By clicking the “I Accept” button, or by accessing, participating, or submitting any information, or using the Jabil Global Intelligence Portal or any of its associated software, you warrant that you are duly authorized to accept the Global Intelligence Portal Terms and Conditions on behalf of your Company, intending to be legally bound hereby, and your company shall be bound by the terms and provisions of the Global Intelligence Portal Terms and Conditions, accessible under the following link Portal T&Cs.
Sector Market Report
Energy
Sector Market Report
Energy
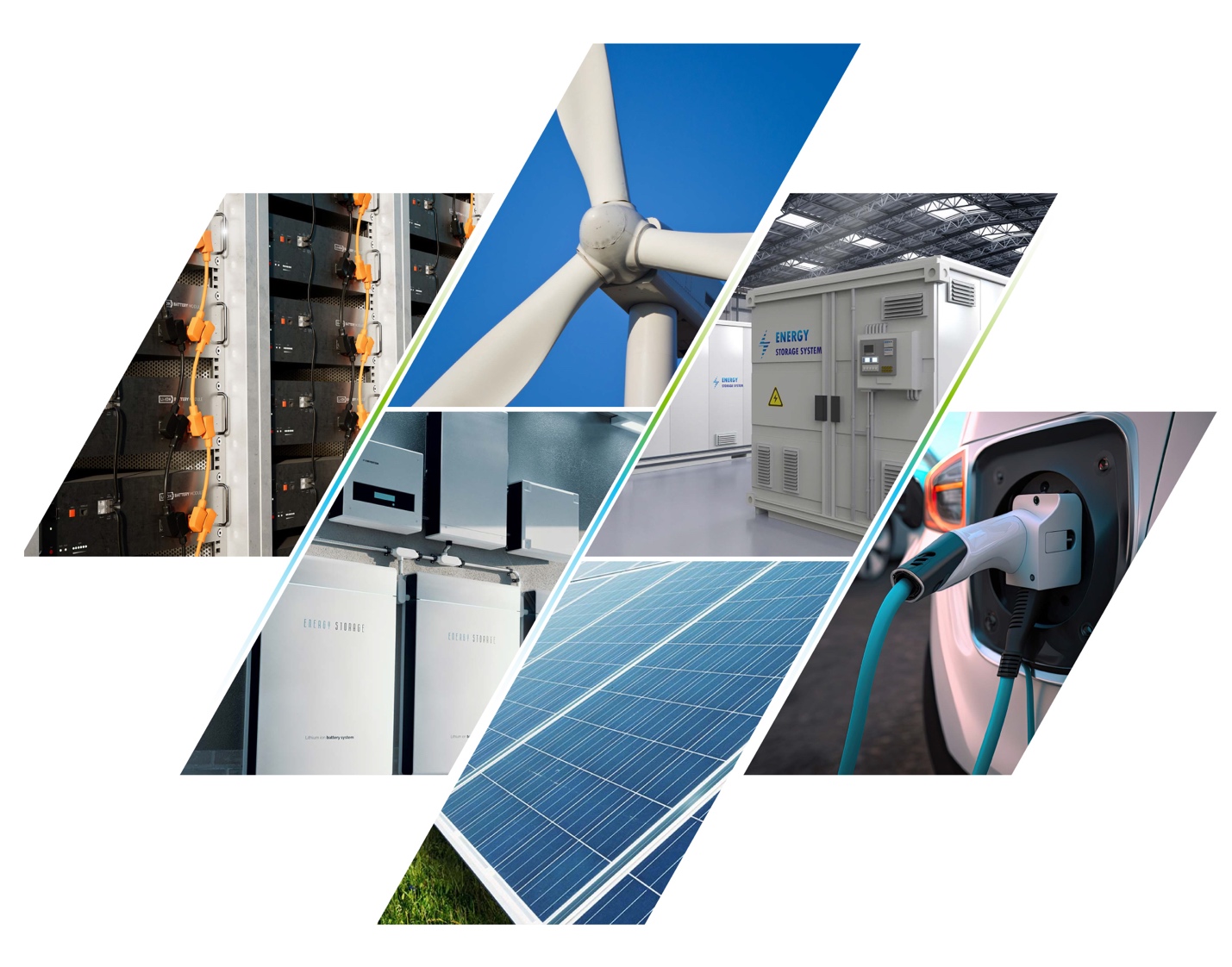
Get an in-depth look at the energy industry's transition to renewable energy, focusing on wind and solar energy growth, energy storage systems, and electric vehicle charging.
Energy Market
Overview
The Energy and Renewables Market update analyzes the industry's sustainable transition, delving into the growth of wind and solar energy, the development of energy storage systems, and the proliferation of electric vehicle charging.
The report covers the existing landscape and challenges, rapidly evolving market dynamics, supply chain, competitive landscape, technology evolution, and the global legislative and regulatory ecosystem.
The report is a strategic tool offering insights and recommendations for stakeholders in the energy and renewables sector. It highlights the opportunities and risks associated with the global energy transformation, providing insights and analysis to support informed decision-making.
Energy Market
Introduction
The energy sector is rapidly transforming, driven by environmental concerns, policy changes, and economic factors. This transition propels a surge in renewable energy, with solar and wind leading the way. The International Energy Agency (IEA) reports a staggering 507 gigawatts (GW) of additional renewable electricity capacity added in 2023 alone.
Despite progress, significant hurdles remain. Limited investment in developing economies hinders the widespread adoption of clean energy solutions. Additionally, integrating variable renewable sources like solar and wind necessitates robust Energy Storage Systems (ESS) to ensure grid stability.
Despite current headwinds in the United States, the global ESS market is expected to grow at a 14% annual growth rate and is projected to reach $32 billion by 2030. Grid-scale lithium-ion batteries currently dominate the space (Frost and Sullivan). Advancements in battery technology, energy management systems, and grid integration are crucial for enhancing ESS efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Key Sectors Driving the Change:
- Energy Storage Systems (ESS): It is critical for grid stability with renewables and plays a role in the EV market. Companies like Fluence, Sungrow, Wartsila, and Tesla are at the forefront, but new players are emerging.
- Renewable Energy Sources:
- Solar Photovoltaic (PV): The global solar PV market is expected to reach $286 billion by 2030, driven by falling costs, government incentives, and the EV boom. Some of the Leaders in the market include SolarEdge, Sungrow, and Enphase. Companies with solutions integrating solar PV with battery storage and EV charging are well-positioned.
- Wind Energy: The wind energy industry is projected to double its market value by 2030, with offshore wind farms experiencing a surge. Vestas, Siemens Gamesa, and GE Renewable Energy are the few players who are leading this revolution. Supply chain considerations like raw material scarcity and manufacturing capacity constraints must be addressed.
The Road Ahead
Achieving net-zero emissions will require continued technological advancements, supportive policies, and investments in infrastructure development. We can expect groundbreaking innovations in energy storage, renewable energy generation, and grid modernization, paving the way for a cleaner and more sustainable future.

Energy Market
Market Overview
The energy sector is undergoing a significant transformation driven by increasing demand, renewable energy expansion, and the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs). This market overview breaks down the key factors influencing the growth of renewable infrastructure, energy storage systems (ESS), EV charging infrastructure, and the markets for lithium-ion batteries, renewable energy, solar, and wind industries.
Global Energy Demand & Renewable Energy Expansion
According to the IEA’s World Energy Outlook, global energy demand will rise by 18% by 2030, with renewable energy accounting for 50% of power generation. Expansion of renewable infrastructure, particularly wind and solar, is essential to meet this demand.
The global energy landscape is significantly transforming as we approach the third decade of the 21st century. The IEA projects that by 2030, the world’s energy demand will surge by 18%. The relentless advance of industrialization, urbanization, and the economic ascent of emerging nations is propelling this increase.
The IEA forecasts a significant shift towards clean energy, with renewables accounting for nearly half of the world's electricity generation by 2030 under current policies. This means that within the next decade, with existing policies in place, renewable sources like solar and wind will be responsible for producing almost 50% of the electricity used globally.
The IEA also predicts a substantial increase in global energy demand by 2050, with renewables leading the way in this growth. This looks further into the future, suggesting that worldwide energy will rise by nearly 50% by 2050. Importantly, renewables are projected to be the main driver of this rise, replacing fossil fuels and fulfilling this growing energy need more sustainably.
Rising energy demands and climate concerns drive a global shift towards renewable energy, particularly wind and solar power. Technological advancements have made these options more cost-effective, offering a promising future for sustainable energy. However, integrating these variable sources requires robust Energy Storage Systems (ESS) to ensure grid stability. Lithium-ion batteries are the current leader in ESS technology, but research continues to explore long-term solutions.
The rise of electric vehicles further increases the need for ESS, particularly at decentralized locations. Upgrading grid infrastructure is essential, but immediate ESS implementation can help manage the load during the transition.
The global renewable energy market is booming, with solar photovoltaics (PV) expected to reach $286 billion by 2030, led by the Asia-Pacific region. Wind energy is also experiencing significant growth, with both onshore and offshore installations expanding.
The Renewables Market in Asia-Pacific
The Asia-Pacific region has firmly established itself as a global solar power market powerhouse. According to analysts, in 2023, it accounted for over 65% of the world's solar PV installed capacity.
- China: China saw the most significant growth, commissioning the same volumes of solar PV in 2023 as the world did a year earlier, while the country’s wind power additions increased by 66% year-on-year. China boasted an astounding 394 GW of installed solar capacity by the end of 2022. In 2023 alone, the country added 210 GW, representing over 60% of the world’s newly added capacity.
