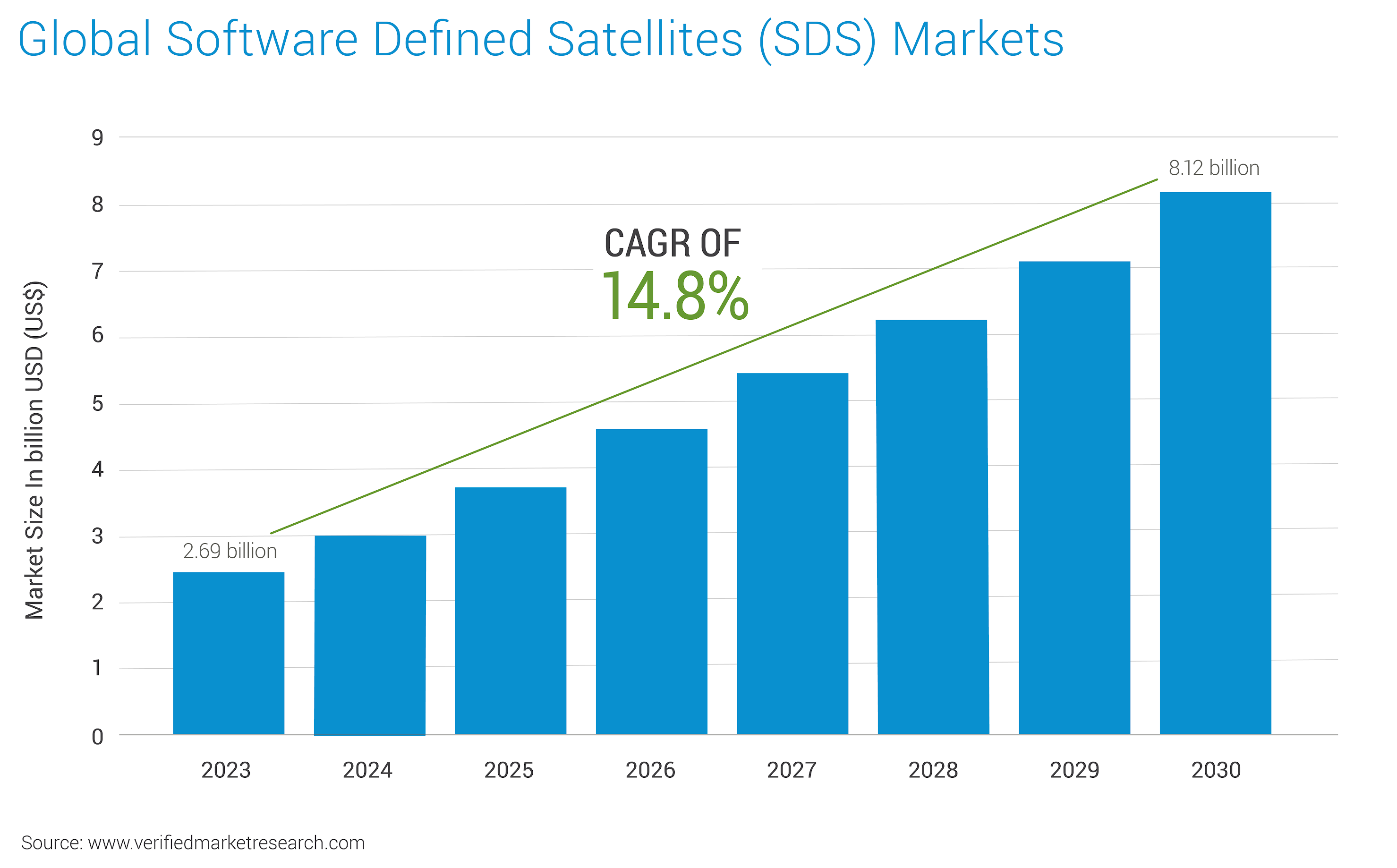
Software-defined satellite (SDS) technology represents a paradigm shift in satellite design and operation, bringing software-defined networking (SDN) flexibility and agility to space. Instead of relying on fixed, hardware-based functionalities, SDS enables satellites to be reprogrammed and reconfigured in orbit through software updates. This allows for greater adaptability, optimization, and longevity of satellite systems. According to a report published by Verified Market Research, the software-defined satellite market is expected to grow from $ 2.69Bn in 2023 to $ 8.12Bn in 2030 at a CAGR of 14.8%. The infographic below is derived from the same source.
Hybrid Satellite Networks
Hybrid satellite technology merges satellite and terrestrial networks (like 5G and fiber optics) to form a more capable communication system. This blend uses the strengths of both satellites for broad coverage and terrestrial networks for high capacity and low latency. User devices switch between the two based on availability, ensuring constant connectivity. This boosts overall network capacity and resilience, as each network can be a backup for the other. It extends coverage to remote areas lacking terrestrial infrastructure, bringing high-speed internet to underserved populations. This versatile solution enhances communication by combining the best of both worlds, bridging the digital divide, and enabling new applications.
