By clicking the “I Accept” button, or by accessing, participating, or submitting any information, or using the Jabil Global Intelligence Portal or any of its associated software, you warrant that you are duly authorized to accept the Global Intelligence Portal Terms and Conditions on behalf of your Company, intending to be legally bound hereby, and your company shall be bound by the terms and provisions of the Global Intelligence Portal Terms and Conditions, accessible under the following link Portal T&Cs.
Sector Market Report
Automotive
Sector Market Report
Automotive
Get an in-depth analysis of the current state, trends, and future of the automotive technology market, including insights into key drivers, changing product lifecycles, and manufacturing challenges.
Automotive Market
Overview
The automotive market presents a promising outlook in 2024 characterized by both emerging recovery trends and persistent challenges. As supply chain issues ease and inventory levels improve, market dynamics show prominent growth in global vehicle sales by 2030. The electric vehicle (EV) segment is poised for significant growth, with an estimated compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of ~18% from 2024 to 2030. Government regulations and strong consumer interest drive this growth. Despite a temporary decline in the demand for EVs in early 2024 due to economic uncertainties and geopolitical tensions, the industry is expected to rebound by mid-year. The resurgence of electric vehicles is expected to be driven by improved supply chains, supportive policies, increased consumer interest, and the availability of more affordable models. These factors are anticipated to make EVs more accessible to a broader market.
The industry is witnessing a significant shift towards new technologies, driven by the adoption of electrified powertrains, advanced driver assistance systems, increased vehicle connectivity, and centralized architectures. As the industry evolves, key players, from manufacturers to suppliers, are reshaping their roles; new entrants are disrupting the traditional automotive ecosystem while established manufacturers and suppliers adapt to new functions. For electronics manufacturing services (EMS) providers and tier-one suppliers like Bosch, Continental, Denso, and Magna International, this transition demands the development of more technical and service competencies to accommodate the changing needs of OEMs.
Sustainability remains a central theme, with automakers investing in eco-friendly manufacturing processes and materials to reduce the environmental impact. The trend towards lighter materials continues, aiming to improve fuel efficiency and vehicle performance. Moreover, the industry is increasingly adopting renewable energy sources within production facilities and prioritizing recycling vehicle components to minimize carbon footprints further. This shift supports global sustainability goals and resonates with the growing consumer preference for environmentally responsible products.
Despite facing challenges such as economic fluctuations and geopolitical tensions, market is optimistic. Innovative new business models that accommodate the swift transition to technologies like autonomous driving, connectivity electrification, and software-defined vehicles (ACES) framework continue to drive the industry forward. The commitment to electrification remains strong as major players recalibrate their strategies to better align with current market dynamics and shifting consumer expectations. This strategic pivot ensures that the industry not only meets the immediate needs but also embraces sustainable and advanced technologies for future growth.
This report delves into various aspects of the automotive industry, including technology trends, supply chain, OEM activities, government policies & initiatives, and the influence of global politics on market strategies and operations. By providing a comprehensive analysis of these elements, the report aims to convey an optimistic view of the future, recognizing the challenges that lie ahead while highlighting the robust initiatives and strategic adaptations that promise to drive the industry forward.
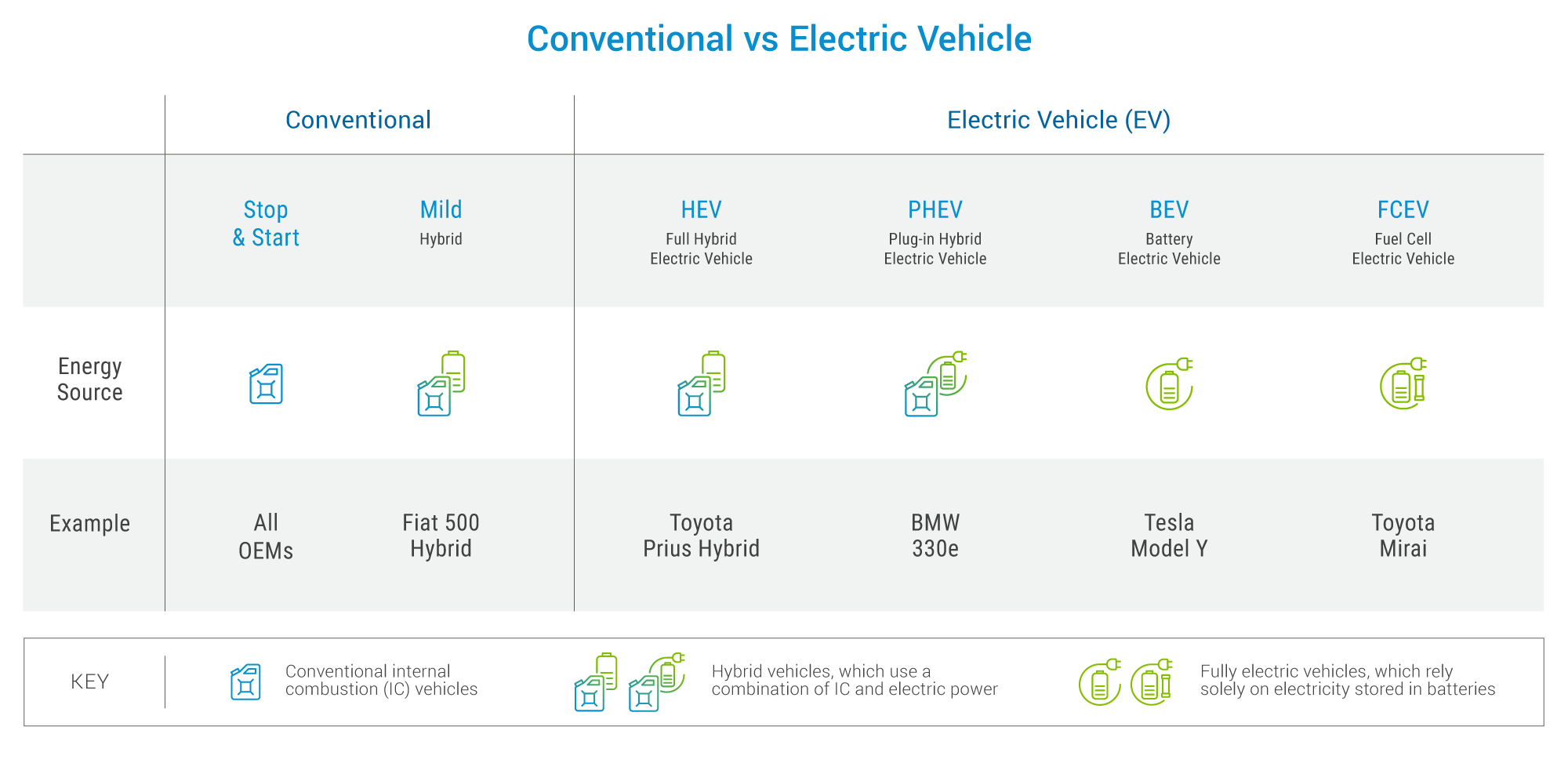
The scope of this report remains on Light Vehicles. Although internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles still hold a significant market share, the report emphasizes the industry-wide shift towards electric vehicles (EVs), including both battery electric vehicles (BEVs) and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs).
Automotive Market
Market Overview
Global Automotive Market Outlook
The automotive market showcased moderate growth in 2023. Looking ahead to 2024, global vehicle sales are forecasted to increase slightly to 89.05 million units from 86.6 million units in 2023 (S&P), reflecting a continued, albeit slower, recovery momentum. This growth was propelled by strong demand across key markets such as China, the United States, and Europe, alongside significant recovery in emerging economies. The sector benefited from easing supply chain disruptions, increased consumer confidence, and a notable surge in EV adoption driven by governmental policies and incentives. The market is expected to navigate challenges such as rising material costs, geopolitical tensions, and evolving consumer preferences toward sustainable mobility.
As we look towards the next five years, the automotive industry is poised for significant transformation, driven by the global shift towards electrification. This supports green and environmentally friendly technologies, which are set to advance the sector significantly by 2030. Additionally, developments in autonomy & connectivity, including innovative features like autopilot and autonomous cars, are expected to enhance the consumer driving experience.
Concurrently, innovations such as augmented reality (AR), artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and 5G communication networks are anticipated to play a significant role in expanding the customer base. AR is expected to augment the driving experience by providing real-time information, such as navigation prompts and traffic conditions directly on the windshield, thereby potentially improving safety and navigation efficiency. AI and ML could enhance vehicle automation by refining the algorithms that drive autonomous vehicle behavior and personalizing user experiences, which may lead to increased driver comfort and engagement. Moreover, the deployment of 5G is likely to facilitate more robust vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communications, enabling faster and more reliable data exchanges that could improve traffic management and vehicle diagnostics. These technological advancements are anticipated to subtly reshape the automotive landscape, potentially positioning the industry to lead in technological innovation and customer satisfaction through 2030.
In terms of production, the automotive industry faces a period of strategic adjustment, marked by modest production levels and inventory recalibration aimed at aligning with shifting market demands in 2024. Over the long term, through to the end of 2030, the industry is expected to see a gradual increase in production. Technological advancements and strategic operational improvements will support this growth, although the increase is anticipated to be conservative.
After a period of rebuilding inventory to counter past disruptions, S&P Global notes that the production outlook for 2024 is relatively flat, reflecting a shift towards a more traditional demand-driven model. This shift involves maintaining average inventory levels below pre-pandemic norms, indicative of a strategic focus on leaner inventories. In alignment with this, global automotive production is expected to slightly decrease by about 0.5% from 2023, resulting in an estimated total of 89.64 million units (S&P). This careful management reflects the industry’s disciplined approach to responding to ongoing market conditions and consumer trends, including integrating new technologies and vehicle types. Additionally, the political landscape is expected to be particularly volatile in 2024, a year marked by significant elections, i.e., in the US and in India, which could lead to shifts in policy affecting the industry.
Looking further ahead, the landscape from 2024 to the end of the decade is poised for significant change. As the automotive industry embraces new technologies and adapts to changing market conditions, production volumes are projected to gradually increase. Investments in operational efficiencies and sustainable practices are anticipated to stimulate production growth, culminating in a robust increase in production capabilities by the decade's end. This evolution reflects the industry's commitment to resilience and adaptability in meeting future challenges.
Navigating the Road Ahead
- The Impact of Interest Rates: High-interest rates can discourage car purchases in general, and the greater upfront price of EVs compared to internal combustion engine vehicles compounds this effect. Balancing affordability and interest rate sensitivity is crucial for driving sales.
- Charging Infrastructure Development: Expanding reliable, accessible, and rapid charging networks is essential to assuage consumer anxieties and bolster EV confidence.
- IRA Refinement: Clearer regulations regarding the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act (IRA), particularly around vehicle qualifications for tax credits, will allow automakers to align their strategies and streamline consumer decision-making.
Regional Outlook
The United States
The United States automotive market experienced a notable recovery in 2023, with vehicle sales increasing by 12.4% to reach 15.6 million units. In 2024, sales are projected to rise modestly to 16 million units. The market is anticipated to continue this stable growth trajectory, reaching 16.68 million units by 2027, indicating a gradual increase. This growth is supported by the continued expansion of the electric vehicle segment, supported by federal incentives and a growing consumer appetite for sustainable mobility solutions. Federal tax credits up to $7,500 are available for certain new electric vehicles that meet specific U.S. manufacturing criteria. Additional state-level consumer rebates further support these initiatives. The National Electric Vehicle Infrastructure Formula Program contributes significantly, allocating billions to build a nationwide network of EV charging stations. Regulatory measures, such as the Zero-Emission Vehicle Standards set by the California Air Resources Board and adopted by many states, mandate automakers to increase the sales of zero-emission vehicles.
Despite these growth factors, the market faces several challenges. High vehicle prices, increasing interest rates, and tighter lending conditions are persistent issues. Moreover, the complex regulatory environment introduces additional uncertainty. Policies like the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) aim to accelerate the transition to cleaner transportation modes but have encountered implementation challenges, leaving manufacturers and consumers to navigate a maze of requirements. Recent policy adjustments, such as the mechanisms for transferring clean vehicle tax credits, are positive yet highlight the restrictive criteria for tax credit eligibility, reflecting the ongoing struggle to align policy goals with market readiness.
The evolving labor dynamics within the automotive industry also pose a significant challenge. New labor agreements between the United Auto Workers (UAW) and major car manufacturers like GM, Ford, and Stellantis are reshaping the cost structure of EV production. While these agreements push for equitable compensation and signify a commitment to fair labor practices, they could increase production costs as the industry evolves.
Europe
The European light vehicle market experienced a significant upturn in 2023, with sales increasing by 14% to a total of 14.8 million units. This surge was primarily driven by an improved supply chain situation, which effectively meeting the demand. Looking ahead, the automotive market in Europe is expected to see a modest increase in sales to 15.3 million units in 2024, followed by a projection of 15.8 million units in 2027. This forecast suggests a continued, albeit slower, recovery momentum. The anticipated growth is supported by several factors, including the gradual normalization of inventory levels, the introduction of new EV models, and consumer adaptation to evolving economic conditions. Additionally, interest rates are estimated to have peaked, which may encourage consumer financing and spending. Expecting price cuts, especially for xEVs, as subsidies have expired or lowered, should stimulate market demand. The launch of Chinese brands like BYD and MG in the European market is expected to lower entry prices for battery electric vehicles and increase competition and price pressure on traditional OEMs. However, this growth faces challenges such as rising material costs and regulatory changes that could impact vehicle prices and availability.
Europe continues to lead in green energy initiatives, with many countries setting aggressive targets for carbon neutrality. For example, the UK established a goal in 2019 to achieve a net-zero economy by 2050. The sales of EVs in Europe, which constituted about 6% of total automotive sales in 2019, are projected to reach nearly 16% by 2024. This increase signifies the onset of a major technological shift in the automotive industry, evidenced by several regulatory initiatives aimed at fostering this transformation:
- EU CO2 Emissions Standards: The European Union has implemented increasingly stringent CO2 emission standards for new cars. These standards are designed to encourage automakers to accelerate the development of electric vehicles.