- China's vast land area and dominance in PV panel manufacturing contribute to its remarkable achievements.
- Renewables capacity is set to continue its upward trajectory over the next five years. Solar PV and wind power installations are expected to account for 96% of new capacity over the period, with additions predicted to double by 2028 compared to 2022 levels, reaching almost 710 GW.
- India: Not to be outdone, India surged forward, surpassing 81 GW of solar capacity in 2023 (adding 25 GW that year alone). Driven by the ambitious Jawaharlal Nehru National Solar Mission (JNNSM) and substantial investments, India is a rising star in the solar arena.
- Japan: Spurred by the Fukushima disaster, Japan reached approximately 90 GW of installed solar capacity by the end of 2023. Generous feed-in tariffs initially fueled its growth.
- Australia: Down Under, rooftop solar installations have soared, with over 3.60 million installations by the end of 2023, adding 3.8 GW of capacity that year. Thanks to falling installation costs and rising electricity prices, nearly 21% of Australian households harness solar energy.
- South Korea: Demonstrating dedication to clean energy, South Korea aims to increase its renewable energy share to 30-35% by 2040. Solar power plays a pivotal role in achieving these targets.
The Asia-Pacific solar photovoltaic (PV) market is on an upward trajectory, fueled by innovation, investment, and a commitment to cleaner energy. As solar capacity soars, the region's contribution to global sustainability becomes increasingly significant.
The market is projected to reach USD 2,738.9 billion by 2032, up from USD 349.6 billion in 2023, at a CAGR of 25.7% from 2024 to 2032. The market size is also expected to grow at a CAGR of 10.22% between 2023 and 2029. The declining cost of solar PV module prices and growing distributed solar power generation drive this industry's remarkable growth. The future shines bright as the Asia-Pacific region harnesses the sun's power to illuminate a sustainable tomorrow.
The Renewables Market in EMEA
Renewable Energy Market Surge in the EMEA (Europe, Middle East, and Africa) region stands at the forefront of the renewable energy revolution. With solar PV leading the charge and wind returning, the path to a sustainable, cleaner energy future is well-lit. Policymakers, investors, and innovators are collaborating to ensure that the sun and wind power our tomorrows.
Unprecedented Growth in Renewable Capacity:
In 2023, global renewable capacity is set to rise by 107 gigawatts (GW)—the most significant increase on record. This surge catapulted the total renewable capacity to over 440 GW, equivalent to more than Germany's and Spain's installed power capacity.
Expanding policy support, growing energy security concerns, and improved competitiveness against fossil fuels are driving growth. Despite challenges like rising interest rates, higher investment costs, and supply chain disruptions, renewables are gaining ground.
Solar Photovoltaic (PV):
- Energy Security and Affordability: European policymakers actively seek alternatives to imported fossil fuels. The recent surge in electricity prices caused by the global energy crisis has intensified this quest. Solar PV, primararily residential and commercial systems, provides a rapid solution to the growing demand for renewable energy. These smaller distributed PV applications are on track to account for half of this year's overall solar PV deployment—surpassing the total deployment of onshore wind.
- As an important note, the war in Ukraine has had a significant impact on energy prices in Europe:
- Russia is a significant supplier of natural gas to Europe. Since the war began, sanctions and disruptions have limited gas flow, causing shortages and price hikes.
- The geopolitical situation creates uncertainty in the energy market, leading to speculation and further price volatility.
- As an important note, the war in Ukraine has had a significant impact on energy prices in Europe:
- Onshore Wind: Solar PV takes the spotlight, but onshore wind is no wallflower. After two consecutive years of decline, onshore wind capacity additions are poised to rebound by 70% in 2023, reaching a record of 107 GW. The commissioning of delayed projects in China and faster expansion in Europe and the United States contributes to this resurgence.
- Offshore Wind: the majestic turbines that harness the ocean's breath. While offshore wind growth won't match the record expansion achieved two years ago, it remains a vital player. Challenges outside of China limit the volume of projects under construction, but the winds of change persist.
Outlook for 2024
Solar PV Continues: Declining module prices, greater adoption of distributed solar PV systems, and unwavering policy support drive higher annual solar capacity additions across major markets like China, the European Union, the United States, and India.
Wind Challenges: On the wind front, without rapid policy implementation, the Global Wind Energy Council expects global onshore wind additions in 2024 to decline by around 5% from 2023 levels. China's wind energy additions will rise, but undersubscribed auctions and permitting delays in Europe may offset this growth.
The EMEA region embraces renewable energy fervently, and the sun is at the heart of this transformation. Let's explore the key highlights:
- Unprecedented Growth in Renewable Capacity:
- In 2023, global renewable capacity additions are set to soar by 107 GW, the most significant increase ever recorded.
- The EMEA region contributes significantly, pushing the total renewable capacity to over 440 GW—equivalent to Germany and Spain's installed power capacity.
- Solar Photovoltaic (PV) Dominance:
- Solar PV capacity steals the spotlight, accounting for two-thirds of this year's global renewable capacity increase.
- Policymakers seek alternatives to imported fossil fuels, making solar PV—especially distributed systems—a rapid solution.
- Onshore Wind Rebounds:
- After two years of decline, onshore wind capacity additions rebounded by 70% in 2023, reaching a record of 107 GW.
- Offshore wind, though not matching previous records, remains crucial.
- Outlook for 2024: Solar PV continues to shine, driven by falling module prices and policy support. Wind faces challenges, but China's wind energy additions rise.
The Renewables Market in the Americas
The Americas are experiencing a significant expansion in renewable energy deployment. This growth is driven by a confluence of factors, including:
- Abundant natural resources: The Americas boast significant wind, solar, geothermal, and hydropower potential across the continent.
- Supportive policies: Governments across the Americas increasingly implement policies that incentivize renewable energy development, such as tax breaks, feed-in tariffs, and renewable energy targets.
- Falling technology costs: Technological advancements have significantly reduced the cost of renewable energy technologies, making them more cost-competitive with traditional fossil fuels.
- Environmental concerns: Growing awareness of climate change drives a shift towards cleaner energy sources.
The United States is a leader in the renewable energy sector, boasting the world's second-largest installed capacity. Wind, solar, and hydropower are the leading renewable sources in the US, with wind and solar surpassing hydropower as the primary source of renewable electricity generation in 2019 and 2024, respectively.
Canada offers a stable market for renewable energy investment, with a well-established sector that prioritizes grid integration. Notably, Canada is the world's third-largest producer of hydroelectricity, providing a clean and reliable baseload for its energy grid.
Latin America is emerging as a critical player in the global energy transition. Blessed with abundant renewable resources and falling technology costs, the region is witnessing a surge in clean energy development. Brazil, one of the regional leaders, boasts the most extensive installed renewable capacity, dominated by hydropower. However, Brazil is actively expanding its wind and solar power generation. Costa Rica is one of the global leaders in renewable energy adoption, generating over 98% of its electricity from renewables in 2023.
Mexico, Colombia, and Argentina represent emerging markets with significant potential for renewable energy development. These countries possess abundant solar and wind resources, and ongoing regulatory reforms are expected to accelerate renewable energy adoption further.
Challenges remain in fully integrating renewable energy sources into the grid across the Americas. Grid modernization and upgrades to transmission infrastructure are necessary to ensure seamless integration of variable renewable sources like solar and wind. Additionally, innovative financing solutions are needed to address potential funding gaps for renewable energy projects.
Despite these challenges, the Americas are well-positioned to become a major global renewable energy market force. With abundant resources, supportive policies, and continued technological advancements, the region is on track for a future powered by clean energy sources.
Market Growth Enablers
Government Initiatives
Government policies and incentives play a pivotal role in accelerating the adoption of renewable energy by creating a favorable market environment and reducing financial barriers. These measures aim to stimulate investment, innovation, and deployment of renewable energy technologies.
One common policy tool is the implementation of Renewable Portfolio Standards (RPS), which mandate that a certain percentage of electricity generation must come from renewable sources. For example, California has set an ambitious target of achieving 100% clean electricity by 2045, driving utilities to invest in solar and wind power. Additionally, tax credits, such as the Investment Tax Credit (ITC) in the United States, offer financial incentives to businesses and individuals investing in renewable energy systems. This has spurred the growth of rooftop solar installations across the country. Other incentives include feed-in tariffs, which guarantee a fixed price for electricity generated from renewable sources, providing long-term revenue stability for project developers.
Environmental Concerns
Heightened environmental concerns, particularly climate change and air pollution, have driven the global shift towards renewable energy. Burning fossil fuels for electricity generation and transportation is a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, which are the primary cause of global warming. Renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, offer a clean alternative as they produce minimal to no emissions during operation.
The detrimental health impacts of air pollution, caused by particulate matter and other pollutants released from fossil fuel combustion, have further fueled the urgency to transition to renewable energy. Smog-filled cities and rising rates of respiratory diseases have underscored the need for cleaner air. In response, governments and communities increasingly embrace renewable energy to mitigate climate change, improve air quality, and protect public health. For instance, China, a nation grappling with severe air pollution, has become the world's largest investor in renewable energy, aiming to reduce its reliance on coal and improve environmental conditions.
Energy Security
Energy security, the reliable access to affordable energy sources, has become a paramount concern for nations worldwide. The volatility of fossil fuel prices and geopolitical tensions in regions rich in oil and gas reserves can disrupt energy supplies and create economic instability. Renewable, domestically available, and inexhaustible energy sources offer a pathway to enhanced energy security.
