By clicking the “I Accept” button, or by accessing, participating, or submitting any information, or using the Jabil Global Intelligence Portal or any of its associated software, you warrant that you are duly authorized to accept the Global Intelligence Portal Terms and Conditions on behalf of your Company, intending to be legally bound hereby, and your company shall be bound by the terms and provisions of the Global Intelligence Portal Terms and Conditions, accessible under the following link Portal T&Cs.
Sector Market Report
Cloud & Storage
Sector Market Report
Cloud & Storage
This report explores current Cloud & Storage Market trends, covering market dynamics such as key growth drivers, challenges, competitive landscape, and insights from Jabil to provide a comprehensive view of the industry's future.
Cloud & Storage Market
Introduction
The 2024 market intelligence report provides an in-depth analysis of the rapidly evolving Cloud and Storage sector. Understanding the factors driving growth and the challenges impeding progress is crucial for informed decision-making and strategic planning in this dynamic environment.
The cloud and storage industry is experiencing significant expansion, driven by the widespread adoption of Internet-connected devices and the increased use of Big Data and real-time analytics. These elements create a fertile ground for innovation and growth.
Businesses increasingly incorporate cloud and storage into their modernization strategies to enhance agility, scalability, and operational efficiency. Integrating Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) further enhances these capabilities, creating new growth opportunities and value.
The global increase in Internet-connected devices generates large volumes of data, necessitating cloud-based storage, processing, and analysis solutions. This trend fuels demand for cloud-based IoT platforms, edge computing solutions, and real-time analytics services. Additionally, the exponential growth of data from diverse sources emphasizes the need for scalable storage and processing. Cloud-based big data platforms and analytics tools enable organizations to derive actionable insights, foster innovation, and maintain a competitive edge.
Integrating IoT, Edge Computing, and 5G technologies is transforming the landscape, facilitating real-time data processing and analysis. Cloud providers are leading this transformation by offering integrated solutions that leverage edge computing to drive innovation.
Exploring adjacent opportunities within the market can lead to new avenues for growth, diversification, and strategic partnerships. These adjacencies offer a roadmap for meeting evolving customer needs and staying competitive.
Despite the industry's rapid growth, challenges such as intense competition, security concerns, and environmental considerations remain. Addressing these challenges is essential for sustaining long-term growth and ensuring the industry's resilience.
Intense competition among cloud service providers highlights the importance of strategic partnerships and collaborative engagements. Forming alliances to meet evolving market demands is crucial for driving innovation and fostering growth. Ensuring robust security measures and compliance standards is critical in an environment with many Internet-connected devices. Cloud providers must proactively address security concerns to safeguard sensitive data and build customer trust.
Moreover, increasing energy and water consumption in data centers poses environmental challenges, necessitating sustainable practices and resource-efficient technologies. Balancing operational efficiency with ecological responsibility is vital for long-term viability.
Looking to the future, the cloud and storage industry is poised for continued innovation and expansion. By leveraging advancements in AI, IoT, Edge Computing, and 5G, organizations can unlock unprecedented opportunities for growth and efficiency. However, staying ahead will require addressing complex challenges, such as enhancing security measures and adopting sustainable practices. Strategic collaborations and a proactive approach to emerging trends will be essential for navigating this rapidly changing landscape and ensuring long-term success in the cloud sector.
Cloud & Storage Market
Market Dynamics
Market Overview
The Cloud & Storage industry is rapidly evolving, and it is crucial to understand the factors that drive growth or hinder progress.
Growth enablers include the increasing digital transformation across businesses, the growing adoption of Internet-connected devices worldwide, the increasing use of Big Data, Edge Computing, 5G, and real-time analytics driven by AI/ML, and finally, what we call “Adjacencies”—adjacent areas within the market that present opportunities for expansion, diversification, or strategic partnerships.
Growth inhibitors include the increasing level of competition coupled with challenges in finding suitable partners, data security and online security concerns, and growing problems with aspects of the Cloud Market that have potentially adverse environmental and regulatory impacts.
In 2023, the Cloud & Storage Market reached a valuation of USD 587.78 billion. Forecasts show significant expansion, with projected figures from USD 676.29 billion in 2024 to USD 1.44 trillion before the end of this decade and up to an impressive USD 2.29 trillion by 2032, according to Fortune Business Insights.