- Euro 7 Regulations: The adoption of Euro 7 regulations marks a critical step towards stricter emission controls. Initially, these regulations were designed to compel traditional vehicles to adhere to more stringent environmental criteria. However, recent modifications to the timeline of these regulations will allow internal combustion engine vehicles to remain operational and commercially viable for several additional years.
China
China's automotive market experienced robust growth in 2023 and is projected to continue this trend into 2024, with sales expected to reach 26.66 million units. The growth trajectory is anticipated to extend, with sales projections reaching 29.01 million units by 2027. This anticipated growth is largely fueled by the increasing consumer interest in electric vehicles and the sustained expansion of the electric vehicle sector. Chinese automakers are well-positioned to meet this demand, benefiting from both strong domestic sales and exports.
The positive outlook for the sector is supported by strategic government policies that promote the development of EVs. Noteworthy initiatives include the National Key Technology R&D Program for New Energy Vehicles, the Ten Thousand Talents Program aimed at attracting global innovation talent, and local government subsidies for EV development in specific regions. These policies underline the Chinese Government's commitment to fostering the EV market. Further, to oversee and manage the technological shift towards EVs, the Chinese government has designated specific responsibilities to various regulatory bodies. The State Council and the National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC) set overarching industry policies and define the regulatory framework for electric vehicles. Meanwhile, the Ministry of Transport (MoT) and the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) are tasked with ensuring market access for EV manufacturers, quality and safety control, and the implementation of regulations concerning various aspects of the EV industry, such as charging infrastructure and battery standards. Additionally, the Standardization Administration of China (SAC) is responsible for establishing and publishing national standards for the EV industry, covering key components and operating systems, battery technology and management systems, and basic charging infrastructure. These efforts are shaping a promising future for China's automotive industry, particularly in the electric vehicle sector, which is supported by strong governmental support and global competitiveness.
On the regulatory front, the Chinese government is aggressively promoting EV adoption through incentives. The EV purchasing tax-cut benefit has been extended to 2027, offering a maximum tax deduction of ~$4,150 (30,000 CNY) for 2024-2025, and $2,100 (15,000 CNY) for 2026-2027, to encourage further uptake of environmentally friendly vehicles. Additionally, in a significant move to curb pollution and transition to cleaner energy vehicles, the Chinese government has been intensifying efforts to phase out internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. China plans to increase the vehicle scrappage rate for models that meet or fall below Euro III standards by 50% by 2025, and by 100% by 2027, compared to 2023 levels. Euro III standards refer to a set of European emission regulations that define the acceptable limits for exhaust emissions of new vehicles sold in EU and EEA member states. Introduced in 2000, these standards specifically target the reduction of pollutants such as nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide, and particulate matter from diesel engines, among others. The scrappage policy specifically targets older, more polluting vehicles by offering incentives for owners to retire these vehicles early. This initiative is expected to accelerate the replacement cycle, thereby reducing the number of high-emission vehicles on the road and promoting the adoption of electric vehicles. This aligns with China's broader environmental goals and supports the national strategy to achieve carbon neutrality by 2060.
Price competition in China's EV market is becoming increasingly fierce. BYD has significantly reduced the prices of its product lineup by $2,800-4,200 (20,000 to 30,000 CNY). Tesla had also reduced prices for its Model 3 and Model Y/Model 3 by up to $2,100 (15,000 CNY) earlier in the year 2024 (which they later raised for Model Y by $700 [5,000 CNY] in April 2024). Li Auto increased incentives by approximately $4,200 (30,000 CNY) in January 2024. Meanwhile, the Xiaomi SU7 BEV has garnered significant market acceptance, as evidenced by an extensive waiting period of up to 32 weeks. Innovations such as BEVs with 800v fast charging and new offerings from Xiaomi are set to potentially disrupt the market further in 2024.
In response to these market dynamics and supportive policies, Chinese EV startups like NIO, Xpeng, Zeekr, and Li Auto have shown varied delivery performances, underlining the highly competitive nature of the market. In April 2024, Zeekr, a premium brand under Geely Holding Group, reported a remarkable 99% year-over-year growth, with deliveries of 16,089 vehicles. This success follows the introduction of a new, more affordable entry-level variant of their Zeekr 007 RWD, which saw a reduction in base price by ~$2,800 (20,000 CNY). Similarly, NIO's deliveries surged to 15,620 vehicles, a 134.6% increase from the previous year, boosted by the launch of the updated ET7 sedan. Xpeng also contributed to the competitive momentum with a 33% increase in deliveries, primarily due to its popular G9 electric MPV. In contrast, Li Auto experienced more modest growth, with a marginal 0.4% increase, despite the launch of its new L-series SUV, the L6. These developments are a direct reflection of the aggressive pricing strategies, enhanced incentives, and continuous innovation spurred by the regulatory and policy landscape, illustrating the vibrant and evolving nature of China's EV market.
India
India's automotive market is poised for growth in 2024, with projections indicating a 5.3% increase in sales to 4.97 million units. Further, the market is expected to maintain this upward trajectory, reaching 5.63 million units by 2027.
The Indian market is expected to face major challenges, such as the need for enhanced infrastructure to support the promising EV segment. In response, India is focusing on augmenting manufacturing capabilities and attracting foreign investment, which are expected to drive innovation and further growth in the automotive sector. Complementing these efforts are India's National Electric Mobility Mission Plan (NEMMP) and the Phased Manufacturing Programme (PMP). These policies are specifically designed to boost local manufacturing capabilities and reduce dependency on imports, particularly in the domains of batteries and critical minerals. By fostering a localized supply chain, these strategies are essential for the sustainable growth of the EV market in India, ensuring that the industry's expansion is both robust and resilient.
Key regulatory entities play a pivotal role in facilitating the smooth introduction and standardization of new technologies in the Indian automotive market. These include:
- Automotive Research Association of India (ARAI): ARAI is instrumental in developing automotive standards and regulations in India. It provides testing and certification services for vehicles and components, ensuring they meet established safety and quality benchmarks.
- Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS): As the national standards body, BIS is responsible for setting and implementing standards across various sectors, including the automotive industry. Compliance with BIS standards is mandatory for automobile manufacturers operating in India.
These organizations are integral to maintaining safety standards, fostering innovation and technology development, and overseeing the certification and standardization of automotive features. For example, in February 2024, ARAI launched a pilot scheme under the National Green Hydrogen Mission (NGHM) aimed at integrating green hydrogen as a fuel for buses and trucks. The objectives of this initiative include supporting the development of green hydrogen fuel on a pilot basis, evaluating the technical feasibility and performance of hydrogen-operated vehicles in real-world conditions, assessing the effectiveness of hydrogen refueling stations, and demonstrating the safe and secure operations of hydrogen-based vehicles and infrastructure.
*Sales and production numbers in the regional outlook section are sourced from S&P
Market Growth Enablers
Government Regulations and Incentives
Emissions standards, EV subsidies, and infrastructure investments heavily influence the shift towards electrification.
Governments worldwide are implementing increasingly stringent emissions regulations. These regulations, such as California's Zero-Emission Vehicle mandates and the European Union's CO2 fleet targets, are accelerating the automotive industry's shift towards electrification. Major automakers, including Ford, GM, and VW, are aligning their long-term strategies with these mandates, committing to aggressive EV production timelines.
Simultaneously, governments are offering various incentives to stimulate EV adoption. Substantial tax credits like those in the US Inflation Reduction Act, along with direct subsidies in markets like China, are making EVs more affordable. China's extensive EV subsidy programs have played a pivotal role in nurturing domestic EV champions like BYD and Nio. These incentives, coupled with infrastructure investments for public charging networks, are proving crucial in driving EV market growth.
Furthermore, there have been several efforts to streamline permitting processes for charging station installations, along with the standardization of charging protocols, it’s vital for building a seamless and convenient user experience, making a switch to EVs easier for consumers. This is expected to propel the EV market in the next 5 years.
Advances in Battery Technology
Decreasing costs, increasing energy density, and faster charging speeds are making EVs more viable.
The cost of lithium-ion batteries, the core technology powering most EVs, has dropped over the last decade due to manufacturing efficiencies and technological breakthroughs. This downward cost trend is expected to continue, making EVs increasingly price-competitive with internal combustion vehicles. Furthermore, research into next-generation battery technologies like solid-state batteries promises to deliver breakthroughs in energy density. The resultant is smaller, lighter batteries with greater range. Automakers like Toyota, BMW, Stellantis, and other major players see solid-state batteries as a key step and are expected to invest significantly in their development. Alongside battery innovation, rapid advancements in EV charging technology are reducing charging times, with ultra-fast chargers now capable of adding hundreds of miles of range in mere minutes. Companies like Electrify America and Ionity are expanding these networks globally.
While range and charging times are critical, the long-term health of batteries is also paramount to consumer confidence. Developments in battery diagnostics, thermal management systems, and advanced recycling techniques, are extending battery lifespan, and building trust in the longevity of EVs while minimizing environmental impact.
Shifting Consumer Preferences
Prioritization for tech-savvy vehicles, connectivity, and brands with strong sustainability commitments.
Consumer preferences are evolving rapidly, and sustainability is increasingly a deciding factor in vehicle purchases, especially among younger generations. EVs are perceived as technologically advanced and environmentally responsible. Tesla's rapid rise is largely attributed to its software-centric approach, redefining the in-vehicle user experience. This success is forcing legacy automakers to invest heavily in their digital capabilities and connected services. Consumers and investors are also scrutinizing automotive companies through the lens of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors. This means it's now essential for automakers to demonstrate commitments to ethical sourcing, responsible manufacturing, and a sustainable product lifecycle.
EV Charging Infrastructure Expansion
Growing networks to accelerate EV adoption.
The availability of a robust charging infrastructure is essential to alleviate range anxiety and accelerate EV adoption. Private companies, governments, and public-private partnerships are rapidly expanding charging networks worldwide. Major players are focusing not only on increasing the number of charging stations but also on their speed and distribution. Workplace charging is another area of growth, with employers recognizing the importance of providing this amenity. Ultra-fast charging stations, capable of delivering power at rates exceeding 350kW, are being strategically deployed along major travel routes, making long-distance travel in EVs increasingly practical.
Successful infrastructure rollout goes beyond just chargers. Power grid upgrades and intelligent load management systems will be crucial to support the increasing power demand that comes with widespread EV adoption. Moreover, vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technologies hold promise, potentially turning fleets of EVs into distributed energy storage assets, further bolstering the transition to renewable energy sources.
Market Inhibitors
High Upfront Cost of EVs
Price disparity with ICE vehicles, though narrowing, remains a barrier for consumers globally.
Despite declining battery costs, the upfront price of electric vehicles is still higher than their ICE equivalents. This price gap poses a significant barrier to mainstream adoption, particularly for budget-conscious consumers. While government incentives and subsidies can offset this cost difference in some markets, they might not be available in all regions and for all models, and their permanence is tied to the political landscape – recent changes to EV tax credit eligibility in the US demonstrate this volatility. The EV tax credit eligibility in the US depends on various factors, including the vehicle's purchase date, final assembly location, battery component and critical mineral sourcing, and the buyer's modified adjusted gross income (AGI). For vehicles purchased in 2023 or after, the maximum tax credit is $7,500. However, to be eligible for the full credit, the vehicle must meet certain requirements, such as final assembly in North America and specific sourcing requirements for battery components and critical minerals. Additionally, there are price caps for eligible vehicles ($80,000 for vans, SUVs, and pickup trucks, and $55,000 for other vehicles) and income limits for buyers.
Moreover, the resale value of EVs is still developing, with concerns over battery degradation impacting long-term value and influencing consumer hesitancy. While battery technology is steadily improving, the lifespan and resale value of a five-year-old EV can be difficult to predict compared to ICE vehicles. However, programs focused on end-of-life battery collection and recycling are starting to alleviate these concerns. For instance, the expanded agreement between Toyota and Redwood Materials in 2023 aims to create a closed-loop battery recycling system and repurpose key battery materials, potentially boosting residual values. Additionally, manufacturers offering extended battery warranties or battery health guarantees can further improve consumer confidence in the long-term viability of EVs.
Limited EV Range
Some models still don't match the range of fuel vehicles, impacting long-distance travel suitability.
While EV ranges are continuously improving, most of the models still fall short of typical fuel-powered vehicles in terms of how far they can go on a single charge/tank. This range concern is a major psychological barrier for consumers, particularly those accustomed to the flexibility of long-distance travel in internal combustion engine vehicles. While fast-charging infrastructure is expanding, it's still not as ubiquitous as fuel stations, which adds another layer of planning complexity. A prime example is that in sparsely populated regions, even a 300-mile range EV might necessitate careful route planning due to limited charging infrastructure.
Cybersecurity Risks
Connected/SDX vehicles increase vulnerability to hacking and data breaches.
Modern vehicles, especially electric ones, are software-defined systems with extensive connectivity for features like over-the-air updates, remote diagnostics, and even entertainment. This reliance on software introduces potential vulnerabilities that hackers can exploit. The risks aren't limited to remote vehicle control. Hackers could gain access to sensitive user data, such as location history, payment information, and even driving habits.
The cybersecurity threat landscape facing automakers is complex and ever evolving. Attack vectors can range from exploiting software bugs in the infotainment system to interfering with critical vehicle safety functions. Connected charging infrastructure also presents potential vulnerability points. The automotive industry must approach cybersecurity holistically, from the initial design stages through to the entire vehicle lifecycle. This includes rigorous software testing, implementing robust encryption and authentication protocols, having over-the-air update capabilities to patch vulnerabilities, and building safeguards to protect critical systems, even in the event of a compromised network.
Furthermore, the growing amount of user data collected by connected vehicles highlights the need for strong privacy policies and transparency in data handling. Automakers need to clearly communicate how data is collected, stored, and used, giving consumers granular control over their data. Failing to do so could erode trust and lead to regulatory scrutiny.
According to Upstream’s Automotive Cybersecurity Report 2024, a significant rise in cyberattacks targeting connected vehicles is anticipated. In 2023 alone, the number of high-impact incidents potentially affecting thousands of vehicles increased by 165% compared to 2022. Attackers are now targeting telematics and application servers more than ever, accounting for 43% of all attacks in 2023, up from 35% in 2022. They further expect GenAI's influence on automotive cybersecurity to be significant. While it is poised to enable large-scale attacks but also capable of introducing advanced techniques for stakeholders to detect, investigate, and mitigate these threats.