Countries can insulate themselves from price shocks and supply disruptions by diversifying the energy mix and reducing reliance on fossil fuel imports. For instance, Germany, aiming to phase out nuclear power and reduce its dependence on Russian gas, has invested heavily in solar and wind power, bolstering its energy security. Similarly, many island nations vulnerable to fuel import disruptions turn to solar and wind energy to achieve energy independence and resilience. Renewable energy enhances national security and empowers local communities by generating jobs and fostering economic development.
Corporate Sustainability Goals
The growing emphasis on corporate sustainability has emerged as a significant driver in the renewable energy market. As businesses face increasing pressure from investors, consumers, and employees to address their environmental impact, many are setting ambitious sustainability goals, including reducing carbon emissions and transitioning to renewable energy sources.
For example, tech giant Google has committed to operating on 24/7 carbon-free energy by 2030, investing heavily in renewable energy projects and innovative technologies. Retail giant Amazon has pledged to reach net-zero carbon emissions by 2040, investing in large-scale solar and wind farms to power its operations. These commitments and similar initiatives by countless other companies are creating a substantial demand for renewable energy. Furthermore, companies recognize that investing in renewable energy can reduce their carbon footprint, provide long-term cost savings, and enhance their brand image.
Market Growth Enablers
Transmission and Distribution Challenges
Renewable energy sources are often located in remote areas with abundant sunlight or wind, far from population centers with high electricity demand. This necessitates the construction of extensive transmission lines to transport the generated power, which can be expensive and encounter regulatory hurdles. For instance, offshore wind farms require undersea cables to connect to the mainland grid, adding complexity and cost to the project.
Moreover, the existing grid infrastructure, primarily designed for centralized fossil fuel power plants, may not be equipped to handle the variable nature of renewable energy generation. This can lead to grid congestion and instability, necessitating upgrades and investments in smart grid technologies to optimize power flow and maintain grid reliability.
High Upfront Costs
Renewable energy projects, especially large-scale solar and wind farms, require significant upfront investments in equipment, land acquisition, permitting, and construction. While the operational costs of renewable energy are relatively low, the initial capital outlay can deter potential investors and developers. For example, developing a utility-scale solar project can cost hundreds of millions of dollars, making it difficult to secure financing, especially in developing countries with limited access to capital.
However, the cost of renewable energy technologies has declined rapidly in recent years, making them increasingly competitive with fossil fuels. Government incentives, such as tax credits and grants, can also help to offset upfront costs and attract investment in the sector.
Intermittency and Grid Integration
Solar and wind power are inherently intermittent, meaning their output varies depending on weather conditions. This variability challenges grid operators to balance supply and demand in real-time to maintain grid stability. For example, a sudden drop in wind speed can cause a significant decrease in power generation, potentially leading to blackouts if not properly managed.
Integrating intermittent renewable energy sources requires advanced forecasting tools, flexible generation resources, and energy storage solutions. Battery storage systems, pumped hydro storage, and demand response programs are some technologies that can help mitigate the intermittency challenge and ensure a reliable power supply.
Materials and Supply Chain Constraints
The production of renewable energy technologies, such as solar panels, wind turbines, and batteries, requires various raw materials, including rare earth metals, lithium, and other critical minerals. The demand for these materials is growing rapidly, raising concerns about their availability, price volatility, and potential geopolitical risks associated with their supply chains. For example, China dominates the global production of rare earth metals, essential components of wind turbines and electric vehicles.
To address these challenges, efforts are underway to diversify supply chains, develop alternative materials, and improve recycling and reuse practices. This includes investing in domestic mining and processing capabilities, exploring new sources of critical minerals, and developing innovative technologies that reduce or eliminate the need for scarce materials.
Workforce Development
The rapid growth of the renewable energy sector is creating a surge in demand for skilled workers in various fields, including engineering, construction, installation, operation, and maintenance. However, there is a shortage of qualified professionals with the necessary expertise to meet this demand. This skills gap can hinder deploying renewable energy projects and increase costs.
To address this challenge, governments, educational institutions, and industry stakeholders must invest in training and education programs to develop a skilled workforce. This includes promoting STEM education, providing apprenticeships and on-the-job training, and establishing certification programs to validate skills and knowledge in the renewable energy sector.
Cybersecurity Risks
As renewable energy systems become more integrated into the grid and rely on digital technologies for monitoring, control, and communication, they become vulnerable to cyberattacks. Hackers could disrupt power generation, steal sensitive data, or cause physical damage to equipment. These risks can undermine the reliability and security of the energy system, potentially leading to blackouts and other disruptions.
Renewable energy developers and operators need to implement robust security measures, such as encryption, firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and regular security audits, to mitigate cybersecurity risks. Collaboration between government agencies, industry stakeholders, and cybersecurity experts is crucial to developing comprehensive strategies to protect critical energy infrastructure from cyber threats.
Use Case Analysis
Use Cases: Solar Energy
|
Owner |
Country (Location) |
Status |
Key Features |
|
Adani Green Energy |
India (Rajasthan) |
Fully Operational |
World's largest solar-wind hybrid power plant (2.24 GW) |
|
ACWA Power |
UAE (Dubai) |
Fully Operational |
World's largest single-site solar park (5 GW) |
|
Huanghe Hydropower Development |
China (Qinghai Province) |
Fully Operational |
World's largest solar power plant by area (16 million solar panels) |
|
Sun Cable |
Australia (Northern Territory) |
Under Development |
Planned to be the world's largest solar farm and battery storage facility (10 GW) |
|
SolarReserve |
Australia (South Australia) |
Under Development |
Planned to be world's largest solar thermal power plant with molten salt storage (150 MW) |
Note: Reference links for each development are listed in the Appendix Section
Use Cases: Wind Energy
|
Owner/Developer |
Country (Location) |
Status |
Key Features |
|
Orsted |
UK (North Sea) |
Fully Operational |
World's largest offshore wind farm (1.3 GW capacity) |
|
SSE Renewables |
UK (Scotland) |
Fully Operational |
World's largest floating offshore wind farm (50 MW capacity) |
|
Dogger Bank Wind Farm |
UK (North Sea) |
Under Development |
Expected to be the world's largest offshore wind farm upon completion (3.6 GW capacity) |
|
GE Renewable Energy |
China (Gansu Province) |
Fully Operational |
World's largest single onshore wind farm (7.5 GW capacity) |
|
Vineyard Wind |
USA (Massachusetts) |
Under Development |
First commercial-scale offshore wind farm in the US (800 MW capacity) |
Note: Reference links for each development are listed in the Appendix Section
Use Cases: Energy Storage System Installment
|
Owner/Operator |
Country (Location) |
Technology |
Capacity (MWh) |
Status |
Key Features |
|
Vistra Energy |
USA (California) |
Lithium-ion battery |
400 |
Operational |
World's largest battery energy storage system (BESS) at the time of completion |
|
Neoen |
Australia (Geelong) |
Lithium-ion battery |
450 |
Under Development |
Expected to be one of the largest BESS in the Southern Hemisphere |
|
Fluence |
USA (California) |
Lithium-ion battery |
400 |
Operational |
Part of a larger project to support grid reliability and integrate renewable energy |
|
Hydrostor |
Canada (Ontario) |
Compressed air energy storage (CAES) |
1,600 |
Operational |
World's first commercial Advanced CAES facility, using excess electricity to compress air into underground caverns |
Note: Reference links for each development are listed in the Appendix Section
Energy Market
Supply Chain
The supply chain is the backbone of the renewable energy sector, enabling the development, production, and deployment of clean energy solutions. However, this complex system faces challenges that must be addressed to ensure a sustainable and resilient future.
Critical Stages
- Raw Materials: Securely sourcing raw materials for renewables (metals, minerals, rare earths) is critical, considering availability, responsible practices, and environmental impact.
- Manufacturing: Building renewable components needs a strong, spread-out manufacturing base. Raw material shortages, transport issues, or political tensions can disrupt this.
- Transportation and Logistics: Delivering oversized and often delicate components, particularly for offshore wind farms, requires complex logistics strategies. Trade policies, infrastructure limitations, and potential disruptions further complicate this stage.