Experts predict a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 16.5% from 2024 to 2029, with some envisioning an even more robust CAGR of 18.8%.
Public cloud spending is estimated to reach USD 592 billion by 2027, mainly driven by Software as a Service (SaaS). The Cloud & Storage Market is increasingly driven by generative AI-based cloud services, which are expected to revolutionize industries worldwide and thus become an attractive investment avenue.
Opportunities for Growth
The key drivers behind the Cloud & Storage Market's continuing expansion include digital transformation, the ever-increasing utilization of Internet-connected devices, the growing reliance on Big Data and real-time analytics, and related adjacencies.
Increasing Digital & AI Transformation Across Businesses
Digital transformation necessitates a multifaceted approach, with cloud computing central to many businesses’ modernization efforts. This shift towards cloud-based solutions empowers companies to move away from legacy systems, fostering agility, scalability, and operational efficiency. Cloud services are the foundation, offering adaptable infrastructure, on-demand scalability, and universal accessibility. These attributes empower businesses to streamline operations, foster collaboration, and accelerate innovation – all critical aspects of a successful modernization journey.
Despite the widespread adoption of digital and AI transformations by 89% of large companies globally, they have only realized 31% of the projected revenue increase and 25% of the anticipated cost savings, as reported by Harvard Business Review. Utilizing McKinsey's Finalta benchmark to monitor and analyze the performance of 80 global banks over four years, it's evident that companies at the forefront of digital transformation are generating substantially higher shareholder value than their counterparts lagging. They often achieve this by creating value that proves difficult for competitors to replicate.
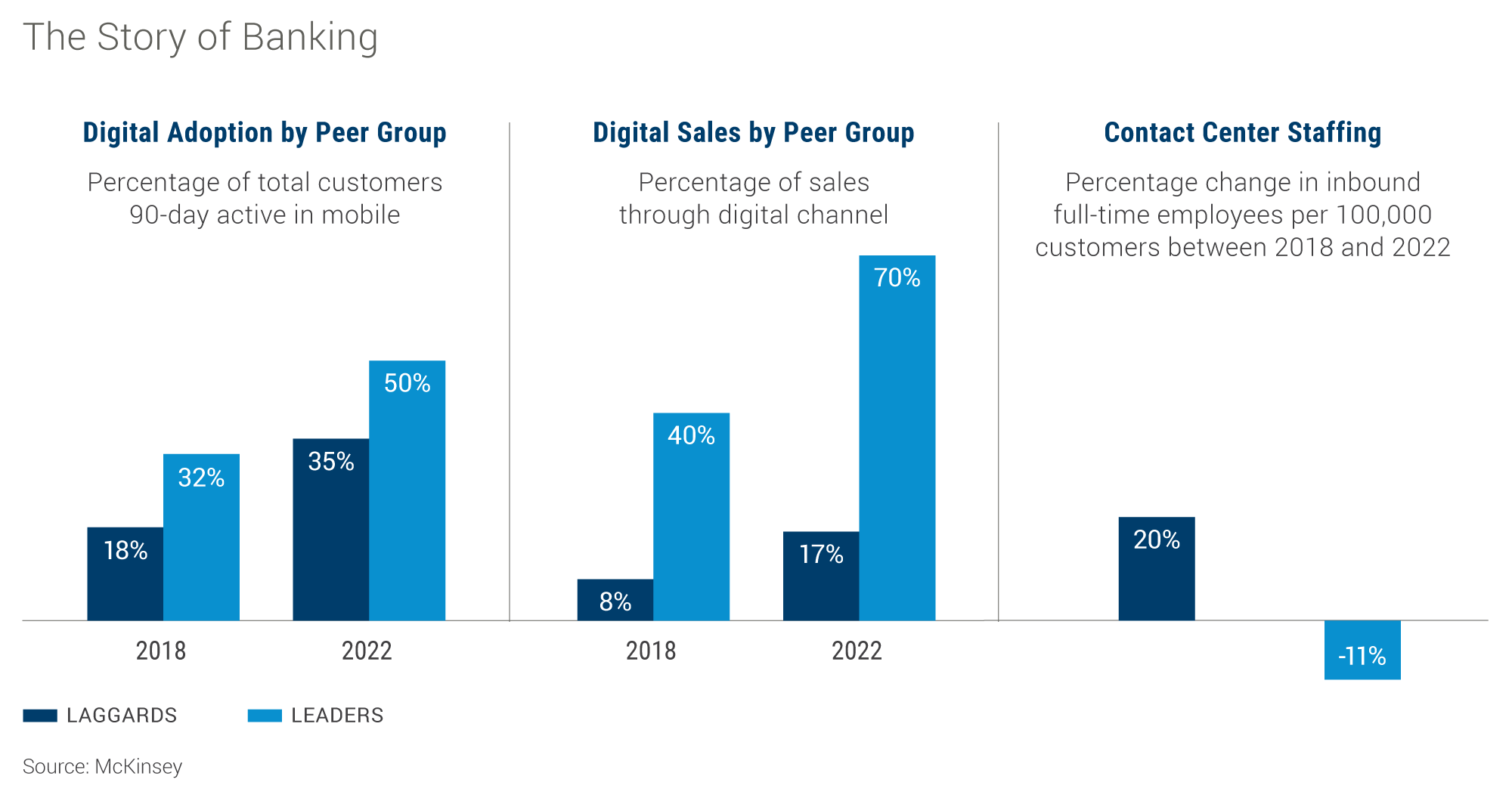
Data sourced from McKinsey
This shift presents market opportunities as the demand for cloud-based solutions supporting digital transformation initiatives continues to surge. Services like cloud migration, cloud-native application development platforms, and integrated cloud ecosystems enabling seamless data sharing and collaboration across various entities are in high demand as businesses strive to stay ahead in the digital age.
Growing Internet and Mobile Device Adoption Across the Globe
The proliferation of Internet-connected devices, including smartphones, IoT sensors, and intelligent appliances, generates vast amounts of data that require storage, processing, and analysis in the cloud, fueling the demand for cloud computing services.