Regulatory Uncertainty
Varying emissions standards and EV policies across regions can impact sales.
A lack of harmonization in emissions regulations and EV incentives across different markets creates complexities for automakers. Navigating a patchwork of policies can lead to increased costs and delays. The recent surge in protectionist policies tied to EV production requirements has further added uncertainty, potentially restricting the free flow of vehicles and technology. Protectionist policies related to EV production typically involve requirements for domestic content or assembly, tariffs on imports, and incentives for local manufacturing. These measures aim to stimulate domestic EV industries and reduce reliance on foreign-made components, but can also lead to increased costs and limited consumer choice. For example, automakers might need to produce certain models in the same region where they are sold to qualify for incentives. This lack of regulatory predictability could hinder investment decisions and limit the economies of scale needed for the EV market to fully mature.
Challenges and implications from raw material
The production of electric vehicles relies heavily on critical raw materials, such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel. Supply chain disruptions, concerns over ethical sourcing in certain regions such as the Democratic Republic of Congo for cobalt (The DRC accounts for a significant share of global Cobalt production), and geopolitical tensions surrounding these minerals introduce potential bottlenecks in EV production. As demand for EVs soars, securing a reliable and sustainable supply of these raw materials becomes paramount. Moreover, the environmental impact of resource extraction for batteries warrants consideration throughout the lifecycle of an EV, with responsible recycling and battery reuse playing an increasingly vital role.
Automotive Market
Technology Trends
In this report, the acronym ACES has been used to examine the core technology trends within the automotive industry. ACES stands for Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS), Connectivity, Electrification, and Software-Defined Vehicles (SDVs). This framework enables systematic exploration of the technological advancements driving the industry forward.
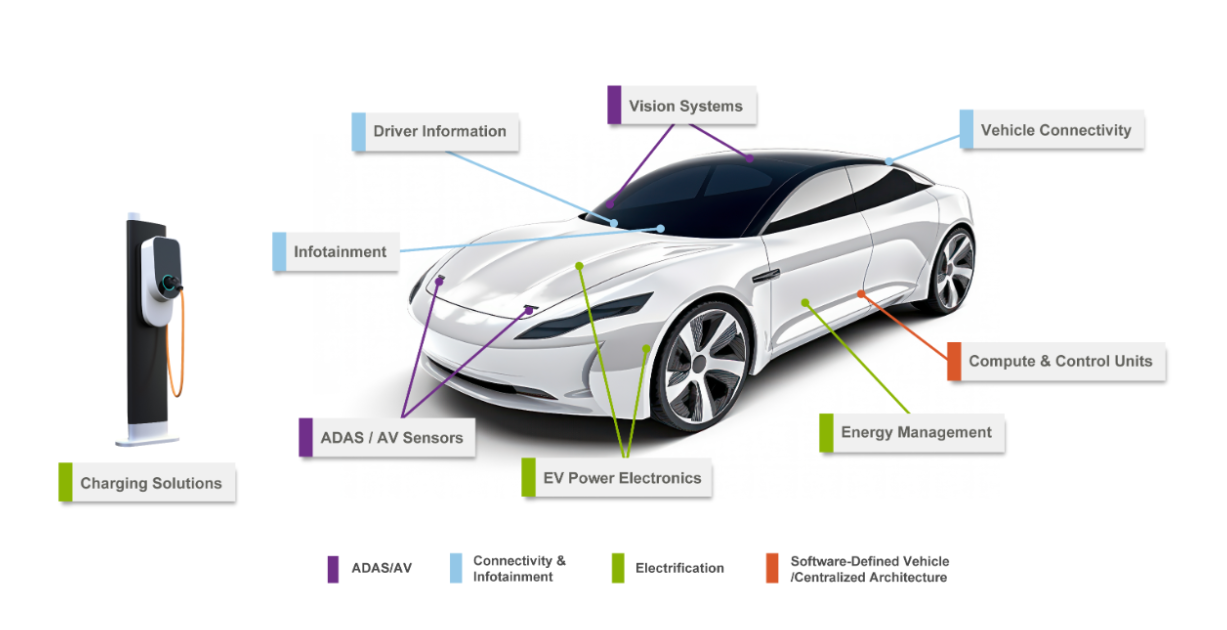
Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS)
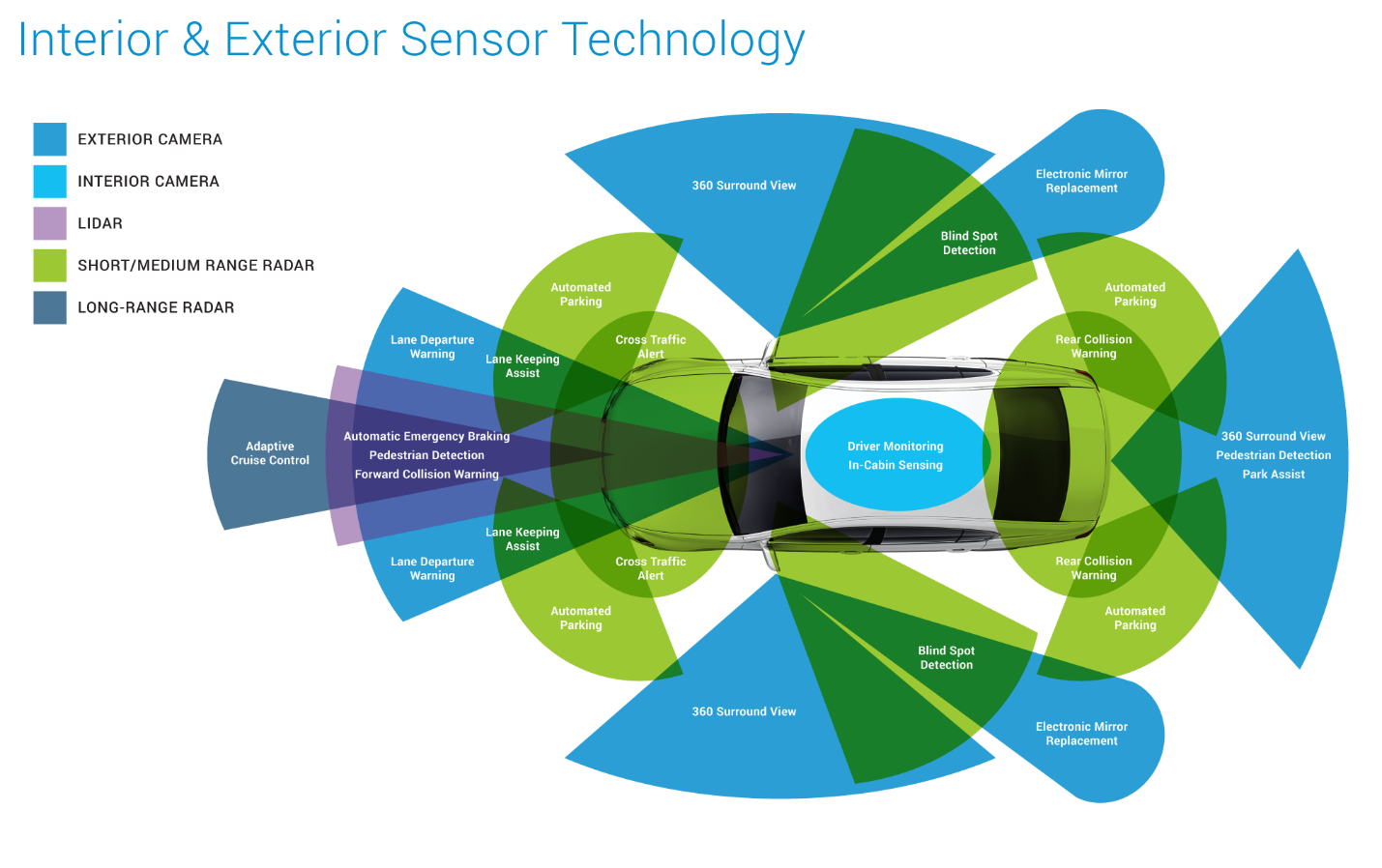
ADAS encompasses a suite of intelligent technologies that enhance vehicle safety, automate routine driving tasks, and lay the groundwork for the future of autonomous transportation. While ADAS has been around for some time, recent years have seen a significant acceleration in the availability and affordability of advanced safety features. Systems such as adaptive cruise control (ACC), automatic emergency braking (AEB), lane departure warning (LDW), and blind-spot monitoring are steadily transitioning from luxury options to mainstream necessities.
Regulatory bodies, driven by substantial evidence of life-saving potential are planning to mandate the inclusion of these features in upcoming vehicles. This regulatory push, combined with growing consumer awareness, is propelling the widespread adoption of ADAS safety technologies. For instance, Subaru has rolled out its advanced EyeSight® Driver Assist Technology as standard equipment across a significant fleet. This suite includes AEB, ACC, and other crucial safety features – a move that could help highlight the increased use of ADAS within the industry. Additionally, the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS) has recognized numerous automakers for their advanced ADAS implementations, with Toyota/Lexus, Honda, and Hyundai frequently recognized for safety innovation.
 Data sourced from secondary research
Data sourced from secondary research
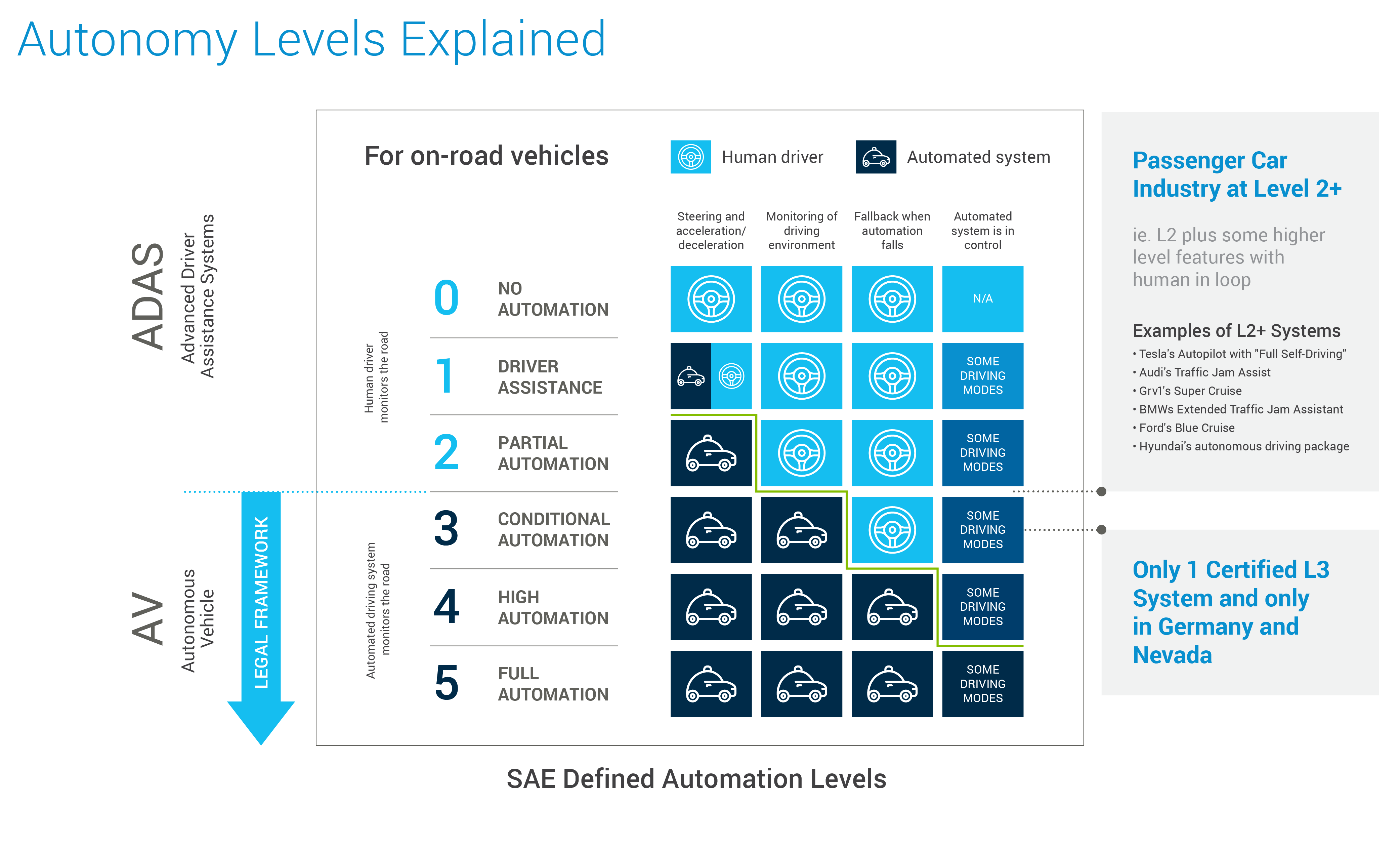
Stride Towards Levels 2+, 3, and beyond
Achieving higher levels of autonomous driving is the key to unlocking the full potential of ADAS technology. While fully self-driving vehicles (Level 4/5) remain a long-term target, the industry is witnessing rapid advances in semi-autonomous capabilities, generally termed Level 2+ or Level 3. These systems allow for extended periods of hands-free driving under specific conditions. Major players heavily invested in this field include Tesla with its Autopilot system, Ford with BlueCruise®, and Mercedes-Benz with Drive Pilot. The progress of these systems depends on tight integration with players like Mobileye (Intel), whose EyeQ® chips and software play a key role in Level 2+ capabilities.
Innovations in ADAS
Innovations continue to advance in the ADAS sector, where the integration of sophisticated sensor arrays is fundamental. Although LiDAR has attracted considerable attention, the technology within this segment is evolving more rapidly than industry participants initially expected.
- 4D Imaging Radar: Companies like Arbe Robotics and Vayyar are spearheading the development of high-resolution 4D imaging radar, offering an alternative to costly LiDAR systems.
- Software-Defined Sensors: Led by innovators like Aeye and Luminar, LiDAR combined with software-driven configuration suggests increased flexibility and futureproofing of sensing systems.