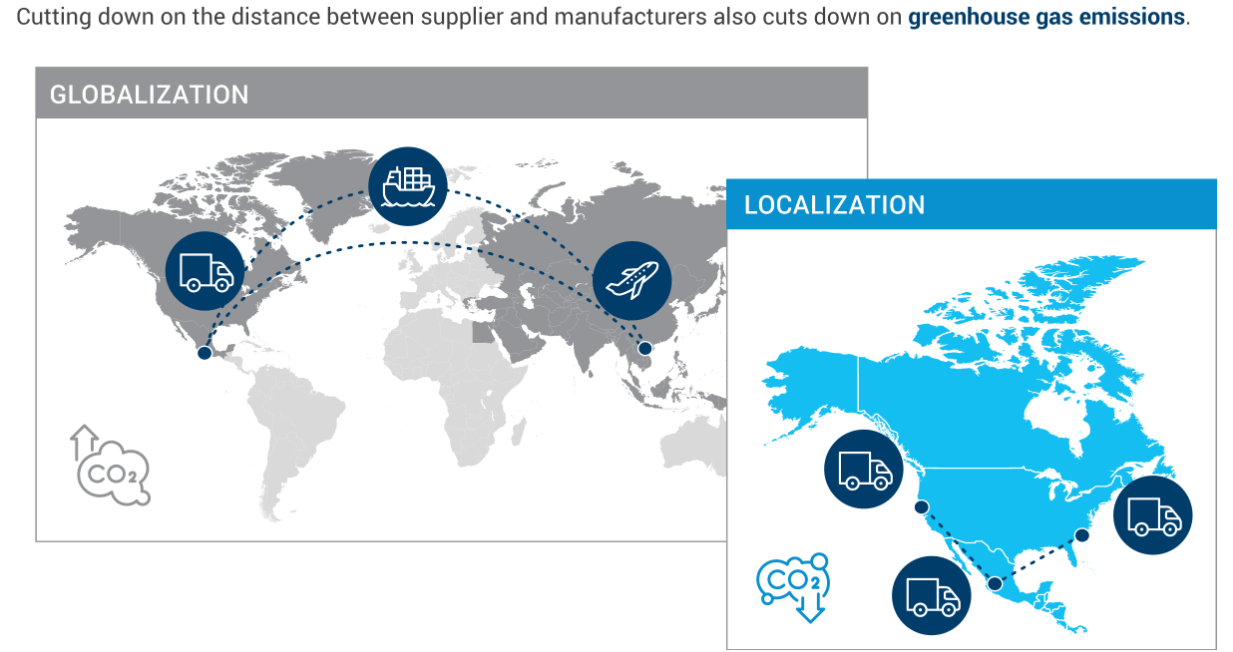
- Localization: Economic incentives and sustainability concerns drive a shift towards localized manufacturing in certain regions, reducing reliance on long-distance transportation.
- Recycling and End-of-Life Management: As the renewable energy sector grows, responsible disposal and resource recovery become essential. Developing a circular economy for materials like lithium and cobalt is critical.
- Workforce and Skills: These new technologies require a skilled workforce to deploy, maintain, and operate. Addressing skills gaps and training programs is crucial for long-term success.
Spotlight on Lithium-Ion Batteries
While dominant in energy storage and electric vehicles, lithium-ion batteries may not be enough to achieve net-zero emissions targets. Research into alternative battery technologies remains crucial. The market for lithium-ion batteries is projected to grow significantly, driven by factors like:
- Electric Vehicle Transition: Government regulations, consumer demand, and technological advancements are pushing the shift towards electric vehicles.
- Renewable Energy Integration: Energy storage solutions are essential to manage the intermittency of renewable energy sources like solar and wind.
- Sustainability Commitments: Corporations and governments aim to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change.
Spotlight on Lithium-Ion Batteries
- Supply Chain Constraints: Accessing critical raw materials like lithium and cobalt is essential for battery production scalability and cost control.
- Technological Limitations: Battery performance needs to improve in energy density, cycle life, and safety to become sustainable and cost-effective.
- Standardization and Regulations: Clear and consistent regulations across regions can streamline production, reduce costs, and boost consumer confidence.
- Innovation: Advancements in battery technology can unlock new applications and improve performance across the board.
- Investment and Policy Support: Government policies encouraging research and development, incentivizing battery production and adoption, and supporting charging infrastructure are crucial for market growth.
OEMs’ Carbon Footprint Reduction due to Localization
Source: Secondary Research
Planning and deploying an onshore wind farm typically require around 24 months. This includes the production and delivery of components alongside the assembly and installation at the site. In addition to the supply of components, wind farm implementation also requires infrastructure, a skilled workforce, and regulatory approval. In such a complex dynamic, several disruptions can be prevented by moving the supply chain closer to manufacturing sites in desired end markets.
Wind energy OEMs and their manufacturing partners are still navigating component shortages and quality issues from the sub-supply chain. The industry felt the impacts of the initial COVID-19 control measures, labor shortages, and supply-demand imbalances — primarily semiconductors and printed circuit boards (PCBs), many of which were reallocated to high-demand industries.
Besides the availability of components, additional challenges in the wind energy supply chain have been pricing and quality. Prices for metals—including steel, copper, and aluminum—have increased exponentially since the beginning of 2020, driving up costs for parts like structural components (towers, castings, and internal steel parts) and bus bars and cables. This requires a strategic approach and purchasing power to minimize the impact.
In 2017, wind OEMs and suppliers joined forces to establish Advanced Product Quality Planning for Wind (APQP4Wind) to manage quality issues. Like its automotive predecessor, APQP4Wind is a framework of procedures and techniques for developing and manufacturing wind turbines to eliminate cost-production errors and reduce LCOE. These standards provide a preventative approach to quality and are being implemented further down the wind energy sub-supply chain.
For wind energy OEMs and their suppliers, building resilience is the key to overcoming supply chain challenges. Localization is one way to do that. Leveraging the knowledge and expertise of supply chain teams already embedded in manufacturing sites can help scale production and avoid installation challenges.
People, processes, and technologies can find and minimize the at-risk areas of this highly specialized supply chain while maximizing efficiencies along the way.
Proprietary and marketplace intelligence, optimizing specialized equipment and expertise, and expanding approved vendor lists can help grow the supply chain while accelerating the time-to-market of new turbine equipment and protecting wind energy supply chains from disruptions and fluctuations.
The Road Ahead
The rapid expansion of renewables, advancements in energy storage, and the rise of electric vehicles are transforming the energy landscape. To achieve ambitious climate goals, all sectors must accelerate growth through continued investment in R&D, supportive government policies, and international collaboration that fosters responsible sourcing and efficient supply chains. By addressing these challenges and capitalizing on opportunities, a cleaner, more sustainable future is within reach.
Impact of AI on Supply Chain
In the face of a complex and disrupted global supply chain, artificial intelligence (AI) is a powerful tool for streamlining operations and enhancing efficiency. Jabil’s 2024 Supply Chain Resilience Survey showed that nearly 200 supply chain and procurement decision-makers from some of the world’s leading product brands are planning for and already using AI in their day-to-day processes. The insights provided by the participants highlight key best practices for successfully integrating AI within our supply chain operations.
- The surge in AI applications within supply chain management largely concentrates on enhancing demand planning and inventory management. By leveraging predictive analytics, organizations aim to improve forecasting accuracy and efficiency, optimize resource distribution, and address the imbalance between supply and demand.
- A "data-first" mentality is critical for harnessing AI's full potential in supply chain operations. Success hinges on establishing a robust data management infrastructure and governance framework before deploying AI tools. This foundation ensures data reliability and fosters meaningful insights, underscoring the importance of collaboration and data sharing among stakeholders.
- Preparing the workforce for AI integration involves addressing potential concerns about job displacement and emphasizing AI's role in augmenting human skills. By providing training and hands-on experience with AI technologies, companies can facilitate a smooth transition towards more automated and efficient supply chain processes.
“China+1” Strategy for Global Supply Chains
The "China+1" strategy, increasingly adopted by global entities in the renewable energy sector, is a response to diversify manufacturing and reduce dependency on China due to various risks, including geopolitical tensions, supply chain disruptions, and rising costs. This strategy pushes component suppliers in solar panels, wind turbines, energy storage systems, and other renewable technologies sectors to explore investment opportunities outside China, notably in regions like South Asia and Mexico.
Countries like India and Vietnam are becoming significant beneficiaries of this strategy. With its robust growth in renewable energy component manufacturing, India is positioned as a global hub, drawing interest due to its improving technology implementation and capacity for high-volume production. This shift addresses the de-risking of supply chains and taps into India's substantial renewable energy market, which has seen growth in domestic installations and exports.
Similarly, Vietnam has made considerable developments, especially focusing on enhancing infrastructure to support increased manufacturing demands in the renewable energy sector. This includes the development of industrial zones and logistics networks, which are essential for bolstering their role in global supply chains.
Moreover, Mexico is emerging as a crucial player due to its proximity to the US, the largest renewable energy market, and its capacity to manufacture multiple renewable energy products locally, which is attractive for nearshoring strategies.
The China+1 strategy in the renewable energy sector has the potential to mitigate risk and leverage the technological and manufacturing strengths in alternate destinations, fostering a more resilient and diversified global supply chain landscape.
Geopolitical Tensions and Supply Chain Realignment
The renewable energy industry faces increased complexity and risk due to heightened geopolitical tensions, particularly between major technology-producing nations. These tensions have led to stricter trade policies, tariffs, and restrictions on technology transfers, significantly impacting the global supply chain of renewable energy components and materials.
In response, companies in the renewable energy sector are urgently reassessing and realigning their supply chains to reduce dependency on regions with high geopolitical risks. This includes diversifying sourcing and manufacturing locations to more geopolitically stable or neutral countries and friend-shoring or nearshoring critical components to areas with similar regulatory and political frameworks. This strategic shift aims to safeguard access to essential materials and components, such as rare earth metals for wind turbines, polysilicon for solar panels, and advanced semiconductors for inverters and power electronics, pivotal for developing renewable energy infrastructure.
Moreover, companies increasingly invest in technology and infrastructure to enhance supply chain visibility and resilience, enabling more agile responses to future geopolitical shifts. This includes utilizing blockchain technology for transparent material tracking, implementing predictive analytics to identify potential disruptions, and establishing strategic stockpiles of critical components.
The geopolitical landscape is expected to remain complex and unpredictable in the foreseeable future. Therefore, companies in the renewable energy sector must continue to adapt and innovate their supply chain strategies to ensure the uninterrupted flow of essential components and materials, supporting the global transition to clean energy.
Legal & Regulatory Landscape
The global energy and storage market is undergoing a significant transformation driven by climate change concerns, energy security considerations, and technological advancements.