IOT Connectivity
IoT connectivity for satellites refers to the ability of devices to communicate with and transmit data through satellite networks rather than relying solely on terrestrial infrastructure like cellular or Wi-Fi. This is crucial for enabling IoT applications in remote areas beyond the reach of traditional networks. Devices use specialized satellite communication modules to send data to orbiting satellites, which then relay the information to ground stations for processing and analysis. This technology allows for widespread coverage, supporting applications like environmental monitoring in remote regions, asset tracking across vast distances, and infrastructure monitoring in isolated locations. Satellite IoT connectivity offers a reliable and cost-effective solution for expanding the reach of the Internet of Things, bridging the connectivity gap, and enabling data collection from even the world's most remote corners.
High Throughput Satellites
High-throughput satellites (HTS) provide significantly more data capacity than traditional satellites. They achieve this through advanced technologies like frequency reuse and spot beams, which allow them to focus power and bandwidth on smaller, more targeted areas. This results in faster data speeds, lower latency, and improved overall performance. HTS satellites operate in higher frequency bands (like Ka-band) to provide more bandwidth, and they often employ multiple spot beams to cover a given area, enabling frequency reuse and increasing overall capacity. These advancements make HTS ideal for applications demanding high data rates, such as broadband internet access, in-flight connectivity, and cellular backhaul, particularly in underserved areas with limited terrestrial infrastructure.
Satellite Data Services
Satellite data services encompass valuable information obtained from Earth-observing satellites. These services provide a wealth of data about our planet, including imagery, environmental monitoring data, and location-based information. This data is used for various applications such as weather forecasting, environmental monitoring (e.g., deforestation tracking, pollution detection), disaster management, agriculture (e.g., crop monitoring, yield prediction), and urban planning. Satellite data services are instrumental in understanding Earth's systems, managing resources, and responding to natural disasters. They provide valuable insights for scientific research, governmental agencies, and commercial businesses, contributing to various fields and applications. According to Global Market Insights, the satellite data services market is expected to grow with a CAGR of more than 19% from 2023 to 2023. The infographic below is also derived from the same source.
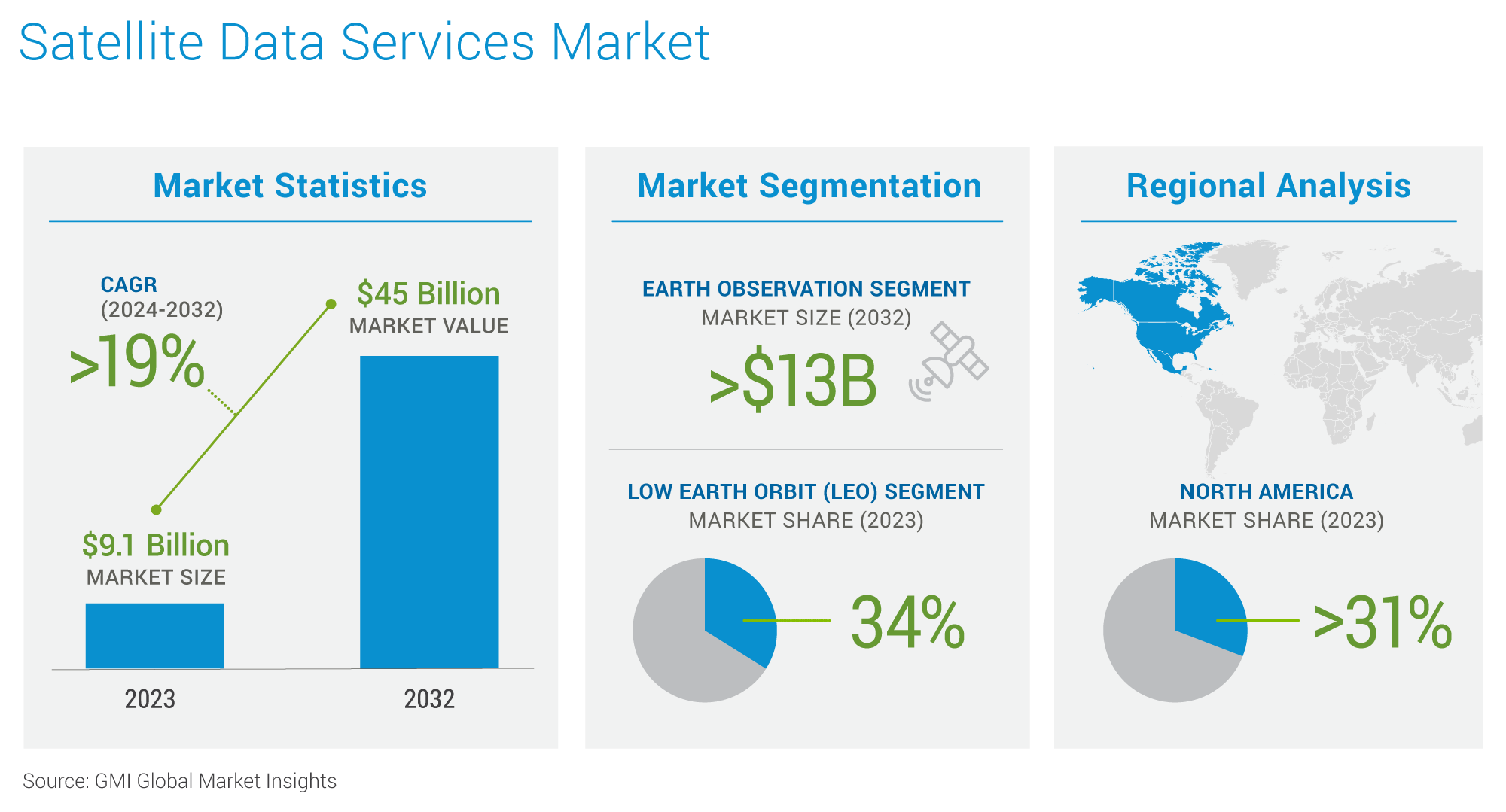
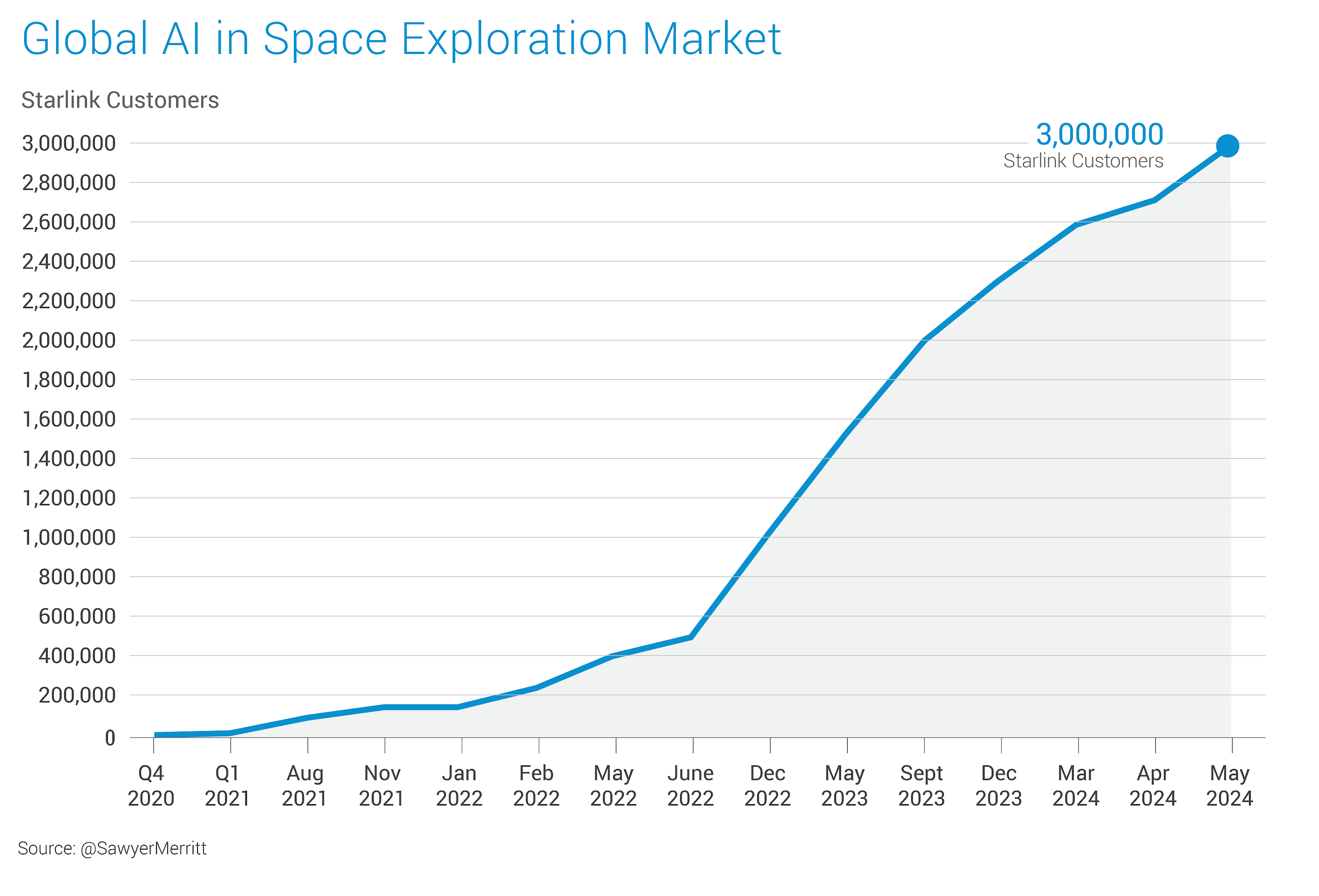
In May 2024, Starlink reached ~3 million customers in the Satellite Data Services business from more than 100 countries.