- Sensor Fusion: Embedding information from various sensors (radar, LiDAR, cameras, ultrasonic) is expected to take ADAS to the next level. Companies like Elektrobit, dSpace, and Apex.AI excel in developing sophisticated sensor fusion software platforms that OEMs and Tier-1 suppliers leverage for system integration.
- Beyond Sight: Mobileye (Intel) remains one of the dominant players in the vision-based ADAS space, supplying camera-based solutions to numerous automakers.
Data sourced from secondary research.
Edge AI: Driving Intelligence to the Edge
The vast amounts of sensor data generated in ADAS-equipped vehicles necessitate powerful on-board computing. Edge AI, where processing occurs close to the data source (the vehicle itself), is critical for enabling real-time decision-making crucial to autonomous functions. Semiconductor giants Nvidia (Drive) and Qualcomm (Snapdragon Ride™) actively compete for dominance in ADAS-focused chips. Other players such as Hailo, specifically targeting AI acceleration at the edge, demonstrate the dynamism of this market.
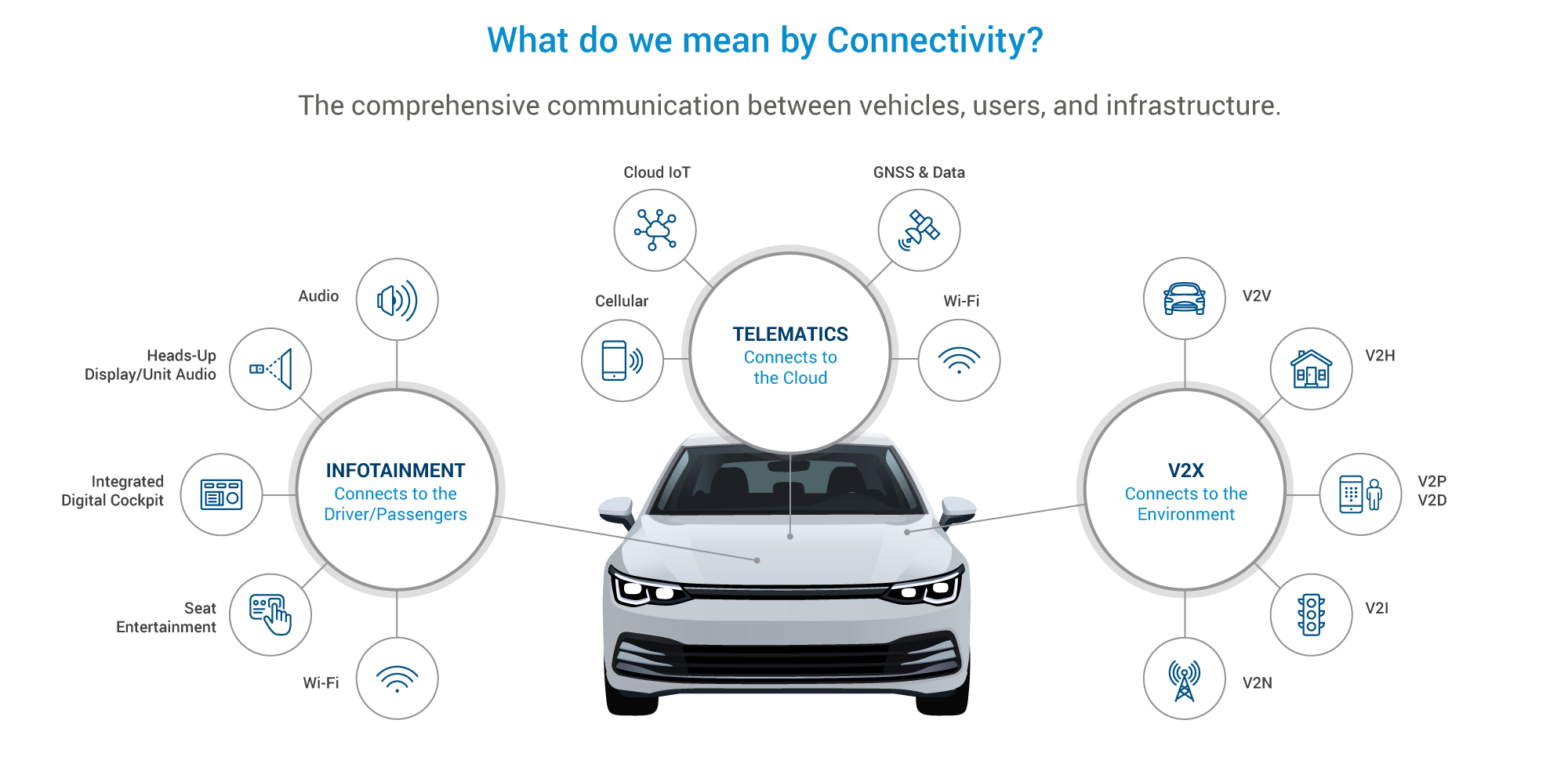
Connectivity
Connectivity is the backbone of the intelligent vehicle revolution. V2X (Vehicle-to-Everything) technology, enabled by 5G's low latency and high throughput, transcends traditional communication. V2V (Vehicle-to-Vehicle) and V2I (Vehicle-to-Infrastructure) create a mesh network of real-time data exchange, empowering vehicles to 'talk' to each other and surrounding infrastructure.
- Collision Avoidance: V2X systems alert drivers to potential hazards, like vehicles in blind spots or upcoming traffic disruptions, even beyond their line of sight. This proactive approach has enormous safety potential.
- Traffic Flow Optimization: Real-time traffic data, facilitated by smart infrastructure like connected traffic lights, assists in congestion reduction. Vehicles can adjust routes or speeds based on this information.
- Fleet Management: V2X connectivity streamlines delivery routes, monitors vehicle health, and improves fuel efficiency through real-time data for commercial fleets.
Data sourced from secondary research.
Semiconductor giants like Qualcomm, NXP, and Autotalks are instrumental in developing V2X chipsets and communication modules. Expect partnerships between these companies and automakers to accelerate deployment.
The future of connected vehicles lies in the expansion and refinement of V2X networks. Increasing deployment, standardization of communication protocols, and robust cybersecurity will be crucial. As 5G coverage grows and V2X technology matures, led by companies like Qualcomm, NXP, and Autotalks, we anticipate a higher rate of increase in intelligent vehicle features. We also expect further innovation in sensor fusion and data analytics, transforming connected cars into nodes within a larger intelligent transportation system.
Electrification
The trend towards vehicle electrification stands as a significant driver in key global markets, accentuated by the critical role of government policies in promoting the rollout, particularly concerning the introduction of new models and the enhancement of consumer engagement. A significant issue is the sustainability of electric vehicle (EV) demand in an environment where governments may reduce policy-driven support, including financial incentives, subsidies, vehicle scrappage schemes, EV-related industrial strategies, and targets set by original equipment manufacturers (OEMs). Short-term projections indicate a tempered demand trajectory, attributed to enduring high interest rates and overall concerns regarding affordability.
The global EV production forecast is expected to reach 18.1 million units in 2024, according to S&P Global. The proportion of BEV relative to total vehicle production globally is predicted to be approximately 14.8% in 2024, marking an increase from 11.7% in 2023. In terms of sales, Bloomberg anticipates that global passenger EV sales will increase by ~20% to 16.7 million units in 2024, estimating about 70% of them to be fully electric vehicles.
The global EV production is expected to reach approximately 47.5 million units by 2030, with a staggering CAGR of approximately 18% from 2024 to 2030 (S&P). Government policies focused on emissions reduction are correspondingly promoting the rapid technology development of EVs. The developments include improved battery technology and wider charging infrastructure which increase range and convenience. Consumers are warming to the idea of EVs given their environmental benefits, improved performance, and sleek designs. Also, the decrement in EV battery pricing, and the increase in mass production facilities for EV component & system manufacturing, are some of the factors responsible for the reduction in EV pricing, which also fuels the EV acceptance rate among global customers. All these factors contribute to a rapidly expanding EV market that's outpacing the growth of traditional vehicles. By 2030, S&P estimates ~49% of the cars produced globally will be EVs.
PHEVs (Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles) combine gasoline engines and electric motors, offering flexibility in fuel use and reduced emissions. In 2024, the adoption of PHEVs is experiencing a notable increase, driven by stricter emissions regulations and growing demand for fuel-efficient transportation options. The ability of PHEVs to switch to gasoline in areas with underdeveloped charging infrastructure also enhances their appeal, providing a flexible solution for users. Despite the current surge in popularity, the long-term outlook for PHEVs indicates a shift. As global efforts to expand and improve EV infrastructure gain momentum, consumer preference is expected to tilt significantly towards fully electric vehicles. This shift is anticipated to lead to a flattening in PHEV market growth post 2026-27, culminating in a stagnant market share by 2030. The rapid development and deployment of comprehensive EV charging networks will likely diminish the strategic advantage of PHEVs, steering the market towards a future dominated by fully electric solutions.
Data sourced from secondary research
The United States presents the most uncertain market, with companies like Ford and General Motors reporting a short-term decline in EV demand, in contrast to Tesla's continued success and steady sales from other manufacturers like Hyundai and Kia. Navigating the complexities of the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) tax credits is expected to become more challenging in 2024. According to Bloomberg, EV sales in the U.S. are projected to be ~ 1.9 million units, making up 13% of new car sales, though there is potential for unexpected downturns due to increasing political polarization.
According to Bloomberg, EV sales in China are anticipated to nearly reach 10 million units, constituting nearly 60% of the global EV market share. However, the growth rate within China is expected to decelerate due to a saturated market in high-growth regions coupled with more challenging economic conditions.
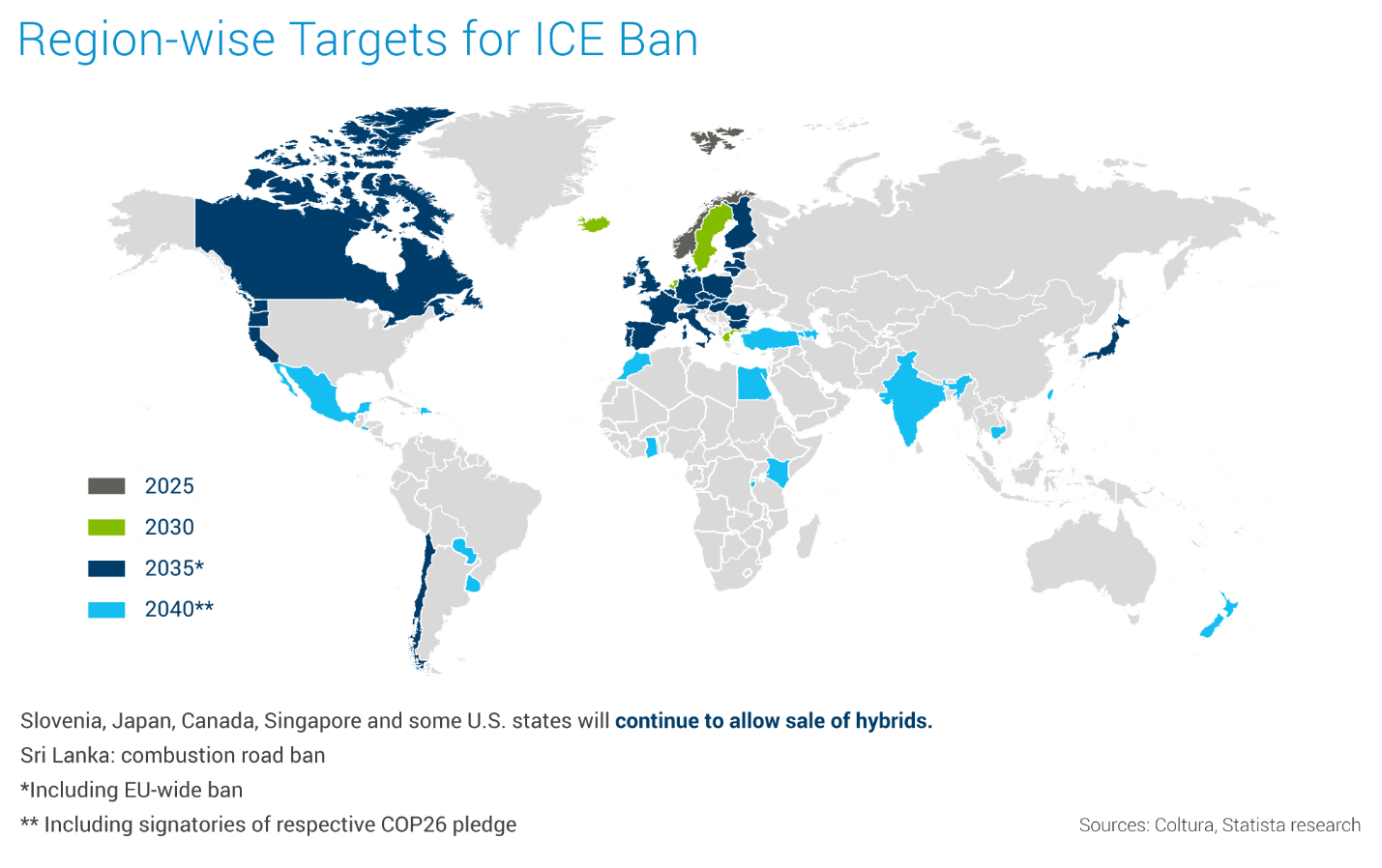
In Europe, EV sales are projected to remain steady as manufacturers anticipate stricter CO2 regulations set for 2025. The reduction of subsidies in key areas and a growing reliance on favorable company-car tax policies are influencing the European EV market, which is expected to see sales of around 3.4 million units, a growth of 8% (Bloomberg). However, EV growth will continue to accelerate over the next five years. Still, EVs could reach a 70% share of the European car market by 2030 (S&P), largely driven by strong regulations. The European Union has agreed to ban the sale of ICE vehicles after 2035. Within this evolving regulatory landscape, Renault's CEO, as reported by Automotive World, highlights the industry's need to work with regulators to define the essential conditions for achieving the 2035 transition. This proactive approach will ensure both feasibility and environmental responsibility, reflecting a strategic pivot not only towards compliance but also towards shaping a sustainable future in alignment with global climate goals.