Governments worldwide are heavily influencing the energy and renewables market by implementing laws and regulations to promote clean energy adoption, efficiency improvements, and the development of energy storage solutions.
Importance of Understanding Legal & Regulatory Landscape
By understanding the regulatory landscape in different regions, companies can identify emerging markets for renewable energy technologies and energy storage solutions.
Companies can gain a competitive edge in the energy and storage market by using the legal and regulatory information around strategic sourcing, supply chain resilience, and cost optimization.
Strategic sourcing involves recognizing new market openings by comprehending regulatory landscapes across diverse regions. This understanding aids in spotting emerging markets for renewable energy and storage technologies. Additionally, it facilitates selecting suppliers responsible and compliant with regulations, thus mitigating risks associated with ethical sourcing practices and potential future regulatory issues. Companies can use this information to leverage knowledge of government incentives, such as tax credits, to strengthen their negotiating position with suppliers, potentially securing better pricing.
Supply chain resilience proactively manages risks by anticipating and mitigating disruptions resulting from regulatory changes. This can include diversifying suppliers across different regions or investing in alternative technologies that are less impacted by regulatory changes. Furthermore, it involves future-proofing procurement strategies by adapting them to comply with upcoming regulations, such as the EU Green Deal, through sustainable sourcing and meeting energy standards.
Cost optimization entails identifying opportunities to reduce procurement costs, often by leveraging government subsidies and tax credits for clean energy technologies. Additionally, companies must consider long-term cost implications, such as potential disposal costs associated with battery recycling regulations. Understanding these regulations enables informed decision-making, leading to better lifecycle cost management.
Ultimately, data-driven decisions aligned with regulations lead to more sustainable and future-proof sourcing strategies.
Role of Government Policies
Supportive government policies will significantly impact market growth across all regions. In Asia, China's generous EV subsidies have been instrumental in propelling EV sales and fostering a robust domestic EV industry. Similarly, the EU's ambitious electrification targets and investments in charging infrastructure are creating a favorable environment for DCFC deployment in EMEA. The Americas have implemented policy frameworks to incentivize EV adoption and infrastructure development, including tax credits for vehicle purchases and substantial investments like the National Electric Vehicle Infrastructure (NEVI) program and the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law. However, challenges in execution and implementation have slowed progress. For instance, as of July 2024, only a small fraction of planned charging stations have been deployed under the NEVI program, highlighting the need for improved efficiency and coordination to realize the potential of these initiatives and accelerate the transition to electric mobility in the region.
Asia: Regulatory Impacts and Outlook
The regulations impacting the sector across Asia, EMEA, and the Americas include:
China
14th Five-Year Plan (2021-2025): This national economic and social development plan prioritizes green development and sets ambitious targets for renewable energy deployment and storage development.
New Energy Vehicle (NEV) Policy: China's supportive policies for electric vehicles have spurred significant EV adoption and created a robust market for battery storage.
India
National Solar Mission (2010): This ambitious program aims to achieve India's large-scale grid-connected solar power capacity. It has significantly driven the growth of the country's solar energy market.
Storage Policy Framework (2020): This framework aims to promote the development of the energy storage market in India by establishing guidelines for grid integration of storage systems and tariff mechanisms.
Japan
Feed-in Tariff (FIT) Scheme: Japan's FIT scheme incentivizes renewable energy generation by offering fixed prices for electricity produced from renewable sources. This has contributed to the country's growth in the renewable energy market.
Strategic Energy Plan (2021): This plan outlines Japan's long-term energy goals, including targets for renewable energy deployment and energy storage development.
Asia: Regulatory Impacts and Outlook
European Union (EU)
Fit for 55 Package (2021): This ambitious package of EU regulations aims to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 55% by 2030 compared to 1990. It includes targets for renewable energy deployment, energy efficiency improvements, and emissions trading.
REPowerEU Plan (2022): This plan outlines strategies to reduce reliance on Russian fossil fuels and accelerate the transition towards clean energy. It includes measures to diversify energy supplies, invest in renewable energy sources, and develop energy storage solutions.
EU Battery Directive (2006) & Battery Regulations (2020): These regulations aim to ensure the EU's sustainable production, use, and disposal of batteries. This is crucial for the development of the energy storage market.
Middle East
Several Middle Eastern countries have ambitious renewable energy targets and are investing in solar and wind energy projects to diversify their energy mix and reduce dependence on oil. However, the regulatory frameworks for energy storage are still under development in most countries.
Africa
Renewable energy is rising prominently in Africa, driven by increasing energy demand, falling renewable energy costs, and supportive policies from some countries. However, regulatory frameworks and grid infrastructure development need improvement to unlock Africa's energy storage market's potential fully.
The Americas: Regulatory Impacts and Outlook
United States
New Biden Tariffs (2024): President Biden has instructed his Trade Representative to raise tariffs under Section 301 of the Trade Act of 1974 on $18 billion worth of imports from China. This measure aims to safeguard American workers and businesses.
- The tariff rate on electric vehicles under Section 301 will increase from 25% to 100% in 2024.
- The tariff rate on lithium-ion EV batteries will increase from 7.5%% to 25% in 2024, while the tariff rate on lithium-ion non-EV batteries will increase from 7.5% to 25% in 2026. The tariff rate on battery parts will increase from 7.5% to 25% in 2024.
- The natural graphite and permanent magnets tariff rate will increase from zero to 25% in 2026. The tariff rate for other critical minerals will increase from zero to 25% in 2024.
- The tariff rate on solar cells (whether or not assembled into modules) will increase from 25% to 50% in 2024.
Inflation Reduction Act (2022): This landmark legislation allocates significant funding for clean energy technologies, including tax credits for renewable energy projects, battery storage, and electric vehicles. This is expected to drive significant growth in the energy storage market.
New Electric Vehicle Initiative (2021): The $5 billion NEVI Formula Program is part of the $1.2 trillion Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA), which was signed into law in November 2021. IIJA commits significant federal funding to clean transportation and energy programs throughout the U.S. to reduce climate-changing greenhouse gas emissions.
Clean Power Plan (2015): While the previous administration repealed this regulation, which aimed to reduce carbon emissions from power plants, individual states have implemented their clean energy standards, promoting renewable energy adoption.
Investment Tax Credit (ITC) and Production Tax Credit (PTC): These federal tax credits incentivize the development of renewable energy projects, including solar and wind energy
Canada
Canadian Net-Zero Emissions Roadmap (2021): This ambitious plan outlines strategies to achieve net-zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050. It includes targets for renewable energy deployment and investments in clean energy technologies.
Carbon Pricing: Canada has implemented a carbon pricing scheme that puts a price on carbon pollution, incentivizing industries to reduce emissions and invest in clean energy solutions.
Latin America
Many Latin American countries have established renewable energy targets and policies promoting clean energy generation. Examples include auctions for renewable energy projects and net metering programs for distributed generation.
Regulatory frameworks in some countries still evolve, creating uncertainties for investors of energy and storage.
Energy Market
Technology Evolution
The energy industry faces a technological hurdle as it integrates more renewables into the grid. Solar and wind, while plentiful, are variable resources with fluctuating output. To bridge this gap, robust energy storage solutions are crucial. Batteries have emerged as a key technology, with large-scale systems capable of storing excess renewable energy and releasing it when demand is high. Battery technology continues to evolve, offering a wider range of capacities suitable for various applications. Residential systems typically have a capacity of around 5-10 kW, while utility-scale deployments can reach hundreds of megawatts. However, maximizing renewable integration requires advancements beyond just storage capacity. Research into different battery chemistries and energy storage technologies like flow batteries and compressed air energy storage (CAES) also hold promise for a more versatile renewable energy future.
Advancements in Battery Technology
Batteries, with a power range from 10 kW to 150 MW or more and discharge capabilities spanning minutes to hours, are pivotal to tackling both issues effectively. However, overcoming the technological challenges discussed above is essential for ensuring their long-term viability and widespread adoption. Continued research, development, and innovation in battery technology are key to a clean and sustainable energy future.
- Endurance: The Achilles' heel of many battery chemistries is their cycle life, or the number of charge-discharge cycles they can withstand before degrading. Lithium-ion batteries, currently dominating the market, offer a decent cycle life but fall short of large-scale, long-duration energy storage needs. The quest for "grid-scale batteries" with significantly longer lifespans is a top priority for researchers, with technologies like sodium-ion and lithium iron phosphate (LFP) showing promise.
- Energy Density: Packing a bigger punch in a smaller package is crucial for maximizing storage capacity and minimizing footprint. While lithium-ion batteries offer a good balance of energy density and power density (the rate at which they can deliver or absorb energy), pushing the boundaries can come at a cost. High-density batteries often translate to faster degradation and potential safety concerns. Finding the sweet spot between energy density, cycle life, and safety remains a key challenge.
- Cost: The upfront cost of battery storage systems is a significant barrier to broader adoption. While lithium-ion prices have dropped significantly in recent years, further reductions are needed to make them truly competitive with traditional generation sources. This necessitates advancements in material science, manufacturing processes, and innovative recycling technologies to create a more circular battery economy.
- Safety: Thermal runaway, a phenomenon in which a battery cell suffers a catastrophic overheating event, is a major safety concern. While lithium-ion batteries are generally safe when used properly, incidents can occur, particularly with lower-quality cells or those nearing the end of their lifespan. Research into inherently safer battery chemistries and robust thermal management systems is crucial to alleviate these concerns.