Emerging Technologies
AI & ML
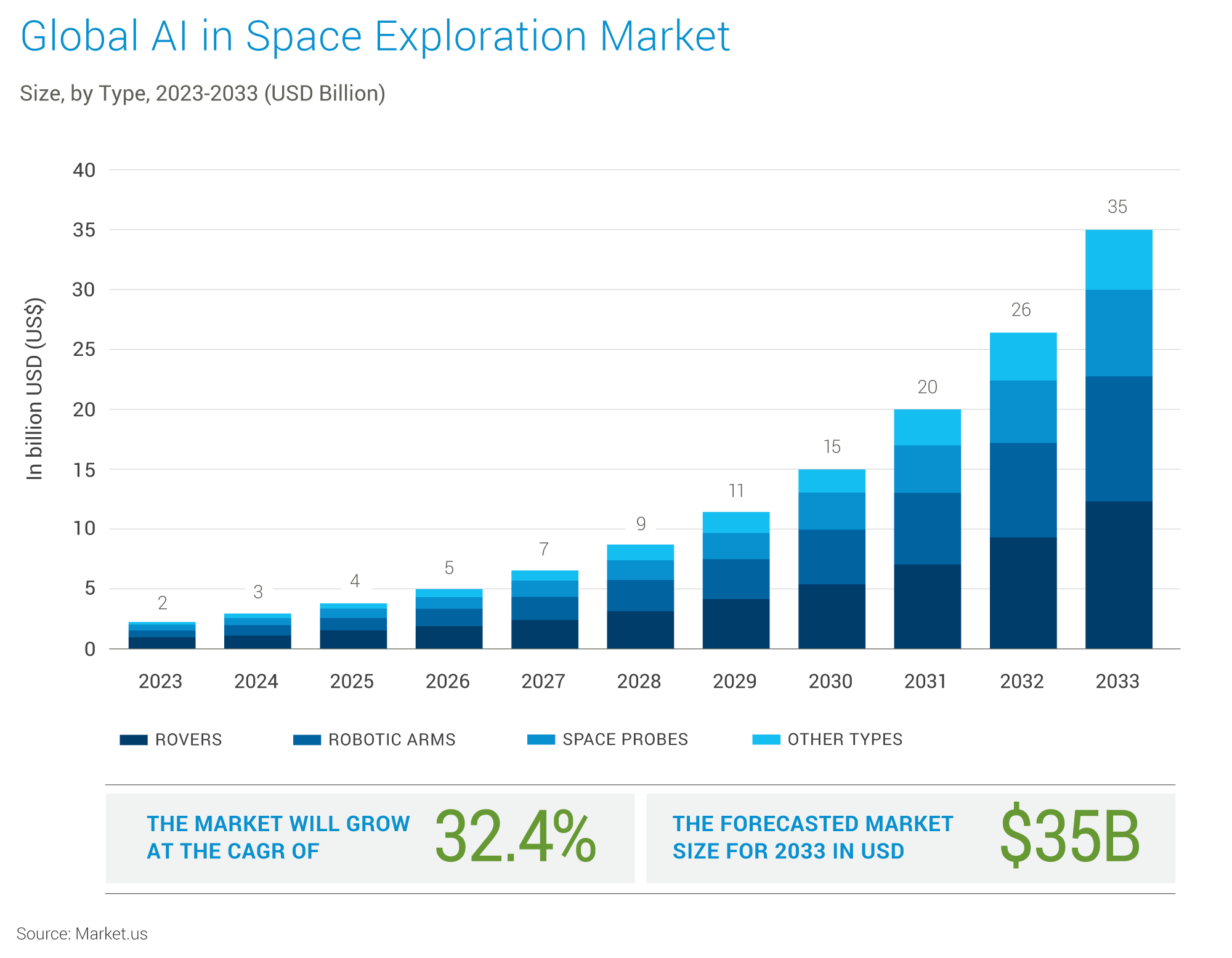
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) technologies are expected to play a transformative role in the evolution of SATCOM infrastructure, enhancing its efficiency, resilience, and capabilities. By leveraging the power of data analysis, automation, and intelligent decision-making, AI/ML can address many of the challenges facing the SATCOM industry and unlock new opportunities for innovation. According to Markets.us, the AI in Space Exploration market is expected to grow from ~$ 2Bn in 2023 to ~$ 35Bn in 20233. The infographic below is derived from the same source.
5G Technology
5G's demand for widespread connectivity and high data capacity fuels the need for satellite communication infrastructure. Satellites extend 5G coverage to remote areas, provide backhaul connections, and link the dense network of small cells required for high performance. Additionally, they enable 5G connectivity for ships and airplanes while offering crucial redundancy for terrestrial networks during outages. Essentially, 5G's ambitious goals are pushing the limits of terrestrial infrastructure, creating a significant opportunity for satellite communication to play a vital role in expanding coverage, enhancing capacity, and ensuring the resilience of next-generation networks.