In the meantime, the EU has set intermediate emissions reduction targets for 2030 as part of the “Fit for 55” climate package — a 55% reduction for cars and 50% for vans — and created incentives for OEMs to produce ZLEVs even sooner. Manufacturers who produce vehicles with emissions between zero to 50g CO2/km, like BEVs and plug-in hybrid vehicles between 2025 and 2029 are eligible for these incentives.
Data sourced from Coltura and Statista Research
The EV market is rapidly expanding, influenced by new entrants and heightened competition among established brands. This competitive dynamic is exemplified by the ongoing pricing wars between giants such as Tesla, BMW, and Mercedes-Benz. Among the newcomers, Afeela, a collaboration between Honda and Sony, is poised for a 2026 launch, adding to the market's diversity.
Established players are employing varied strategies to navigate this evolving landscape. Renault has launched Ampere as a distinct EV and software entity, illustrating a different approach compared to Ford and Mercedes-Benz, which have integrated EV development within their existing structures.
Traditional automakers in North America and Europe have initially focused on higher-margin luxury and performance EV models, reflecting a more cautious approach to fully embracing the electric transition. In contrast, leading Chinese EV manufacturers like BYD have prioritized affordability, targeting a broader market with budget friendly EVs before introducing luxury models. This strategy leverages China's well-established battery supply chain, which significantly lowers battery costs for local manufacturers due to its robustness. Additionally, labor costs in China are generally lower than in North America, enhancing the cost competitiveness of Chinese EVs. India's manufacturing base, while still developing, offers cost advantages that contribute to lower production costs for EVs. Consequently, the average price of locally produced EVs in North America and Europe is estimated at around $60,000, whereas in Asian markets like China and India, it is approximately $25,000.
Chinese EV manufacturers, including BYD, aim to capitalize on their cost-effective production capabilities to expand into the European market, which has shown a strong interest in adopting EVs. However, the starting price for some of the most affordable European-made EVs remains high, around $60,000. With BYD's entry into the European market, offering innovative and more affordable urban-friendly EVs, traditional European EV manufacturers are pressured to reduce their prices to maintain competitiveness. For example, as reported by Forbes, European EV manufacturers, including Tesla, have reduced the price of their models.
ELECTRIC VEHICLE PRICING AND TOP MANUFACTURERS BY REGION
|
Region |
Average Price (USD) |
Top Manufacturers |
|
North America |
$50,000 - $70,000 |
Tesla Ford General Motors Rivian |
|
Europe |
$40,000 - $60,000 |
Tesla Volkswagen Group (VW, Skoda, Audi, Porsche) Stellantis (Fiat, Peugeot, Citroen) Renault-Nissan-Mitsubishi Alliance |
|
China |
$30,000 - $40,000 |
BYD Tesla SAIC Motor (MG) Wuling Motors |
|
India |
$15,000 - $25,000 |
Tata Motors Mahindra MG Motor India |
Data sourced from secondary research
Electric Vehicle (EV) Batteries
A significant decline in lithium-ion battery prices, to the extent of around 30% in 2023 compared to 2022 has been observed in recent years (S&P). Further, battery costs are expected to decrease significantly by 2030. This trend is attributed to a surplus of raw materials and components across the battery value chain, coupled with lower-than-anticipated EV demand. According to data from the US Energy Information Administration, the average price of an EV in the US dropped to $50,798 in December 2023, reflecting a 24.2% decrease from the peak price recorded in the second quarter of 2022. Furthermore, the price of battery-grade lithium carbonate, a critical material, plunged by 80.9% from its 2023 high, settling at $13,575 per metric ton, ex-works China, as of December 27th, 2023 (S&P).
.2024-07-10-17-24-40.png) Data sourced from secondary research
Data sourced from secondary research
The transition to electric vehicles is being led by Chinese OEMs, who are increasingly sourcing battery packs from Chinese suppliers such as CATL with 38.4%, and BYD with 13.1% of the global EV battery market in Jan-Feb 2024 (according to SNE Research). Other major global EV battery suppliers include South Korea’s LG Energy Solutions (13.7%) and Japan’s Panasonic (6.7%).
800V Architectures
The move towards 800V electrical architectures in EVs directly tackles users’ range challenge by enabling ultra-fast charging speeds. It's a leap beyond traditional 400V systems.
- Sub-20-minute Charge Times: 800V-equipped vehicles, when paired with compatible DC fast chargers, can replenish a significant portion of their battery capacity in under 20 minutes, rivaling conventional refueling times. Porsche, Hyundai, and Kia are among the front-runners in this domain along with others.
- Reduced Vehicle Weight: Higher voltage allows for thinner cabling and smaller components, reducing overall vehicle weight and improving efficiency.
- Enhanced Power and Performance: 800V systems support high-performance electric motors, delivering thrilling acceleration and driving dynamics.
The transition to 800V systems will gain significant momentum across the automotive industry with Porsche, Hyundai, and Kia leading the charge. Advancements in power electronics, notably wide-bandgap semiconductors like SiC from companies such as Wolfspeed, are critical enablers. Demand will surge for efficient silicon carbide (SiC) semiconductors, capable of handling the higher voltages and delivering superior switching performance compared to traditional silicon devices. A series of new EV models designed with 800V architectures are expected to be launched in the near future, setting a new standard for fast-charging capability, performance, and overall efficiency.
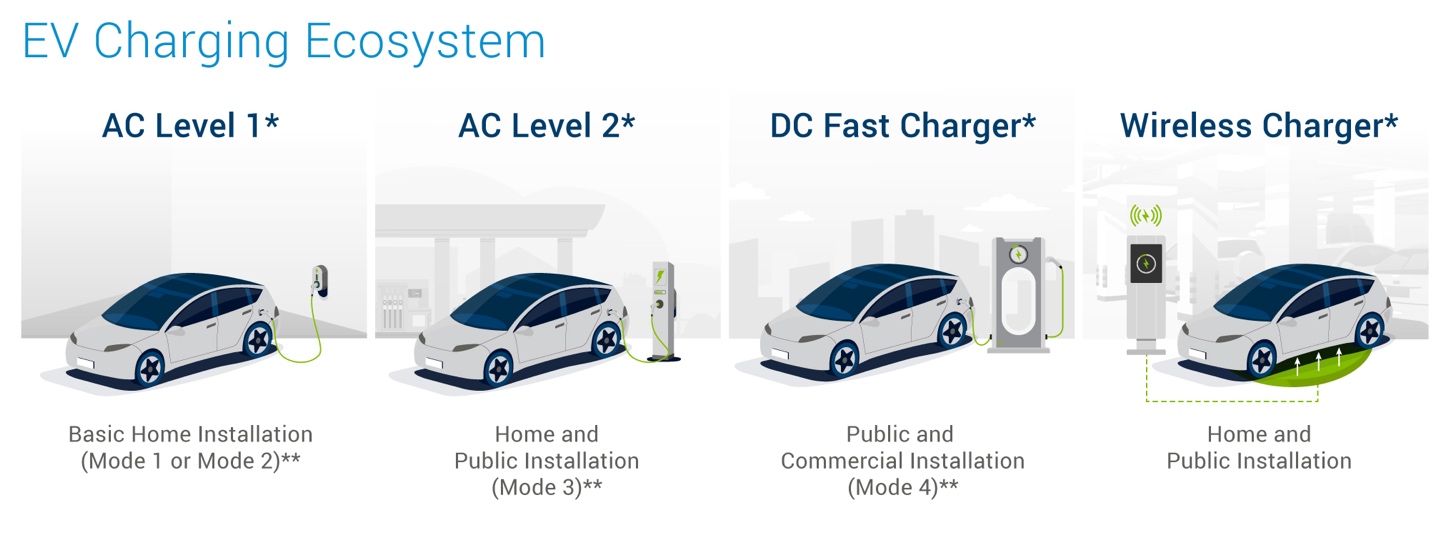
EV Charging Infrastructure
The rapid adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) hinges on the parallel expansion of accessible and reliable charging infrastructure. Global markets reflect regional disparities in charging networks, spurred on by factors like government incentives and consumer demand. The US Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, with its $7.5 billion allocation for a national EV charger network, signals a regulatory push toward standardization.
Data sourced from secondary research
Public DC fast charging is poised for a speed boost as 800-volt systems become more prevalent. Companies like Tesla, Electrify America, and ChargePoint are leading the way in upgrading infrastructure. This technological leap will reduce charging times significantly, mitigating range anxiety and boosting EV appeal.
Automakers are increasingly venturing into the charging business, aiming to supplement vehicle production with strategic control over EV charging networks. Mercedes-Benz exemplifies this shift with its 2023 initiative to deploy a North American network featuring 10,000 chargers, signaling a broader industry move towards OEM-backed charging solutions. General Motors (GM) has joined forces with EVgo to introduce 3,250 DC fast chargers by 2025, aiming to enhance urban and suburban charging accessibility through its Ultium Charge 360 program. Similarly, Ford connects drivers to an extensive charging network via partnerships with Ionity, facilitating easier long-distance EV travel. Rivian is targeting adventure seekers by establishing chargers near outdoor recreational destinations, aligning with its brand ethos.
Even Tesla, known for its Supercharger network, is gradually opening its chargers to other EV brands in Europe, adapting to global EV infrastructure regulations. This strategy not only broadens service offerings but also paves the way for new revenue streams, underscoring automakers' commitment to a comprehensive EV ecosystem. This trend highlights a pivotal industry shift towards integrating vehicle production with charging infrastructure development, demonstrating a strategic approach to fostering EV adoption and enhancing consumer convenience.
While AC chargers have dominated home and office settings, there's a growing shift toward DC chargers in these environments. This offers convenience and faster charging for users without the infrastructure demands of high-powered DC fast-charging stations. We also expect to see these public DC fast chargers getting faster (increasing from 500 volts to 800 volts) and even the replacement of AC chargers in residential, office, or campus settings with slow DC chargers to accelerate that charging solution.
The confluence of these trends indicates a continued expansion of the EV charging market through 2024. While challenges like upfront costs and grid capacity persist, the mix of public investment, technological breakthroughs, and OEM involvement paint a promising picture for large-scale EV adoption soon.
Smart Charging
Smart charging marks a paradigm shift in EV adoption. It goes beyond simply refueling vehicles with electricity, addressing challenges like grid stress, cost, and user convenience. AI algorithms, combined with connected charging infrastructure, are reshaping the EV charging landscape.
- Dynamic Load Balancing: Smart charging optimizes power distribution across multiple EVs. AI-powered systems can prevent grid overload, maximizing renewable energy integration and reducing charging costs.
- Personalized Charging Plans: AI algorithms can learn user preferences, schedule charging during off-peak hours, or utilize solar energy when available. This optimizes convenience and lowers electricity bills.
- V2G/V2H Integration: EVs are transformed into bi-directional energy units. During peak demand, stored energy can power homes (V2H) or be fed back into the grid (V2G), providing stability and potential revenue streams for EV owners. Fermata Energy and Wallbox are pioneers in this domain.
The widespread implementation of V2G/V2H solutions awaits regulatory evolution alongside broader smart-grid development. Companies like Fermata Energy and Wallbox are blazing trails with their innovative solutions. The convergence of AI, big data analytics, and ubiquitous connectivity will unlock sophisticated charging optimization. This will ease grid strain, incentivize renewable energy integration, and enhance consumer ownership experience, driving increased EV uptake. Partnerships like Ford's recent collaboration with Sunrun on home energy solutions point to the acceleration of this trend.
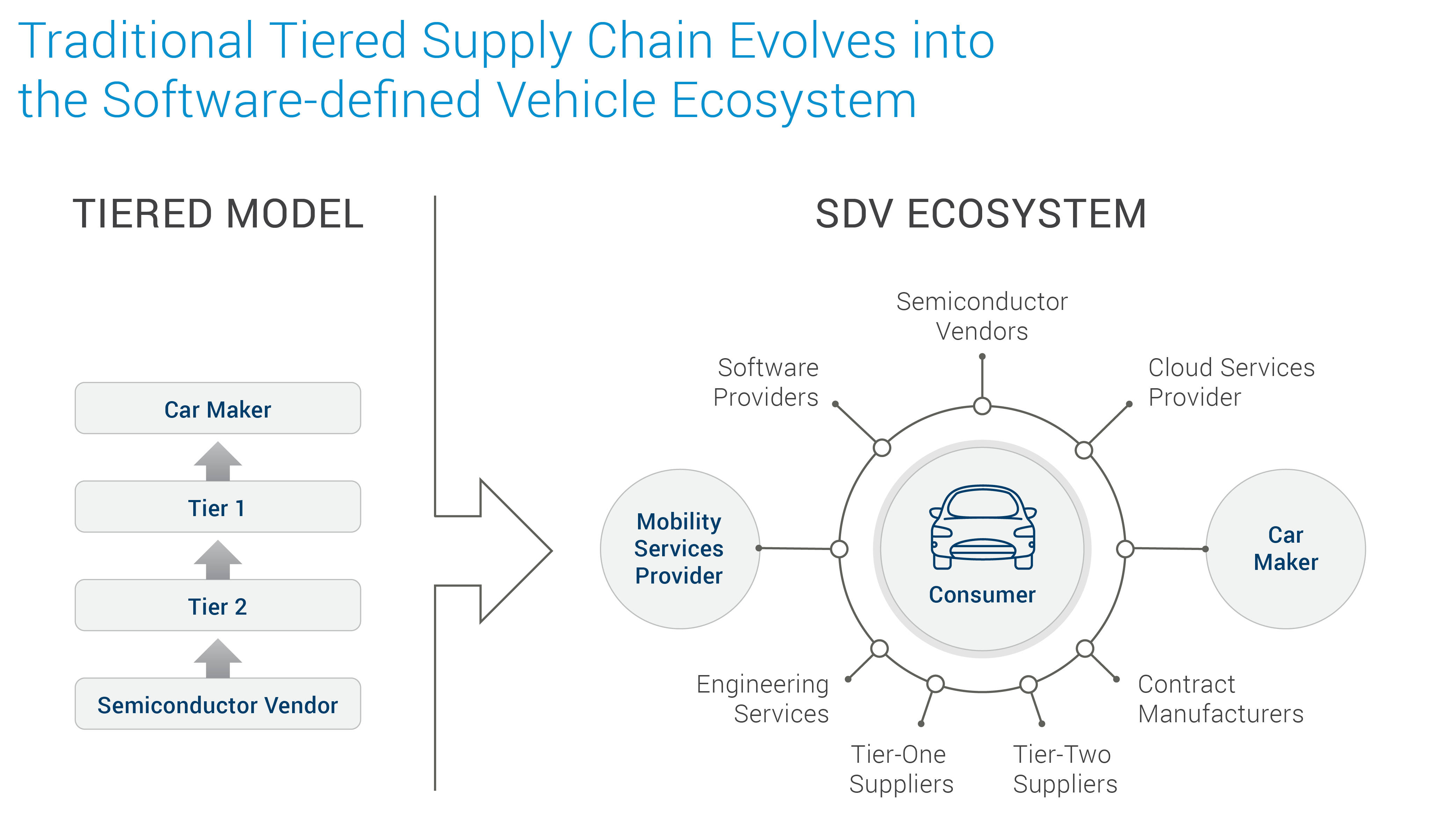
Software Defined Vehicles (SDV)
The automotive industry is on the cusp of a paradigm shift driven by the rapid rise of software-defined vehicles (SDVs). SDVs place software at the core of vehicle design and operation, transforming cars from hardware-centric machines to adaptable, software-driven platforms. This shift allows for unprecedented flexibility, feature updates, personalization, and new revenue streams for automakers. Stating their view on SDVs, IBM highlights the importance of a layered architecture in SDVs, including a strong focus on AI, data platforms, and security, to enable advanced features such as autonomous driving, enhanced user personalization, and robust cybersecurity measures. Standardization and a shift toward a hybrid cloud approach are also noted for their roles in improving developer productivity and enabling scalable, autonomous edge computing solutions within vehicles.