- Environmental Impact: Battery production and disposal have an ecological footprint that cannot be ignored. Mining the raw materials used in lithium-ion batteries can have ecological consequences. Additionally, end-of-life batteries pose a potential environmental hazard if not disposed of responsibly. Developing sustainable sourcing practices, closed-loop recycling processes, and exploring alternative battery chemistries with less environmentally harmful materials are all vital considerations.
Lithium-Ion Dominance and Chemistry Innovations
Lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) dominate the market and are employed in diverse applications, from smartphones to electric vehicles. However, there's an ongoing drive for enhanced power density and safety, leading to the rise of alternatives such as lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries. Despite offering improved safety and power densities, LiFePO4 cells trade off energy density.
Alternate Battery Solutions
While lithium-ion batteries currently dominate the market, there is an ongoing pursuit of alternative chemistries that may address existing limitations. For instance, sodium-ion batteries present the advantage of utilizing abundant and geographically diverse raw materials. Redox flow batteries hold promise for large-scale, long-duration storage due to their inherent scalability. Compressed air energy storage (CAES) and pumped hydro storage represent established technologies with unique advantages but require specific geographical conditions for deployment. Evaluating and optimizing these and other emerging technologies will be critical to creating a more robust and versatile energy storage toolbox.
Emerging Disruptors and Standardization Efforts: Disruptors explore alternative chemistries like graphene-oxide, sodium-sulfur, sodium-chloride, and metal-air batteries. While each presents unique strengths and weaknesses, lithium-ion cells encompass the most sought-after characteristics. Lithium-ion cell manufacturers advocate for standardized battery cells, streamlining production for the cylindrical, pouch, or prismatic cells to simplify supply chains.
Interoperability and Supply Chain Flexibility: Energy storage system (ESS) customers increasingly seek interoperability, preferring control over battery cell selection throughout their products. This has led to a shift towards ESS OEMs designing and building their modules capable of using cells from multiple manufacturers. Such a model offers cost control and bolsters supply chain resilience.
Diversifying Energy Storage Solutions: Beyond lithium-ion, technologies like flow batteries, supercapacitors, compressed air, flywheel, and superconducting magnetic energy storage systems are explored for specialized applications. Hydrogen emerges as a potential storage mechanism, though significant breakthroughs have yet to emerge.
Technological Advancements in Wind Turbines
Technological advancements in the wind energy industry aim to increase turbine power ratings and annual energy production (AEP). Onshore turbines have seen rating increases from 3 to 5 MW, with further growth anticipated to 6 to 8 MW by 2025. Offshore turbines are on a similar trajectory, with capacities rising from 8 to 15 MW.
Digitalization and Value Chain Evolution
Digitalization enhances precision in harnessing wind energy, with AI and ML optimizing turbine performance. As the wind energy value chain evolves, OEMs and independent service providers (ISPs) offer wind farms a wider array of services. Startups and specialist service providers (SSPs) are disrupting the industry by providing cheaper components.
Direct Current (DC) Fast Charging
DC Fast Charging is a technology that enables rapid charging of electric vehicles using a direct-current electrical supply. Unlike regular charging stations that use alternating current (AC) and require on-board conversion to DC within the vehicle, DC Fast Charging bypasses this step, significantly reducing charging times.
While challenges exist, the market rapidly evolves, offering exciting opportunities for energy market stakeholders.
Benefits of DC Fast Charging
- Faster Charging Times: DC Fast Charging can recharge an EV battery up to 80% within 30 minutes, compared to several hours for AC Level 2 charging. This significantly improves user experience and encourages EV adoption by addressing range anxiety, a concern for potential EV owners.
- Increased EV Adoption: Faster charging times make EVs more practical and convenient, potentially leading to a rise in EV ownership and a corresponding decrease in reliance on fossil fuels.
- Grid Integration: DC Fast Charging stations can contribute to grid stability by providing ancillary services. For example, they could help manage peak demand by intelligently charging EVs during off-peak hours and discharging electricity back to the grid during peak hours.
DC Fast Charging: Challenges
- Cost: DC Fast Charging stations are more expensive to install and maintain than AC charging stations.
- Standardization: Multiple charging connector standards exist, creating compatibility issues for EVs. While efforts are underway to create a universal standard, three main players exist today:
- CCS (Combined Charging System): Major European and American automakers, such as Volkswagen Group, General Motors, and Ford, support this system.
- CHAdeMO: Primarily used by Japanese automakers like Nissan and Mitsubishi.
- Tesla Supercharger: This proprietary network was exclusive to Tesla vehicles until May 2024. For instance, Select Tesla Superchargers have opened access to non-Tesla EVs meeting certain requirements. By the end of 2024, at least 7,500 chargers will be available for all EVs, with at least 3,500 being 250 kW chargers located along highway corridors.
- Grid Infrastructure: Integrating DC Fast Charging with the existing grid infrastructure may require upgrades to accommodate the high-power demands, including transmission and distribution line upgrades, transformer upgrades, and/or stationary ESS to support the DC chargers during operation. In addition, multiple standards increase the complexity and cost of deploying DCFC infrastructure. Operators need to consider compatibility with various standards, potentially slowing down the rollout of charging stations.
- Limited Availability: The number of DC Fast Charging stations remains significantly lower than that of AC charging stations. However, the market is rapidly expanding.
DC Fast Charging: Market Trends
- Rapid growth in the DC Fast Charging market is expected due to increasing EV adoption and government incentives.
- Technological advancements are leading to faster charging times and more powerful charging stations.
- Standardization Efforts: Ongoing efforts exist to establish a universal DCFC standard. Industry collaborations and government regulations promoting a single standard can significantly improve user experience and accelerate DCFC infrastructure development.
- Emerging Technologies: The emergence of technologies like the Combined Charging System Combo 1 (CCS1) connector offers promise for a more unified approach. Widespread adoption of such standards can streamline the market and benefit all stakeholders.
- Investment in grid infrastructure upgrades is expected to facilitate wider deployment of DC Fast Charging stations.
Market Prospects for DC Fast Charging: A Deep Dive Across the World
The global DC Fast Charging (DCFC) market is poised for explosive growth, fueled by various factors. At the core lies the surging adoption of electric vehicles (EVs). All regions – the Americas, EMEA (Europe, Middle East, Africa), and Asia – will significantly rise in road EVs, driving the need for a robust DCFC infrastructure. However, the pace of adoption will vary:
- Asia is forecasted to be the frontrunner, propelled by strong government incentives for EV purchases and the presence of established EV manufacturers like BYD and Tesla. These factors have created a thriving EV ecosystem in Asia, fostering consumer confidence and accelerating the transition towards electric mobility.
- EMEA: Following closely behind Asia, the EMEA region is experiencing a surge in EV adoption fueled by supportive government policies and growing consumer interest in EVs. The European Union (EU) has set ambitious electrification targets and is actively investing in charging infrastructure development, accelerating EV adoption.
For instance, strong government policies, combined with the proactive efforts of automakers such as Volvo (with plans to go fully electric by 2030), create a thriving EV market.
- Americas: The Americas are experiencing a rise in EV adoption, albeit slower than anticipated, as the charging infrastructure development needs to catch up. While government incentives like tax credits and infrastructure spending plans have been introduced in the US, policy consistency is crucial to sustaining momentum. Additionally, consumer education and addressing range anxiety through widespread DCFC deployment will be critical for achieving mass EV adoption in the Americas.
Advanced Energy Storage Systems (ESS):
ESS is crucial for managing energy distribution across the grid, especially during peak demand and when renewable sources are inactive. The adoption of electric vehicles further drives the demand for ESS and EV charging infrastructure.
Energy Storage Systems (ESS) are pivotal in balancing energy supply and demand, integrating renewable energy sources, ensuring grid stability, and providing backup power. Their importance has surged with the global push towards renewable energy adoption and energy infrastructure modernization.
Despite current headwinds in the United States, the global ESS market continues to grow at a 14% annual growth rate and is projected to reach $32 billion by 2030. Grid-scale lithium-ion batteries currently dominate the space (Frost and Sullivan).
This growth is primarily fueled by increasing renewable energy deployment, declining battery costs, and supportive government policies.
Interest rates and inflation are having a chilling effect on the US storage market in the near term. Projects are being delayed as funding has become more expensive. This, combined with the slower-than-anticipated clarifications and rulings on the Inflation Reduction Act, has caused a momentary dip in ESS deployments in the US.
According to American Clean Power:
- The first quarter of 2024 saw declines (a 3% fall in MW power and 19% fall in MWh YoY) in US utility-scale energy storage deployments, but the long-term pipeline and outlook remain healthy.
- Quarterly revenues for major battery energy storage system (BESS) integrators Fluence, Stem Inc., and Wärtsila all fell year over year.
The rise of renewable energy sources, particularly intermittent ones like wind and solar, necessitates energy storage to ensure grid stability. Government mandates and incentives and declining battery prices are further propelling market expansion. Additionally, the electrification of transportation is driving demand for ESS to support EV charging infrastructure and manage grid loads.
Competitive Landscape for Energy Storage Systems
Major players such as Fluence, Sungrow, Wartsila, and Tesla dominate the ESS market, with many startups and emerging players driving innovation in battery technology and system integration. Competition fosters advancements in battery chemistries, software solutions, and grid integration capabilities.