Satellite Constellations
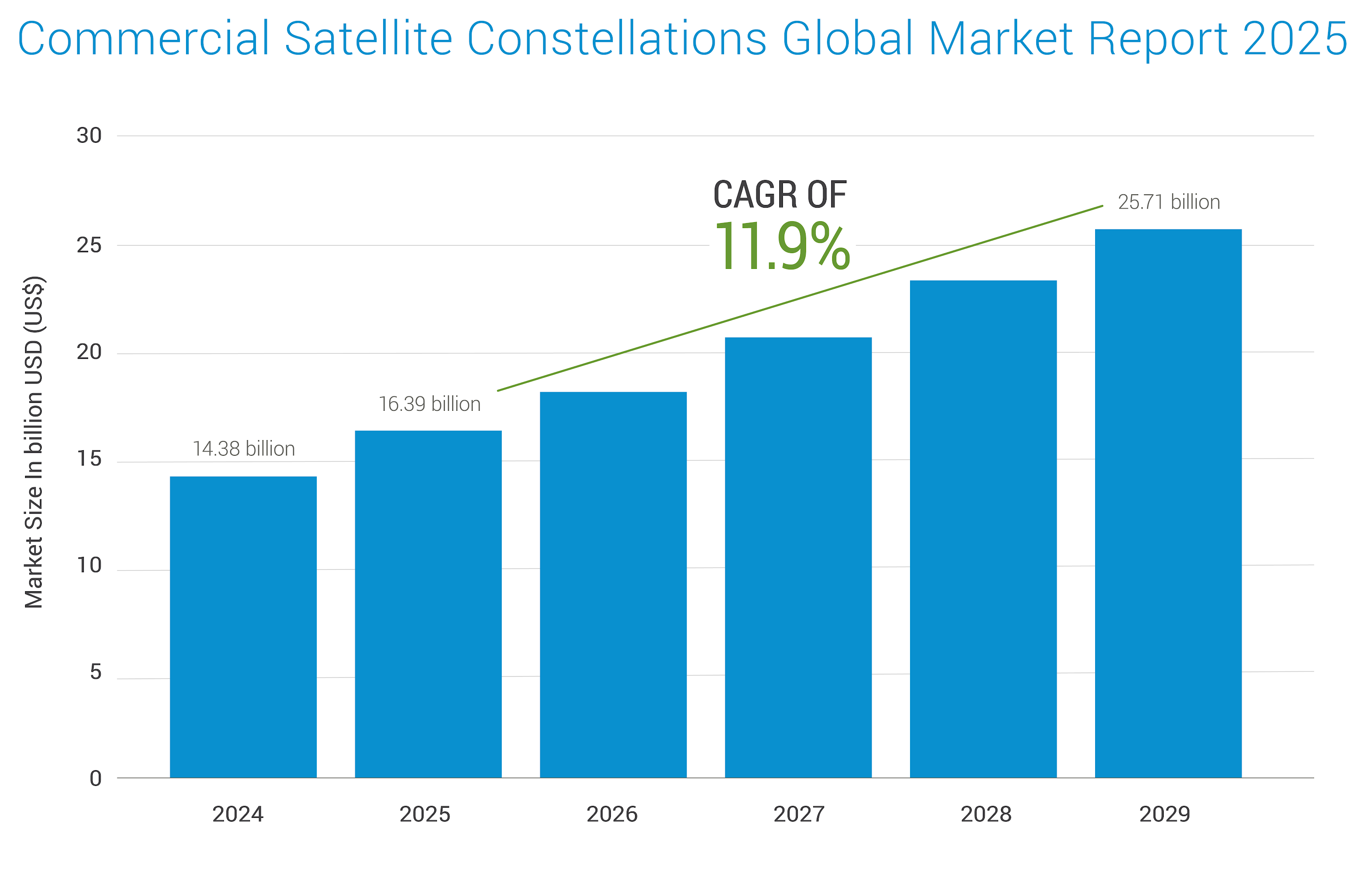
A satellite constellation is a network of multiple satellites working together in various orbits to provide continuous and comprehensive coverage of the Earth. Unlike singular satellite systems, constellations offer enhanced resilience through redundancy, increased capacity for data transmission, and reduced latency due to shorter distances between ground stations and orbiting satellites. This distributed architecture is essential for applications demanding global coverage and high bandwidth, such as navigation systems (e.g., GPS), Earth observation, and global communication networks. Furthermore, satellite constellations are increasingly vital for extending the reach of 5G and IoT technologies, enabling seamless connectivity and data transfer across even the most remote regions. According to Business Research Company, the commercial satellite constellations market is expected to grow from $ 16.39Bn in 2025 to $ 25.71Bn in 2029 at a CAGR of 11.9%. The infographic below is also derived from the same source.
Mobility & Connectivity on the Move
Connectivity on-the-move (COTM) technology ensures uninterrupted network access while traveling, enabling communication services regardless of location or mode of transport. This relies on satellite communication for wide-area coverage, cellular networks for high-speed connectivity in populated areas, and wireless technologies like Wi-Fi for local access. Network handover technology allows smooth transitions between these different networks, ensuring seamless connectivity. This is vital for various sectors, from transportation (cars, trains, and airplanes) to maritime (ships and boats) and even individual users with mobile devices, enhancing productivity, safety, and convenience.
Direct-to-cellular Technology
Direct-to-cellular service, also known as direct-to-cell, is a technology that allows mobile phones to connect directly to satellites in space for network connectivity, bypassing the need for traditional cell towers. This means cell service can even be accessed in remote areas where terrestrial cellular networks don't reach.