SOFTWARE-DEFINED VEHICLES SIMPLIFIED

Data sourced from secondary research
Key Technologies Enabling the SDV Revolution
- Software Stacks: SDVs rely on modular software stacks , which provide core functionalities while allowing flexible integration of new features. This is similar to how a smartphone operating system enables app installation.
- Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates: OTA updates are the lifeblood of SDVs, allowing the vehicle's software to evolve post-production, like modern smartphones or computers.
- Centralized and High-Performance Architectures: Traditional vehicles have numerous ECUs for individual functions. SDVs move towards a centralized computing model with powerful processors, reducing hardware complexity and enabling sophisticated new features.
Data sourced from secondary research
The transition to software-defined vehicles is not just a technological shift but also a significant market opportunity. As per BCG, by 2030, the SDV market is projected to create over $650 billion in value, with OEM revenues from automotive software and electronics expected to nearly triple. This growth is driven by increasing demand for functionalities that enhance the driving experience, including autonomous driving capabilities, connectivity, and in-vehicle services. Innovation through open-source collaboration is expected to play a crucial role in accelerating SDV innovation. For instance, in 2023, the Eclipse Foundation's Software Defined Vehicle Working Group experienced significant growth, launching new projects and expanding its membership, which includes leading OEMs. They aim to establish production-ready software platforms and foster a vendor-neutral ecosystem, enhancing automotive value chains through open-source processes.
Drivers & Opportunities
- Enhanced User Experience: SDVs allow for continuous personalization, tailoring features to driver preferences from in-cabin ambience to performance modes.
- Post-Sale Revenue Streams: SDVs can be subscription-based or offer payment models such as pay-as-you-go and software upgrades, providing recurring revenue for automakers.
- Operational Efficiency: OTA updates for bug fixes and improved performance can minimize costly recalls and streamline maintenance.
- Fleet Management Optimization: SDVs offer fleet managers real-time updates on vehicle status, driver behavior analytics, and route optimization.
Challenges and Considerations
- Cybersecurity: Increased software complexity creates new attack vectors. Robust security is critical.
- Regulatory Landscape: Regulations surrounding autonomous features and data privacy are still developing.
- Legacy Infrastructure: Some automakers may struggle to transition from traditional hardware-centric architectures.
Use Cases
- Personalized Comfort and Convenience: BMW offering heated seat subscriptions; Mercedes-Benz allowing "acceleration boost" purchases to enhance performance.
- Feature-on-demand: Tesla's Full Self-Driving suite is being offered on a subscription or purchase basis.
- Predictive maintenance: Automakers proactively scheduling servicing based on telematics data and algorithm-driven maintenance needs.
- ADAS (Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems) improvement: Vehicles receiving updated lane-keep functionality or adaptive cruise control enhancements via OTA.
Recent Developments
- Qualcomm & Mercedes-Benz: Advancing Connected and Intelligent Experiences
- Stellantis, Amazon & Foxconn: Software & Smart Cockpit Collaboration
- Bosch & Microsoft: Cloud-based Vehicle Software Development
- General Motors & Red Hat: In-Vehicle Operating System Partnership
- NVIDIA & BYD: Enhanced autonomous driving and intelligent in-vehicle applications
Collaborations between automotive manufacturers and tech companies are central to the SDV evolution. NVIDIA's partnership with BYD, the world's largest EV maker, exemplifies this trend. Leveraging NVIDIA's DRIVE Orin™ platform, BYD aims to create programmable vehicles with centralized computing power, capable of running complex AI algorithms for enhanced safety, and introducing cloud gaming services to enrich the in-vehicle experience.
This shift will reshape industry dynamics, creating new opportunities and challenges. Staying ahead in this rapidly evolving market requires continuous innovation, strategic partnerships, and a clear understanding of the SDV landscape.
Cybersecurity
The automotive industry is rapidly advancing towards unprecedented connectivity and automation, encompassing various technologies such as autonomous driving, connected vehicle systems, and smart mobility solutions. While promising enhanced convenience and safety, this transformation also introduces a new battlefront—the digital realm. Cyberattacks present a growing threat, capable of disrupting vehicle systems, stealing sensitive data, and even compromising passenger safety. As automakers navigate increased complexity and regulatory pressures, a robust cybersecurity posture has transitioned from a competitive advantage to an existential necessity.
Evolving Threat Landscape
The connected car is a complex web of Electronic Control Units (ECUs), sensors, and software, communicating both internally and with external networks. This expanding attack surface offers determined hackers numerous potential entry points. Recent incidents highlight these dangers:
- Remote Exploitation: Researchers and malicious actors have demonstrated the ability to remotely compromise critical vehicle functions on popular models, ranging from disabling brakes to controlling steering. While beneficial for patching vulnerabilities, the rise of Over-the-Air (OTA) updates can create new risks if not adequately secured..
- Supply Chain Attacks: The automotive supply chain's globalization presents additional cybersecurity challenges. Vulnerabilities in a third-party software component can propagate to multiple manufacturers, as seen in recent attacks targeting infotainment systems.
- Ransomware and Data Theft: Carmakers and their associated service providers have become targets for ransomware attacks and sensitive data exfiltration. The potential for financial loss, intellectual property theft, and damage to consumer trust is significant.
Emerging Best Practices
- Proactive Hardware-Software Defense: Cybersecurity can no longer be an afterthought bolted onto existing systems. Hardware security modules (HSMs), secure boot functionality, and the principle of least privilege are becoming standard features. Companies such as NXP Semiconductors and Infineon Technologies are major suppliers of HSMs that are purpose-built for the automotive industry. Their solutions underpin secure authentication and encryption within modern vehicles.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention: Advanced onboard networks are increasingly equipped with systems capable of detecting abnormal behavior. Leading players include Karamba Security, whose software uses behavioral analysis to prevent zero-day attacks, and Upstream Security, which offers a cloud-based platform for connected vehicle monitoring. These act as digital tripwires, identifying potential attacks and triggering countermeasures.
- Robust Encryption and Authentication: Safeguarding communications within the vehicle, as well as interactions with external infrastructure, is critical. Strong encryption standards, combined with digital certificates for device authentication, help maintain data confidentiality and integrity. Escrypt, a subsidiary of Bosch, specializes in embedded security solutions, providing key management and cryptography mechanisms widely used by automakers.
- DevSecOps Practices: Integrating security testing and vulnerability scanning into the automotive software development pipeline is essential. This shift-left approach aims to discover and address flaws early in the process, reducing costly downstream remediation.
Regulatory Compliance and Evolving Standards
The automotive industry is subject to various cybersecurity regulations and standards. These include:
- UNECE WP.29: The United Nations regulations on software updates and cybersecurity have become a global benchmark. Manufacturers must demonstrate compliance through robust governance and technical processes.
- ISO/SAE 21434: This evolving standard provides a structured automotive cybersecurity risk management framework. Adoption is expected to accelerate as stakeholders demand greater rigor and consistency.
- ASIL Ratings and Liability
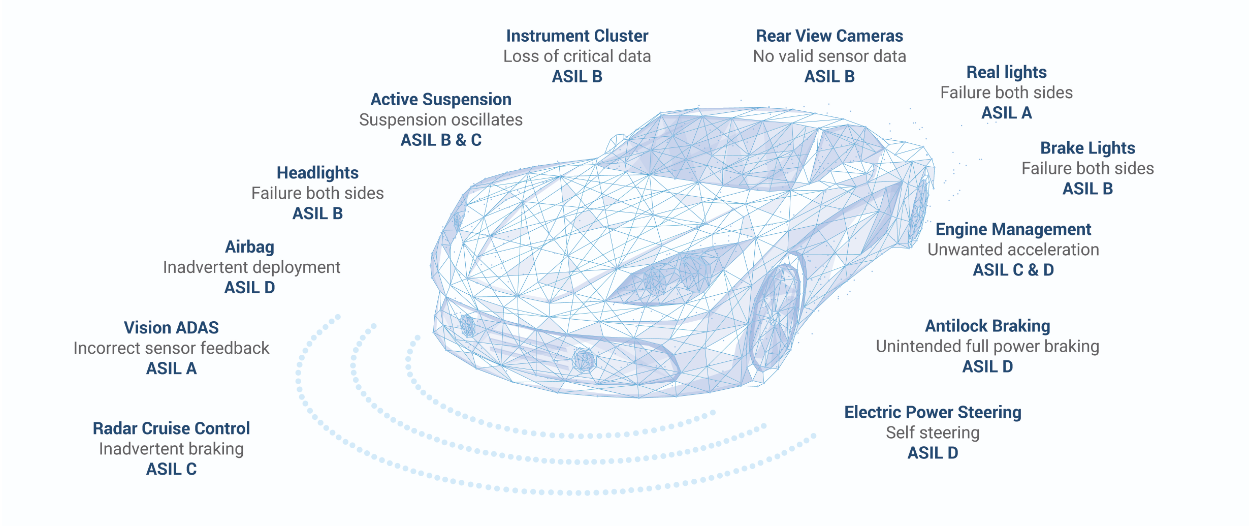
- Automotive Safety Integrity Levels (ASIL) are critical for guiding cybersecurity measures to ensure vehicle safety. ASIL classifications range from A (lowest risk) to D (highest risk), reflecting the potential impact of a component's failure on safety. For instance, components such as braking systems or steering mechanisms, classified typically as ASIL D, require the most stringent security controls due to their direct impact on driver safety.
- As vehicles become increasingly interconnected and reliant on complex software systems, the potential for cyber threats grows. This evolving landscape involves various components and systems, from infotainment units to autonomous driving technologies, each with different ASIL ratings and corresponding security needs.
- Given this complexity, especially within shared ecosystems that include multiple vendors and technology partners, establishing clear liability frameworks becomes crucial. In the event of a cyber incident, determining responsibility can be challenging. For example, suppose a software vulnerability in an infotainment system leads to unauthorized access to vehicle controls. In that case, identifying whether the car manufacturer, software developer, or another third party is liable for damages is vital.
- As a result, the automotive industry is focusing on clarifying these liability frameworks. This involves defining how responsibility is shared among stakeholders and ensuring that all components, regardless of their ASIL classification, meet rigorous security standards to mitigate risks effectively. This comprehensive approach is essential for maintaining trust and safety as automotive technologies advance.
TYPICAL AUTOMOTIVE ASIL CLASSIFICATIONS
Use Cases
- Secure Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates: Tesla has been at the forefront of utilizing OTA updates, not limited to performance enhancements but also to address newly discovered vulnerabilities, demonstrating the agility required in the evolving cyber landscape. HARMAN, leveraging its acquisition of Red Bend Software, offers comprehensive OTA update management platforms, securing the delivery and integrity of software patches to vehicles.
- Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) Security: As vehicles establish communication with infrastructure and each other for safety and optimization, ensuring secure data exchange is paramount. Companies like Argus Cyber Security specialize in V2X-specific security solutions. Major automakers have adopted their multi-layered approach for safeguarding V2X communication channels.
- Collaborative Threat Intelligence: The formation of industry-wide threat-sharing platforms is becoming essential. These platforms enable automakers, suppliers, and cybersecurity firms to exchange information on vulnerabilities, attack patterns, and emerging threats. Industry collaboration in threat intelligence is essential for the automotive sector. By proactively sharing information, the automotive sector can stay ahead of cybercriminals, better protect critical systems, and enhance the safety and security of connected vehicles.
Hydrogen Fuel Cell Technology
Hydrogen-powered vehicle propulsion represents the latest breakthrough in automotive technology with the potential to reduce carbon emissions to nearly zero. Due to its significant environmental benefits, this innovative technology has captured the attention of industry leaders and government agencies in the prototype testing stage.
Leading energy companies such as Shell, which has a strong foothold in the market, are making substantial investments to develop and deploy the necessary hydrogen infrastructure. A notable example of these efforts occurred in August 2022 when Shell, in partnership with H2 MOBILITY Germany, inaugurated a new hydrogen filling station in Wesseling, Germany. This strategic move underscores Shell’s commitment to the hydrogen sector and its goal to become a principal supplier of green hydrogen for industrial and transport applications. Adjacent to the filling station, Shell also operates a 10 MW PEM (Proton Exchange Membrane) electrolysis plant, further bolstering the production of green hydrogen. This infrastructure is pivotal in supporting the widespread adoption of hydrogen-powered vehicles, positioning Shell at the forefront of this transformative industry shift.