Several smaller players are making significant strides in the ESS market by tackling battery technology and system integration from new angles:
- Sila Nanotechnologies, a California-based company, is developing silicon-based anode materials for lithium-ion batteries. These anodes have the potential to hold more energy than traditional graphite anodes, translating to a potentially longer range for electric vehicles and increased storage capacity for stationary applications. While technical hurdles remain, Sila Nano's approach represents a promising avenue for next-generation battery technology.
- Backed by oil giant Chevron, Rondo Energy is pioneering a thermal energy storage system to store energy in cheap, widely available materials like concrete or sand. This heat can then be converted back into electricity when needed, providing a reliable and cost-effective way to store energy from intermittent sources like solar and wind.
Smaller companies like Sila Nanotechnologies and Rondo Energy drive innovation in the ESS market by focusing on specific areas and offering unique functionalities.
Electric Vehicles (EVs) and Charging Infrastructure
- EV adoption contributes to the growing demand for energy storage systems and EV chargers.
- EV charging infrastructure will be worth USD 76 billion by 2030.
- Public charging stations are needed to accommodate thousands of vehicles per day.
- Decentralized ESS is required to manage grid load until transmission and distribution lines are upgraded or replaced.
Technological Innovations in the Solar Industry
Solar industry OEMs grapple with manufacturing challenges, including achieving sufficient barrel fill in PCBAs and increasing automation to enhance product quality and efficiency. Focus areas include exploring lower-cost power electronics packages, substrate advancements, and developing new materials to boost photovoltaic cell efficiency and power inverters' capabilities.
Barrel fill refers to the amount of solder used to fill tiny holes connecting different layers of a circuit board. In the solar industry, proper barrel fill ensures electrical conductivity, prevents component loosening, and reduces the risk of malfunctions in solar inverters.
Space-based Solar Power Technology Concept
Space-based solar power (SBSP) infrastructure is a theoretical system of harnessing solar energy in space and transmitting it wirelessly to Earth. It involves a complex network of components in space and on the ground. Here's a breakdown of its main components:
- Space Segment:
- Solar Power Satellites (SPS): These are large structures in space, often in geostationary orbit, equipped with massive solar panels to collect sunlight. The size of these satellites can range from kilometers to tens of kilometers in length.
- Energy Conversion: The collected solar energy is converted into a suitable transmission form, usually microwaves or lasers. This involves specialized converters and antennas.
- Transmission System: Powerful transmitters on the SPS beam the energy towards Earth. Microwaves are the most common choice due to their ability to penetrate clouds and atmosphere.
- Ground Segment:
- Receiving Antennas (Rectennas): These are large ground-based antennas designed to capture the transmitted energy and convert it back into electricity for distribution into the power grid.
- Power Distribution: Once converted, the electricity is integrated into the existing power grid infrastructure for consumption by homes, businesses, and industries.
- Programs:
- Caltech's Space Solar Power Project (SSPP): This project aims to demonstrate the wireless transmission of solar power from space to Earth.
- European Space Agency (ESA) SOLARIS program: This program investigates various aspects of SBSP, including technology development and economic feasibility.
- China's Bishan Space Solar Energy Station: China has announced plans to build a space-based solar power station by 2035.
Energy Market
Jabil Insights
Navigating the Evolving Regulatory Landscape
- Standardization is Key: Advocate for adopting global safety standards for renewable energy systems, EVs, and battery storage. Reference established guidelines like UL's "Energy Storage Systems Guide" and actively participate in industry forums and consortia shaping these standards. Partner with trade associations to lobby policymakers for harmonized regulations that reduce trade barriers and ensure a level playing field for all participants.
- Stay Informed and Proactive: Develop a comprehensive regulatory intelligence program to track emerging regulations in key markets (US, UK, China) and anticipate potential compliance requirements. Collaborate with legal and compliance experts to ensure your products are future-proofed and meet evolving safety standards across diverse jurisdictions. Consider offering regulatory compliance services as a value-added proposition to your partners.
- Partner with Experts: Collaborate with safety specialists and testing labs to proactively test and certify your products against the latest fire safety standards. Leverage their expertise to identify potential safety concerns early in the design phase and implement preventative measures. This proactive approach can minimize delays and ensure a smoother path to market.
Optimizing Products for a Long Lifecycle
- Embrace Modularity: Design and manufacture energy products with modular components that can be easily swapped out, repaired, or upgraded. This allows for easier maintenance, adaptability to technological advancements, and extension of product lifespans. Invest in design for manufacturing and assembly (DFMA) principles to optimize modularity and streamline production processes.
- Extend Product Lifespan: Partner with OEMs to offer comprehensive lifecycle management programs that include preventive maintenance, repairs, and readily available spare parts. Consider offering extended warranty options to customers and explore opportunities for product buy-back and refurbishment programs. These services can generate recurring revenue streams and enhance customer satisfaction.
- Invest in Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) Tools: Implement robust PLM strategies to track components, manage obsolescence risks, and streamline product evolution. Utilize PLM software to maintain a digital thread throughout the product lifecycle, facilitating collaboration between internal teams, suppliers, and OEMs. This improves traceability, reduces costs associated with managing parts revisions, and allows for proactive planning for end-of-life product management.
Sustainability: A Growing Imperative:
- Prioritize Responsible Recycling: Develop or partner with recycling facilities that recover materials from used batteries (copper, aluminum, nickel, cobalt) through eco-friendly hydrometallurgical processes. Invest in research and development to improve recycling efficiency and explore opportunities for closed-loop supply chains where recovered materials are reintroduced into the manufacturing process.
- Explore Second-Life Applications: Collaborate with OEMs to explore opportunities for repurposing EV batteries in stationary energy storage systems. This will promote resource utilization, waste reduction, and new market opportunities for second-life batteries. Develop a robust battery diagnostics and health assessment program to determine the suitability of used batteries for second-life applications.
- Transparency is Key: Communicate your commitment to sustainability to customers and partners. Highlight your efforts to minimize environmental impact throughout the supply chain, including responsible sourcing practices, energy-efficient manufacturing processes, and eco-friendly product disposal solutions. Publish sustainability reports outlining your environmental goals and progress towards achieving them.
Innovation and Collaboration for a Sustainable Future:
- Diversify Battery Technology: Monitor advancements in alternative battery chemistries (sodium-ion) and invest in research partnerships with universities and startups to explore their commercial viability. Participate in industry consortia focused on battery innovation and actively share your expertise and resources. By staying at the forefront of battery technology, you can position yourself to supply critical components for the next generation of energy storage solutions.
- Mitigate Geopolitical Risks: Develop a comprehensive sourcing strategy to lessen reliance on specific regions for critical raw materials and components. Diversify your supplier base and explore opportunities for near-shoring or onshoring production in key markets to reduce dependence on geographically concentrated supply chains. This strategy can minimize vulnerability to geopolitical disruptions and potential trade wars.
- Embrace Collaboration: Foster collaboration among industry stakeholders (OEMs, suppliers, researchers) to accelerate innovation and achieve net-zero emissions targets. Participate in joint research and development initiatives, share best practices, and leverage collective expertise to address common challenges. By working together, the industry can overcome technological hurdles, unlock new opportunities, and accelerate the transition to a clean energy future.
Following these insights and adopting a proactive, collaborative approach can make you a trusted and valuable partner in the evolving energy and renewables market.
Energy Market
Recommendations
Focus on Core Infrastructure and Innovation
- Scale Up Renewable Energy Infrastructure: Aggressively invest in expanding wind and solar power generation capacity. This can be achieved through public-private partnerships, tax breaks, and loan guarantees to encourage private-sector investment.
- Advance Energy Storage Solutions: Invest in research and development of next-generation Energy Storage Systems (ESS) to address renewables' intermittency and enhance grid stability. Explore diverse technologies beyond lithium-ion, such as flow batteries and solid-state batteries.
Sustainable Practices and Long-Term Strategies
- Prioritize Sustainable Battery Recycling: Develop and implement commercially viable solutions for battery recycling to minimize environmental impact and ensure resource security. This includes investing in hydrometallurgical recycling processes and creating a circular economy for batteries.
- Diversify Battery Technology: Foster research and development of alternative battery chemistries like sodium-ion to overcome lithium-ion batteries' energy density and cycle life limitations.
- Mitigate Geopolitical Risks: Develop comprehensive strategies to mitigate potential disruptions in the supply chain of critical raw materials due to geopolitical complexities. This can involve diversifying sourcing locations, fostering international collaboration, and exploring alternative materials.
- Invest in Workforce Development: Upskill and train the workforce to install, maintain, and operate the next generation of renewable energy technologies and ESS solutions.
Collaboration and Policy Advocacy
- Standardize Regulations for ESS: Collaborate with industry stakeholders and regulatory bodies to establish clear and harmonized safety protocols and standards for energy storage systems.
- Promote Supportive Policies: Advocate for supportive government policies, including renewable energy targets, feed-in tariffs, carbon pricing, and streamlined permitting processes. This creates a stable and predictable regulatory environment for renewable energy investments.
- Foster Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing: Encourage collaboration among governments, industries, research institutions, and NGOs to accelerate innovation and overcome challenges in the transition to clean energy. Facilitate knowledge sharing and technology transfer to drive global adoption of renewables.
- Expand Market Access and Public Awareness: Invest in education and outreach programs to raise public awareness of the benefits of renewable energy and electric vehicles. This builds public support and market demand for clean energy solutions.
These recommendations will help contribute significantly to a smoother transition towards a clean, sustainable, and resilient global energy future.