Examples:
|
Satellite Service Provider |
Direct-to-cellular Offering |
|
SpaceX (US) |
Starlink's goal is to deliver satellite-based internet to regions globally that have historically lacked reliable internet access. To achieve this, SpaceX is seeking partnerships with mobile network operators to facilitate the sale of its services. Current collaborators include T-Mobile in the United States, Rogers in Canada, KDDI in Japan, Optus in Australia, One NZ in New Zealand, and Salt in Switzerland. |
|
AST SpaceMobile (US) |
AST SpaceMobile is developing a unique, space-based cellular broadband network designed to connect directly with existing, unmodified mobile phones. Leveraging its extensive intellectual property, the company aims to bridge connectivity gaps for the billions of mobile users worldwide and to extend broadband access to those currently without it. |
|
Globalstar (US) + Apple Inc. (US) |
Apple's Emergency SOS via satellite feature enables iPhones to transmit brief text messages to emergency responders when traditional cellular and Wi-Fi networks are unavailable. This service, developed in collaboration with Globalstar, utilizes the L and S frequency bands designated for mobile satellite communications by the ITU Radio Regulations. When an iPhone user initiates an Emergency SOS request, the message is relayed by one of Globalstar's 24 low-earth orbit satellites to specialized ground stations located globally. |
Satellite Communication Market
Recent Developments
|
Date |
SATCOM Equipment Supplier/ Manufacturer |
End User (Company 2) |
Development Type |
Description |
Deal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Dec 2024 |
Viasat (US) |
US DoD |
Contract |
Viasat is set to contribute to the U.S. Department of Defense's (DoD) technology upgrades by providing a range of services. These include tactical networking, ground systems, satellite communications, and cybersecurity measures. |
$568Mn |
|
Dec 2024 |
Starlink (US) |
- |
Technology Development & Deployment |
SpaceX has successfully deployed 20 Starlink satellites, marking a milestone in its direct-to-cellphone connectivity initiative. This launch completes the initial orbital layer of the constellation, aimed at providing global cellular service. |
- |
|
Dec 2024 |
Starlink (US) |
- |
Business Expansion |
Starlink anticipates launching its satellite internet services in India, possibly starting in January of the coming year, contingent upon regulatory approvals. This follows the company's continued expansion of its global network through recent satellite deployments. |
- |
|
Dec 2024 |
Airbus Defence & Space (Germany) |
Eutelsat (France) |
Contract |
Eutelsat has contracted Airbus Defence and Space to construct a portion of its expanded OneWeb Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellite network. Airbus will produce the first 100 satellites for this expansion, with deliveries expected to begin in late 2026, ensuring continued and improved services for Eutelsat's clientele. |
- |
|
Dec 2024 |
Parsons Corporation (US) |
GlobalStar (US) |
Partnership |
Parsons Corporation and Globalstar have entered into an exclusive alliance to serve the public, government, and defense sectors. This collaboration has already demonstrated the effectiveness of Parsons' software-based satellite communication system operating on Globalstar's Low-Earth Orbit (LEO) satellite network. |
- |
|
Nov 2025 |
Telesat (Canada) |
SatixFt Communications Ltd, (US) |
Contract |
Telesat has contracted SatixFy Communications Ltd. to create and provide the ground station processing equipment for its Telesat Lightspeed Network. This new agreement tasks SatixFy with designing, developing, and delivering the baseband units required for the ground stations over a 28-month period. These systems will facilitate rapid and effective communication between Telesat Lightspeed's Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites and the ground infrastructure. |
$39Mn |
|
Oct 2024 |
Thales Alenia Space (France) |
European Space Agency (ESA) |
Contract |
The European Space Agency (ESA) has awarded Thales Alenia Space a contract valued at 107 million euros to produce six radar satellites for Italy's IRIDE Earth observation constellation. |
$111.38Mn (€107Mn) |
|
Oct 2024 |
ST Engineering (Singapore) |
PT Pasifik Satelit Nusantara (PSN) (Indonesia) |
Contract |
Following the successful initial phase, ST Engineering iDirect has been chosen to expand Indonesia’s Satria-1 satellite network in its second phase. The first phase involved deploying ST Engineering iDirect’s advanced hub infrastructure to provide connectivity throughout the Indonesian islands. The second phase will add 26 Gbps of capacity through new gateways located in Timika, Manokwari, and Jayapura. This expansion aims to significantly improve access to essential services, such as education and healthcare, reaching approximately 150,000 public service locations, including nearly 94,000 schools and 3,700 medical facilities. |
- |
|
May 2024 |
SKY Perfect JSAT (Japan) |
Thales Alenia Space (France) |
Contract |
A new agreement between SKY Perfect JSAT and Thales Alenia Space will result in the construction of JSAT-31, a state-of-the-art, software-defined satellite. Constructed using Thales Alenia Space's Space INSPIRE platform, JSAT-31 will operate in both Ka and Ku frequency bands. This high-throughput satellite is designed to deliver rapid broadband services across Japan, Southeast Asia, Australia, New Zealand, and the Pacific Islands. Set for launch in 2027, JSAT-31 will possess the hig hest capacity of any SKY Perfect JSAT satellite to date. |
- |
|
Mar 2024 |
Singtel (Singapore) |
- |
Development & Launch |
Singtel has introduced Paragon-S, a digital platform designed to aggregate and orchestrate satellite services. This platform aims to facilitate the digital transformation of satellite operators, enabling them to utilize cutting-edge digital technologies. Paragon-S allows satellite operators to provide edge computing capabilities to business clients who rely on satellite connectivity. This includes hosting vital applications, deploying on-site cloud solutions in remote locations, or establishing multi-tenant edge cloud infrastructures at operator-owned gateways. This flexibility enables businesses to dynamically shift applications between the satellite operator's edge cloud and public clouds, based on their evolving operational needs. |
- |
Source: Company Website & Press Releases
Satellite Communication Market
Supply Chain Overview
Demand Overview
The demand for satellite communication equipment is experiencing robust growth, driven by the increasing need for global connectivity. Key drivers include expanding broadband internet to remote areas, the rising adoption of IoT devices, and the growing need for in-flight and maritime connectivity. High-throughput satellites (HTS) and the deployment of LEO constellations are significantly increasing demand for advanced ground segment equipment. Military and defense sectors also contribute significantly due to their need for secure and reliable communication. However, high initial costs and competition from terrestrial networks present challenges. Despite this, advancements like software-defined satellites and the integration of AI/ML are fueling innovation and further driving demand, particularly for next-generation user terminals and ground station components. The market is thus expected to see continued growth in the coming years.