LIST OF OPERATIONAL HYDROGEN-POWERED VEHICLES AND THEIR MANUFACTURERS
|
Vehicle |
Manufacturer |
Vehicle Type |
Operational Region(s) |
Technology |
Notes |
|
Toyota Mirai |
Toyota |
Passenger Car |
Japan, California, Europe |
Hydrogen Fuel Cell |
Mass-produced, second generation available |
|
Hyundai Nexo |
Hyundai |
SUV |
South Korea, California, Europe |
Hydrogen Fuel Cell |
Mass-produced |
|
BMW iX5 Hydrogen |
BMW |
SUV |
Europe (Pilot Program) |
Hydrogen Fuel Cell |
Not for general sale |
|
Daimler Trucks GenH2 |
Daimler |
Semi-truck |
Europe (Testing phase) |
Hydrogen Fuel Cell |
Development focus |
|
Hyundai Xcient Fuel Cell |
Hyundai |
Heavy-duty truck |
Switzerland (Operational) |
Hydrogen Fuel Cell |
Growing fleet adoption |
|
Solaris Urbino 12 Hydrogen |
Solaris |
Bus |
Europe |
Hydrogen Fuel Cell |
Increasing deployments in public transport |
|
Wrightbus Hydroliner |
Wrightbus |
Double-decker bus |
Operational in the UK, other regions planned |
Hydrogen Fuel Cell |
Focus on urban transit |
Data sourced from secondary research
Automotive Market
Supply Chain
The automotive supply chain is navigating through a period marked by significant transformations, facing unprecedented challenges and opportunities. This dynamic period is characterized by a rapid shift towards electric vehicles (EVs), driven by environmental considerations and technological advancements. The transition is reshaping the automotive landscape for suppliers and manufacturers, compelling the stakeholders to innovate and adapt to capture higher market share.
The past few years have tested the resilience of the global automotive industry, with suppliers at the heart of the storm. From semiconductor shortages to volatile raw material prices, the supply chain has been under constant pressure. Despite these challenges, the industry has not only endured but also uncovered new growth avenues and profitability strategies. A pivotal factor in this resilience has been the shift to EVs, a movement accelerated by consumer demand and governmental policies to reduce carbon emissions.
 Data sourced from secondary research
Data sourced from secondary research
Suppliers are finding themselves at a critical juncture where innovation in EV technology is not just an advantage but a necessity for market survival. This shift has placed an added strain on suppliers, requiring substantial investment in R&D to keep pace with the changing dynamics.
The industry's shift is also reflected in the changing landscape of vehicle production. North American light vehicle production is projected to stabilize, indicating a mature market adjusting to new norms. At the same time, the demand for EVs is expected to expand significantly. This growth, however, is challenged by factors such as geopolitical tensions and the availability of critical raw materials, which continue to influence production costs and market prices.
Manufacturers are responding by streamlining their operations and reducing complexity, which improves efficiency and aligns with EVs' more straightforward design and production processes. While this strategy is beneficial in reducing costs, it poses new challenges for suppliers accustomed to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. The market's evolution demands that suppliers adapt to new technologies and realign their business models to cater to the emerging needs of EV production.
EV Supply Chain
One notable trend in the Electric Vehicle (EV) supply chain is the increasing emphasis on securing domestic raw materials and enhancing supply chain resilience, particularly in the context of reducing reliance on rare earth elements (REEs) and diversifying away from geopolitical risks associated with certain suppliers, such as China. Federal and state incentives in the U.S., aimed at boosting domestic control over the EV supply chain and incentivizing the recycling of critical raw materials, signal a strategic move towards establishing more secure and sustainable supply chains.
Moreover, the automotive industry's commitment to clean energy and sustainability is further stressed by state goals aiming for carbon neutrality by 2050, driving demand for EV manufacturing, battery production, and the development of charging infrastructure. The integration of Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) concepts, such as Vehicle-to-Home (V2H), Vehicle-to-Infrastructure (V2I), and Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G), demonstrates the potential of connected electric vehicles in enhancing energy management and contributing to smart infrastructure.
The trend towards vertical integration, wherein Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) are developing their battery supply chains and venturing into comprehensive energy ecosystem solutions, highlights a broader industry shift. This approach encompasses battery production and extends to energy storage systems, charging infrastructure, and other services, indicating a move toward offering holistic energy solutions derived from EV technologies.
On the innovation front, the EV and battery industries are witnessing the emergence of new battery chemistries and technologies, such as Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) batteries and silicon anode technology, which hold promise for improving battery performance and energy density. The anticipation of solid-state batteries and the exploration of sodium-ion technology further exemplify the ongoing efforts toward advancing battery capabilities and addressing sustainability and resource efficiency challenges.
The journey toward electrification and the consequent reconfiguration of the automotive supply chain creates opportunities for innovation and collaboration. Suppliers are exploring new partnerships, engaging in mergers and acquisitions, and reevaluating their product portfolios to align with the industry's direction toward electrification. This strategic realignment is crucial for suppliers to remain competitive and capitalize on the growth prospects presented by the EV market.
The EV supply chain's future will undoubtedly be shaped by these emerging trends, reflecting an industry at the cusp of redefining the automotive and energy sectors. As OEMs, suppliers, and governments navigate these developments, strategic partnerships, policy alignment, and continued innovation will be crucial in realizing the full potential of electrification and ensuring a sustainable, efficient, and integrated EV landscape.
Reshoring/Nearshoring Automotive Supply Chains
In the evolving landscape of the global automotive industry, automakers and suppliers are increasingly adopting reshoring and nearshoring strategies to mitigate financial risks and adapt to dynamic market conditions. This strategic shift aims to shorten supply chains, thereby not only reducing freight costs amid rising volatility but also enhancing supply chain resilience against disruptions. The trend towards reshoring is fueled by a desire to bring manufacturing closer to home, a response to the disruptions and economic shocks experienced in recent years, including the pandemic and subsequent global uncertainties. However, implementing these strategies comes with challenges, particularly in establishing robust supply bases in regions such as Mexico, where the capacity of large suppliers is often stretched to its limits. The global shift from a 'just in time' to a 'just in case' supply chain model reflects this new focus on resilience and flexibility, away from the cost-minimization approaches that characterized the past few decades.
The automotive industry's supply chain challenges and priorities in 2024 highlight the necessity of such a transformation. Faced with the dual goals of improving performance and overcoming obstacles to process enhancement, the industry is poised to embrace operational innovations and digital transformation as part of its strategic response. For instance, the US government's Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) has incentivized domestic manufacturing investments for vehicles and batteries. The IRA catalyzes long-term EV supply chain development and attracts significant investment in battery capacity, reducing the US-China capacity disparity. In the next five years, North American EV battery manufacturing capacity is expected to increase by about 20X. Battery suppliers and automakers are targeting numerous US and Canadian locations for new plants.
Strategic placement of these plants near vehicle assembly facilities will reduce transportation costs and create advantages such as enhanced supply chain resilience, increased collaboration opportunities, and quicker adaptability to market changes as global sourcing strategies evolve.
In essence, the drive towards reshoring and nearshoring in the automotive sector is a multifaceted strategy aimed at securing supply chains against future disruptions, optimizing costs, and responding to the shifting global economic landscape.
EV battery recycling and its impact on the automotive supply chain
EV battery recycling is poised to become a pivotal element in the automotive supply chain. It offers a sustainable solution to the challenge of securing critical raw materials while also reducing reliance on geopolitically sensitive sources. This movement is driven by automakers' cost-cutting and sustainability goals, significant regulatory pressures, and the promise of creating circular economies within the industry.
Regulatory initiatives, such as the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 and the EU's comprehensive battery life cycle regulations, are creating favorable conditions for the growth of local recycling industries. These regulations not only incentivize the recycling of EV batteries by offering tax credits and setting ambitious recycling and recycled content targets but also impose requirements on the design and transparency of batteries to facilitate their recyclability.
Technological advancements in recycling processes aim to recover up to 95% of materials like nickel, cobalt, lithium, and copper from end-of-life batteries. These processes, including hydrometallurgical and pyrometallurgical methods, are seeing ongoing innovation to increase material recovery rates and reduce environmental impacts. Key players in the industry, such as Redwood Materials and Li-Cycle, are making significant contributions by investing in expanding the U.S. battery supply chain for recycled materials. These efforts reduce the reliance on new raw material extraction and decrease dependency on imports, reflecting a broader shift towards sustainable material sourcing in the sector.
China currently holds a leading position in the global EV battery recycling industry, benefiting from a more mature recycling ecosystem. In contrast, while the EU and the U.S. are still behind, they are making notable progress, supported by regulatory policies and an increasing recognition of recycling's crucial role in securing a sustainable supply of critical minerals for battery production (BCG Global). This is underlined by collaborative efforts and partnerships among automotive OEMs, battery manufacturers, and recycling companies to build integrated recycling solutions that cover the entire value chain, from battery collection to material recovery. For instance, European and North American markets are developing capacities to meet future demands and regulatory requirements, with projections indicating significant growth in recycling revenues and the potential to alleviate supply chain pressures by providing alternative sources of critical minerals.
The “China+1” Strategy for Global Supply Chains
The "China+1" strategy, increasingly adopted by global OEMs, is a response to diversify manufacturing and reduce dependency on China due to various risks, including geopolitical tensions, supply chain disruptions, and rising labor costs. This strategy pushes component suppliers in the semiconductor, passive components, PCBs, and mechanical parts sectors to explore investment opportunities outside of China, notably in regions like South Asia and Mexico.
Countries like India and Vietnam are becoming significant beneficiaries of this strategy. India, with its robust growth in automotive component manufacturing, is positioned as a global hub, drawing interest due to its improving technology implementation and capacity for high-volume production. This shift not only addresses the de-risking of supply chains but also taps into India's substantial export market, which has seen growth in destinations such as the US and Europe.
Similarly, Vietnam has made considerable developments, especially with its 2030 master plan to enhance infrastructure to support increased manufacturing demands. This includes the development of expressways, a deep-water port, and high-speed rail routes, essential for bolstering its role in global supply chains.
Moreover, Mexico is emerging as a crucial player due to its proximity to the US and its capacity to manufacture multiple products locally, which is attractive for nearshoring strategies.
The adoption of the China+1 strategy not only mitigates risks but also leverages the technological and manufacturing strengths of these alternate destinations, fostering a more resilient and diversified global supply chain landscape.
Impact of AI on Supply Chain
In the face of a complex and disrupted global supply chain, artificial intelligence (AI) is a powerful tool for streamlining operations and enhancing efficiency. Jabil’s 2024 Supply Chain Resilience Survey showed that nearly 200 supply chain and procurement decision-makers from some of the world’s leading product brands are planning for and already using AI in their day-to-day processes. The insights provided by the participants highlight key best practices for successfully integrating AI within our supply chain operations.
- The surge in AI applications within supply chain management is largely concentrated on enhancing demand planning and inventory management. By leveraging predictive analytics, organizations aim to improve forecasting accuracy and efficiency, optimize resource distribution, and address the imbalance between supply and demand.
- A "data-first" mentality is critical for harnessing AI's full potential in supply chain operations. Success hinges on establishing a robust data management infrastructure and governance framework prior to deploying AI tools. This foundation ensures data reliability and fosters meaningful insights, underscoring the importance of collaboration and data sharing among stakeholders.
- Preparing the workforce for AI integration involves addressing potential concerns about job displacement and emphasizing AI's role in augmenting human skills. By providing training and hands-on experience with AI technologies, companies can facilitate a smooth transition towards more automated and efficient supply chain processes.
Use Cases – Using Super Trends as Part of Supply Chain
Blockchain in the Automotive Supply Chain
BMW is pioneering the use of blockchain technology to enhance transparency and ensure the ethical sourcing of critical materials like cobalt. The "PartChain" project exemplifies this endeavor by ensuring the traceability of components and raw materials across their international supply chain. By leveraging blockchain, BMW aims to facilitate tamper-proof data sharing across the supply chain, optimize procurement processes, and establish a new level of digitalization in purchasing.
Hyundai has implemented blockchain to streamline the supply chain for replacement parts. This innovative approach targets combating counterfeit parts, thus ensuring the reliability and integrity of automotive components.
AI for Supply Chain Resilience
Toyota leverages AI-powered demand forecasting to fine-tune inventory levels, minimizing waste and maximizing efficiency. This strategic use of AI aids in aligning production with market demand, ensuring a lean and responsive supply chain.
Stellantis employs predictive analytics, another facet of AI, to preemptively identify potential bottlenecks within the supply chain. By adopting such advanced analytics, Stellantis can implement proactive strategies to mitigate risks, thereby enhancing overall supply chain resilience.
Automotive Market
Jabil Insights & Strategic Considerations
The automotive market faces a mixed outlook marked by gradual recovery and ongoing challenges. While easing supply chain bottlenecks and inventory replenishment support moderate growth, persistent inflation, geopolitical turbulence, and rising interest rates restrain further expansion. However, the electric vehicle (EV) segment offers a bright spot, with an estimated CAGR of ~18% between 2024 and 2030, demonstrating the continued appeal of sustainable mobility options. Despite the early 2024 slowdown attributed to a variety of factors, including economic headwinds and geopolitical tensions, the sector is expected to rebound robustly by mid-year. This anticipated recovery is buoyed by improving supply chain dynamics, policy support adjustments, and evolving consumer sentiments toward sustainability and electric mobility.
Technological innovation, driven by ACES technologies (autonomous, connected, electric, and software-defined/centralized architecture), continues to transform the automotive landscape, reshaping consumer choices. The trade-off for consumers is becoming more pronounced: the price of EVs must be weighed against their superior performance, range, and sustainability benefits. Alongside this, while the excitement around autonomous driving technologies persists, a realistic assessment is necessary. Current autonomous driving capabilities offer significant assistance but fall short of full autonomy. Overcoming regulatory hurdles and achieving widespread consumer acceptance will likely extend into 2030 or beyond, however, semi-autonomous vehicles (autonomy levels 2+ & 3) are expected to make significant inroads in the near future.
Geopolitical uncertainties pose significant risks to the industry's global operations. Supply chains remain vulnerable to disruptions caused by conflicts, trade tensions, and political instability. These factors influence regional market dynamics and raw material costs, particularly for vital EV battery components.