Jabil Spend Data
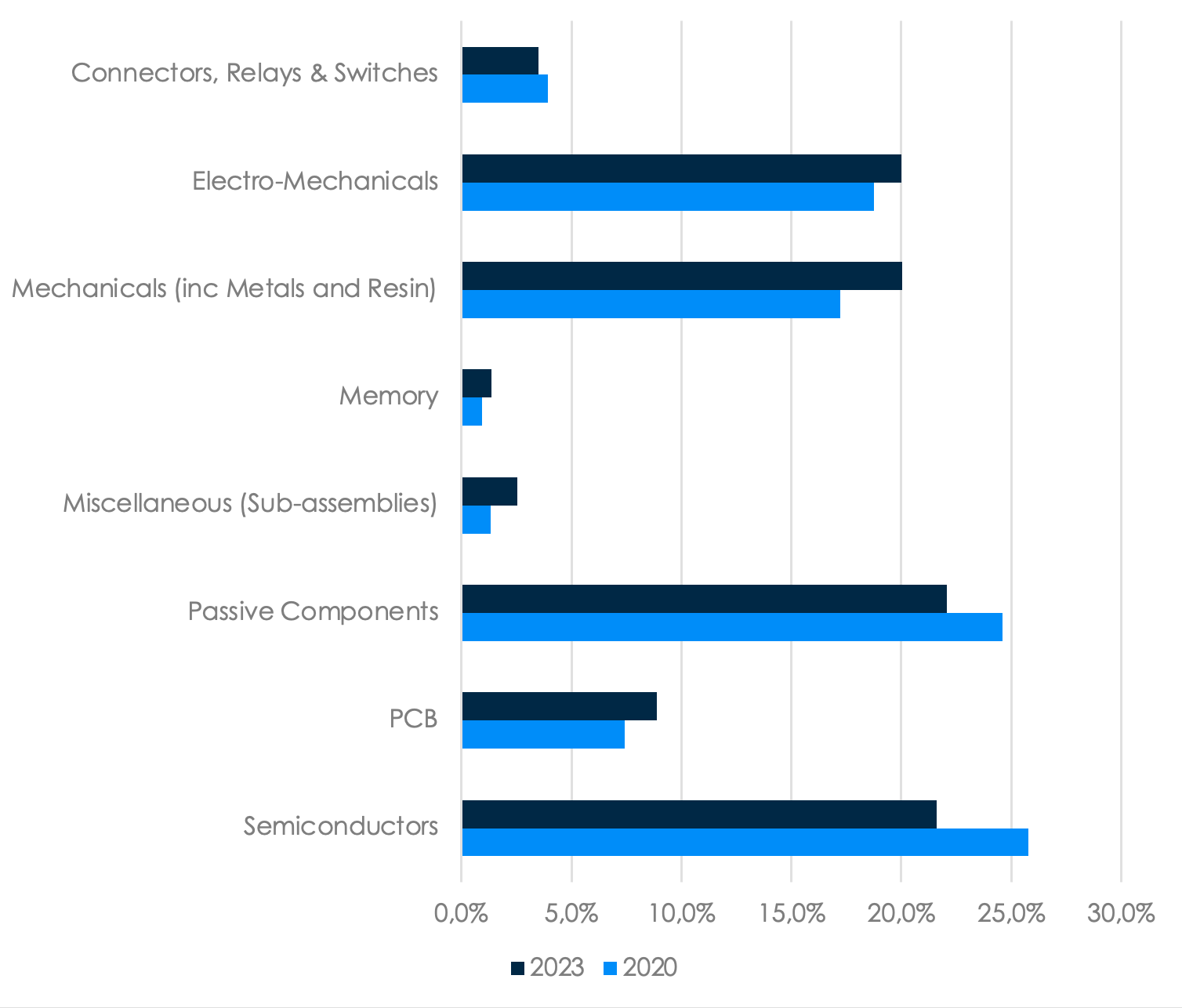 Data based on Jabil's historical spending data for the Energy Customer Segment
Data based on Jabil's historical spending data for the Energy Customer Segment
Jabil Spend on Categories YoY (%)
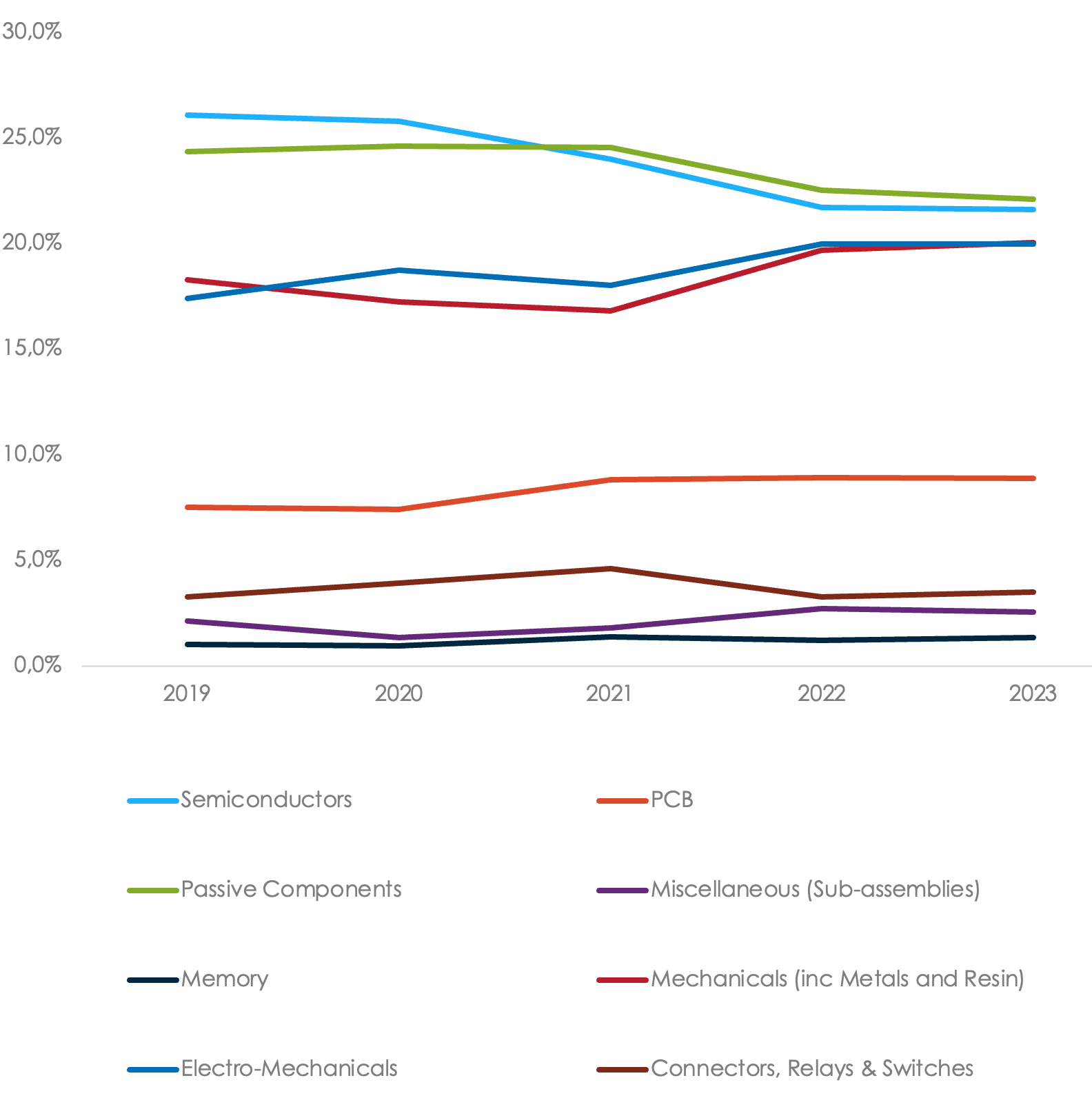
Data based on Jabil's historical spending data for the Energy Customer Segment
Energy Market
Appendix
Key References
- Adani Green Energy Operationalizes 1000 MW Of The 30000 MW Khavda Renewable Energy Park
- Phase 5 of UAE’s Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum solar park launched
- DEWA and Masdar Reach Financial Closing on the Sixth Phase of the Largest Single-Site Solar Park in the World
- China Brings 2.2-GW Solar Park Online
- World’s largest solar plant goes online in China
- Sun Cable reveals full extent of its giant solar-plus-storage project in Australia
- At $16 Billion, Australian Solar Project Would Be the Biggest In The World
- Aurora Solar Energy Project
- Vast Solar to grow Port Augusta CSP to 150 MW at old SolarReserve site
- Hornsea 2 Offshore Wind Farm Powering over 1.4 million homes with green energy
- New wind power milestones reached in UK, France and Egypt
- World’s largest offshore wind farm to add capacity to power 6,000,000 homes
- GE Renewable Energy Announces Expansion of Onshore Turbine Repair Center in Noblejas
- Nation’s first commercial-scale offshore wind project
- Vistra Announces Expansion of World's Largest Battery Energy Storage Facility
- Vistra Completes Expansion of Battery Energy Storage System at its Flagship California Facility
- Neoen starts operating 300 MW Victorian Big Battery in Australia, one of the world’s largest batteries
- Fluence Surpasses 20 GWh of Deployed and Contracted Battery-based Energy Storage Systems Globally
- 100 MW/400 MWh Fluence Energy Storage Project For Long Beach — World’s Largest Li-Ion Battery Storage Project
- Hydrostor air energy storage complements wind, solar power
Back to Top