Supply Analysis
The supply side of the satellite communication equipment market is characterized by a mix of established aerospace and defense companies alongside emerging New Space players. Key manufacturers are investing heavily in R&D to meet the growing demand for advanced technologies like HTS components and software-defined platforms. The supply chain involves specialized component manufacturers, system integrators, and launch service providers. However, the industry faces challenges such as long lead times for specialized components, limited manufacturing capacity for certain advanced technologies, and the complexities of export control regulations. Supply chain disruptions, such as those caused by geopolitical events or global pandemics, can further impact availability. Despite these issues, the entry of new manufacturers, particularly in the small satellite segment, is increasing competition and gradually improving supply. The industry is also moving towards more standardized and modular designs to streamline production and reduce costs.
Satellite Communication Market
Jabil Insights
Jabil Insights
The satellite communication market is experiencing rapid growth, accelerated by advancements in satellite technology, such as high-throughput and low-earth orbit satellites. The market offers significant opportunities, particularly in bridging the digital divide by providing broadband internet access to underserved communities, expanding 5G networks, and developing new applications like disaster management.
Demand for connectivity in remote areas is increasing, with satellite technology bridging the digital divide. The rise of the Internet of Things and autonomous systems, which rely heavily on satellite communication, further fuel market expansion. The integration of satellite communication with 5G networks is revolutionizing mobile connectivity, promising a future of enhanced communication capabilities.
Lead Times
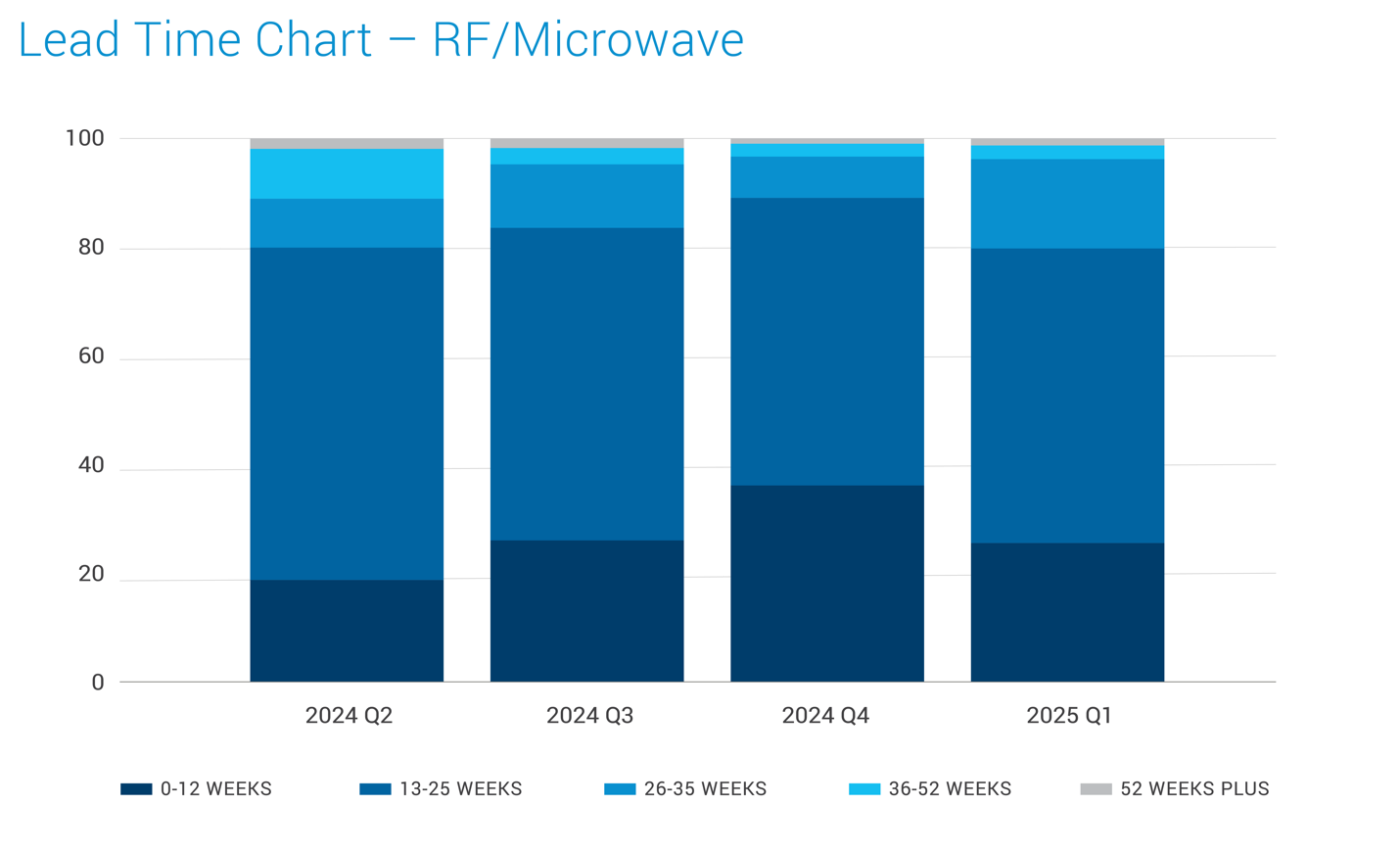
Create with Datawrapper
Note 1: The lead time trends are for the broader market across industries.