Amidst these challenges, strengthening partnerships between Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) and semiconductor manufacturers becomes crucial. Stellantis and Infineon Technologies, for example, have formed a significant alliance with their Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) for a multi-year supply of silicon carbide (SiC) semiconductors. Valued at over €1 billion. This deal is set to enhance the efficiency and performance of Stellantis' EVs using advanced SiC technology. Further highlighting this, a McKinsey report points out that the SiC market is projected to grow from $2 billion in 2024 to $11-14 billion by 2030. This surge is largely driven by the automotive industry, with approximately 70% of SiC demand expected to originate from electric vehicles (EVs), particularly due to their compatibility with inverters. These dynamics underline the critical importance of strategic collaborations between OEMs and semiconductor manufacturers in ensuring a reliable supply of high-efficiency components essential for modern EV powertrains.
Sustainability is becoming a central focus across the automotive industry, transcending specific powertrain types. As part of this comprehensive shift, ethical mineral sourcing, the increased use of recycled and sustainable materials, and effective end-of-life battery management strategies have become essential components of a truly sustainable transformation. While the shift towards EVs highlights these issues, they are relevant and critical to all areas of automotive manufacturing.
The automotive industry is poised to face a pivotal year in 2024, coinciding with the U.S. general elections. Political events of this magnitude often lead to substantial shifts in trade policies, environmental regulations, and government incentives, particularly concerning electric vehicles (EVs) and renewable energy initiatives. Potential revisions in trade agreements and fuel efficiency standards, coupled with federal support for sustainable practices, are likely to influence strategic planning and investment decisions across the sector. As a result, these anticipated changes introduce significant uncertainty, compelling industry stakeholders to carefully navigate their future strategies.
To sum up, the automotive industry in 2024 is navigating a landscape marked by both challenges and opportunities. The temporary downturn in the EV market is seen as a short-term obstacle, with expectations of a significant uptick in growth post-mid-2024. Concurrently, the industry is closely watching the political climate in major markets like India and the U.S., understanding that election outcomes could have far-reaching implications for policy frameworks, market dynamics, and the global push toward sustainable mobility. In this context, agility, foresight, and strategic alignment with evolving regulatory and economic environments will be key to driving success in the coming years.
Key Takeaways
- Measured Recovery with Bright Spots: The automotive industry's rebound faces headwinds, yet the EV sector demonstrates robust growth potential. A predicted short-term slowdown is expected to recover by June 2024.
- ACES Drive Innovation: Technology advancements shape the future, although autonomous driving faces a slower adoption curve.
- Price vs. Performance Dilemma: EV costs must be balanced against sustainability and performance advantages for wider consumer acceptance.
- Geopolitics Disrupt and Influence: Global events continue to introduce volatility into supply chains and regional markets.
- Sustainability: In response to stringent environmental regulations, OEMs are compelled to adopt a comprehensive sustainability framework, particularly in Europe. This encompasses responsible material sourcing, environmentally conscious production processes, and robust end-of-life vehicle recycling programs. These measures are not merely strategic initiatives but essential compliance requirements to meet European legal standards.
- Uncertainty from General Elections: The upcoming elections in India and the US could influence government spending, regulations, and consumer behavior, impacting specific segments and markets.
Jabil Spend Analysis
JABIL SPEND IN THE AUTOMOTIVE SECTOR, BY CATEGORY (2020 VS 2023)
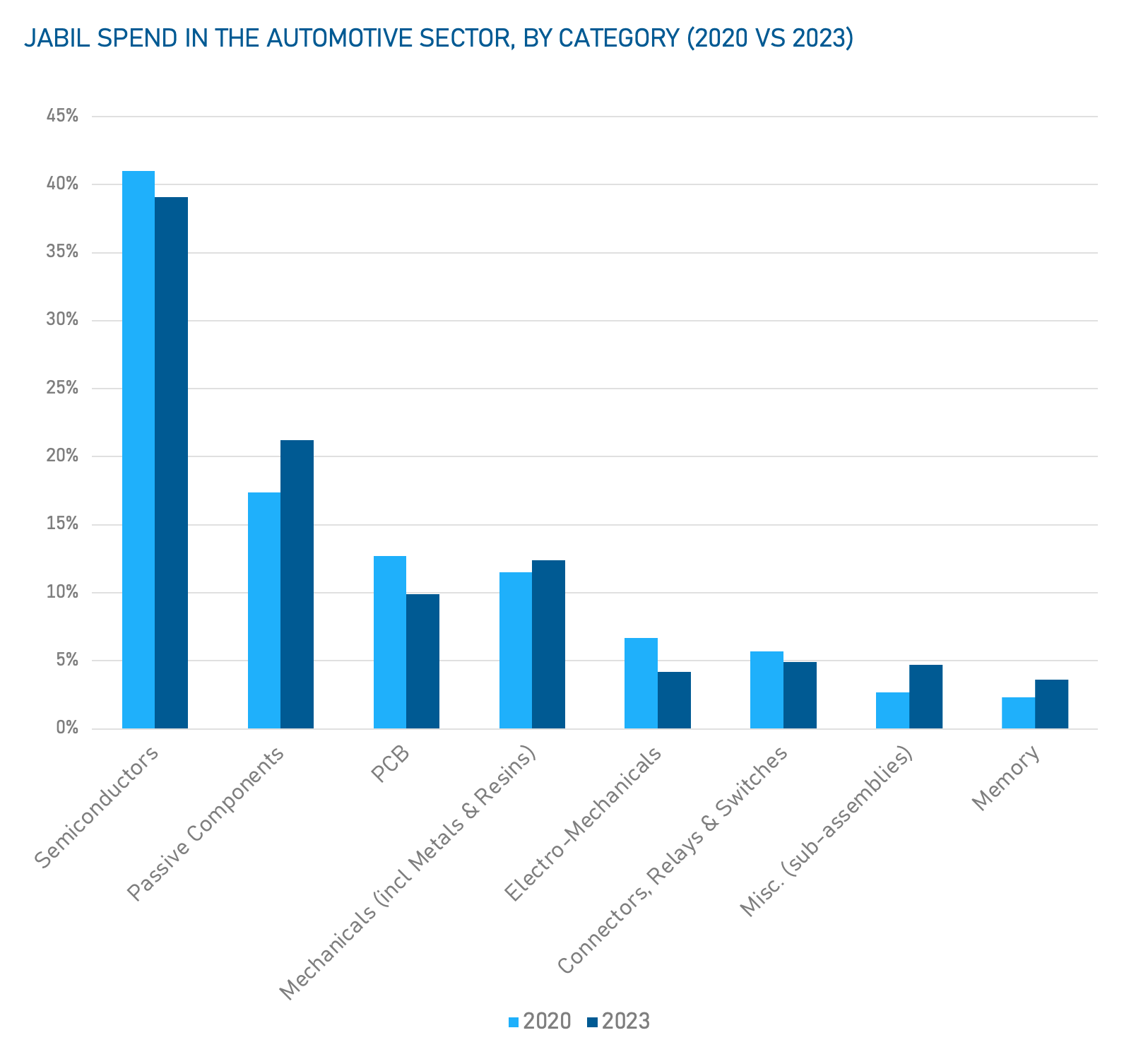
Data based on Jabil's historical spending data for the Automotive Customer Segment
JABIL CATEGORY SPEND IN THE AUTOMOTIVE SECTOR YOY (%)
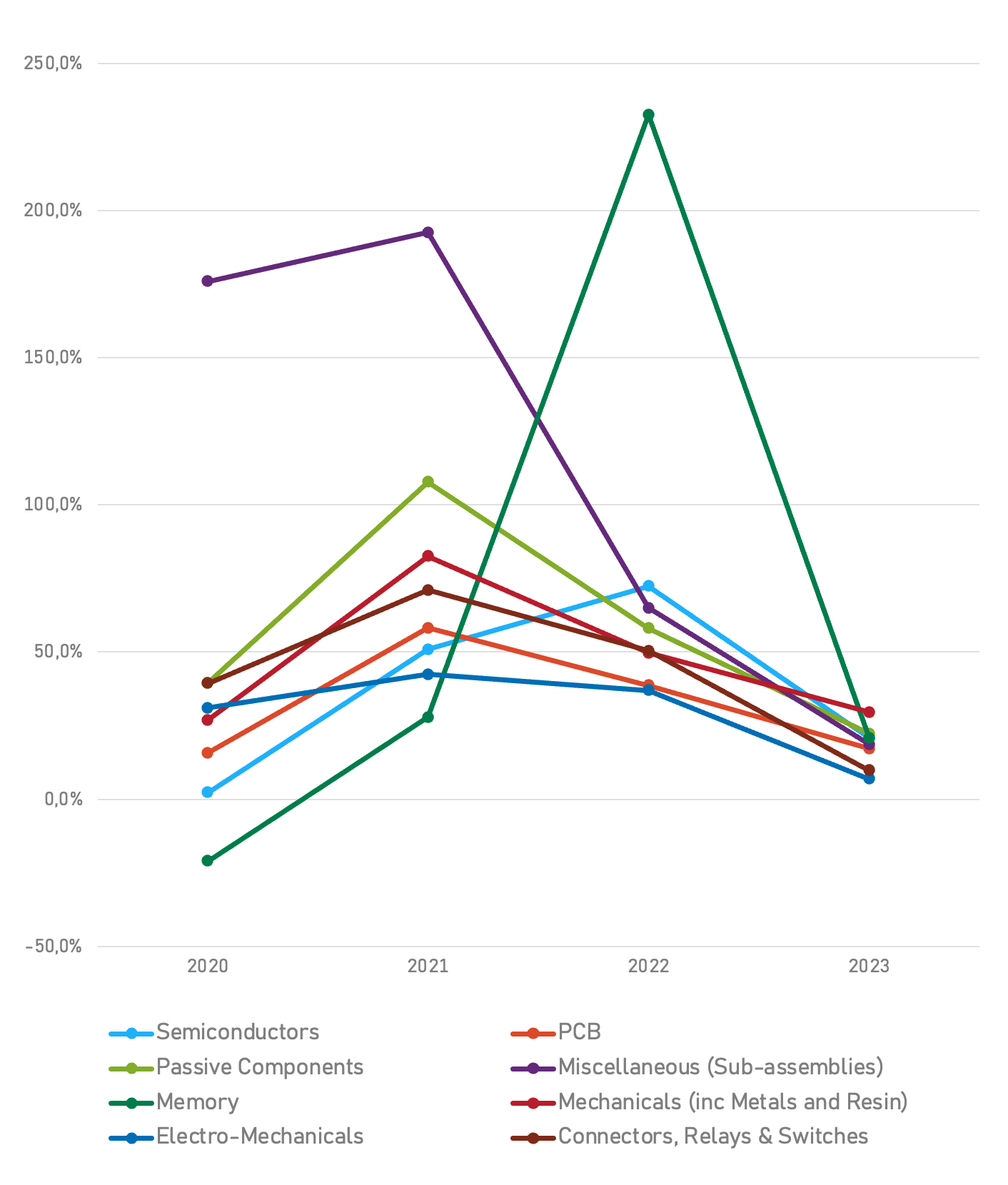
Data is based on Jabil's historical spending data for the Automotive Customer Segment.
![]()
Data based on Jabil's historical spending data for the Automotive Customer Segment
Strategic Considerations
Competitive Scenario
The automotive market is undergoing an extraordinary transformation as tech-focused companies and ambitious EV startups directly challenge the long-standing dominance of traditional automakers. Companies such as Tesla, Lucid, and Rivian have spearheaded the EV revolution, demonstrating the potential of innovative software and sleek electric powertrains. Chinese EV makers like BYD and Nio are rapidly expanding their global presence. Meanwhile, technology giants such as Google (Waymo) and Apple (Project Titan, which has been anonymous but anticipated to be halted now) have been investing heavily in autonomous driving. These investments point to a future where increased vehicle autonomy could profoundly disrupt transportation models, offering end customers more diverse options.
Shifting Business Models
The traditional model of car ownership is evolving. Subscription-based services from companies like Volvo and Porsche offer consumers an alternative to purchase, providing flexibility for those who desire a variety of vehicle experiences. Manufacturers like Tesla and Polestar lean into direct-to-consumer sales models, cutting out dealerships and allowing for better control over the customer experience. Simultaneously, mobility-as-a-service (MaaS) platforms like Uber and Lyft have profoundly altered urban transportation, reducing the perceived need for personal car ownership in many major cities worldwide.
Evolving EMS Relationship
The relationship between automotive OEMs and EMS providers continues to evolve. EMS companies have been moving beyond the standard role of component suppliers and becoming integral to the design, engineering, and production of complex automotive technology. This "EMS+" evolution allows partnerships to develop entire sub-systems like advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) or battery packs.
Co-Creation Model
Co-creation has emerged as a key strategy in the automotive industry over recent years, characterized by joint ventures and technology incubators that drive innovation. This collaborative model enhances the development of cutting-edge technologies, such as battery systems and software platforms, and supports the creation of flexible manufacturing facilities that can quickly adapt to changing market demands. Notable examples include Stellantis and Foxconn's joint effort on advanced infotainment systems and Magna Steyr's partnership with Fisker, which facilitates the rapid scaling of EV production. These partnerships exemplify how co-creation fosters innovation and agility in the fast-paced automotive industry.
Automotive Market
Appendix
Key References
- New IRA guidance limits battery components made in China
- The UAW won big for future EV battery plants
- Upstream’s 2024 Automotive Cybersecurity Report
- Global EV battery market share in Jan-Feb 2024
- Electric vehicles and hybrids surpass 16% of total 2023 U.S. light-duty vehicle sales
- Electric vehicle battery prices are falling faster than expected
- The decline in battery metal costs drives down electric vehicle prices
- Electric Vehicle Market Looks Headed for 22% Growth This Year
- Combustion Going Bust: Global Phase-Outs Of Gasoline Cars
- These states will dominate EV battery manufacturing in 2030
- Renault confirms talks with VW to partner on small EV
- Rewriting the Rules of Software-Defined Vehicles
- BYD, World’s Largest EV Maker, Partners With NVIDIA
- The Future of Supply Chain Management is Risk Management
- Striking Gold with EV Battery Recycling
- AI Deployment in Your Supply Chain Organization
- India is poised to become a global hub for automotive component manufacturing.
- OnSemi reveals electric vehicle silicon carbide deal
- New silicon carbide prospects emerge as market adapts to EV expansion
Back to Top