Note 2: You can Refer to Jabil’s Commodity & Mechanicals Intelligence Reports for extended lead time charts
Jabil Spend Analysis
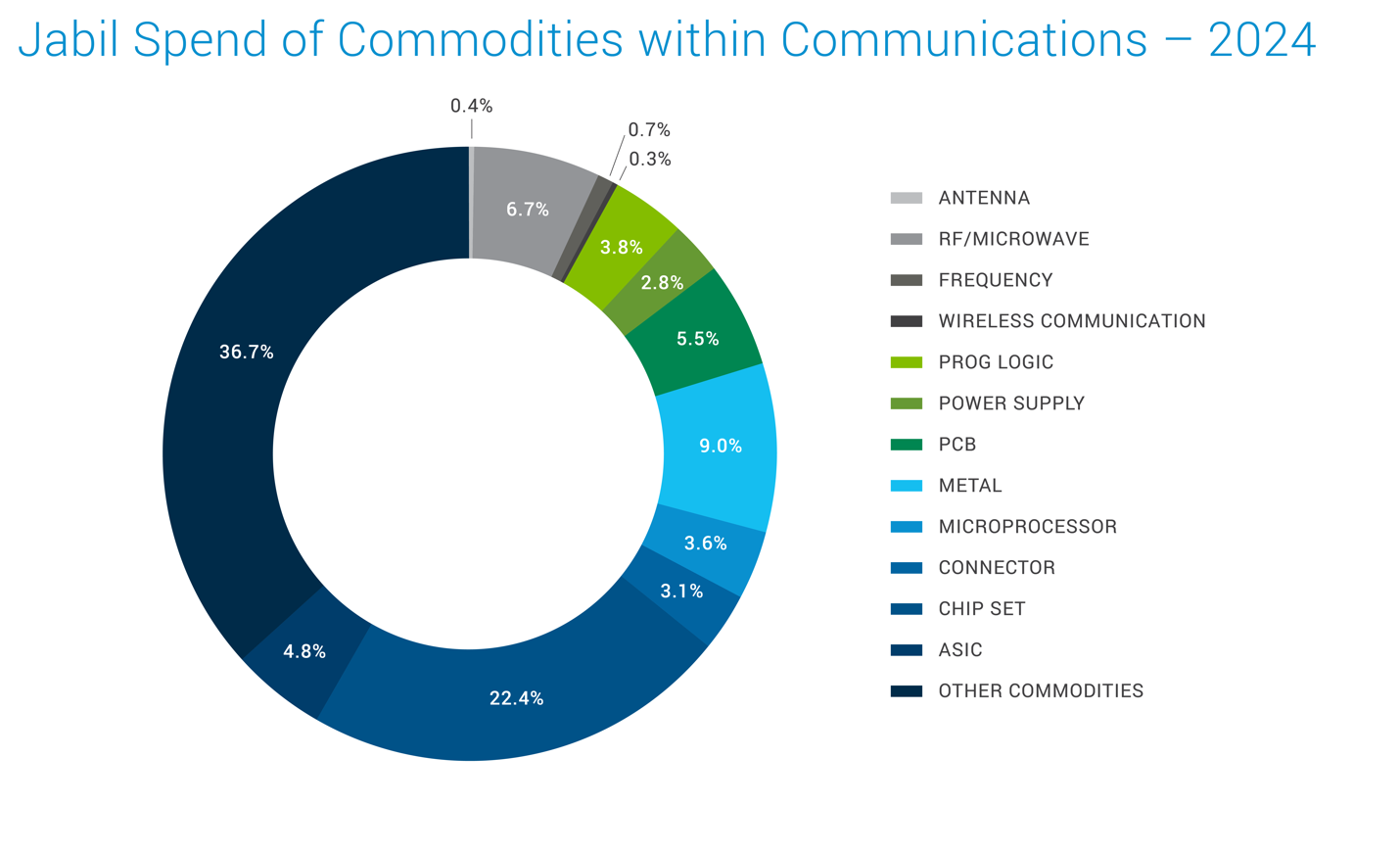
Note: The above spend data is for the broader market across the communication industry.
Back to Top