The implications are that cloud computing is essential in managing and analyzing data generated by Internet-connected devices. It enables businesses to derive actionable insights, improve decision-making, and deliver personalized experiences to customers.
This creates a rising demand for cloud-based IoT platforms, edge computing solutions, and real-time analytics services that efficiently process and analyze data from Internet-connected devices. Additionally, there is a growing need for cloud-based security solutions to protect sensitive data transmitted between devices and cloud servers.
Increasing Use of Big Data and Real-Time Analytics
Data growth from various sources, including social media, sensors, and transactional systems, gives businesses opportunities and challenges to extract value from this data.
The implications are significant, as cloud computing provides scalable storage and processing capabilities for big data analytics, allowing organizations to uncover insights, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions.
The rising demand for cloud-based big data platforms, data lakes, and analytics tools that can handle large volumes of structured and unstructured data is creating opportunities for:
- Innovation in data processing and analysis
- Enhanced decision-making through advanced analytics
- Cost-effective scalability and flexibility in data management
- Improved insights generation and business intelligence
- Accelerated development of AI and machine learning applications
- Expansion of data-driven strategies and initiatives across industries
Additionally, there is a growing need for cloud-based data integration and governance solutions to ensure data quality, consistency, and compliance across disparate data sources.
Implementation of IoT, Edge Computing, 5G, and Real-Time Analytics
With the rise of Internet-connected devices, there is a growing trend toward edge computing, where data processing and analysis occur closer to the source of data generation. Cloud computing providers are incorporating edge computing capabilities into their services to support the efficient data processing from these devices, thereby further driving the adoption of cloud services.
The convergence of IoT, Edge Computing, and 5G technologies decentralizes computing resources and enables real-time data processing and analysis at the network's edge. Analyzing data from Internet-connected devices improves operational efficiency, supports real-time decision-making, and improves user experiences.
During the past year, South Korea and China have seen significant progress in 5G implementation due to their high adoption rates and focus on expanding coverage. One of the leaders in cloud and 5G deployment, South Korea has achieved high adoption rates (around 42.4%) and extensive coverage across cities, according to the industry organization GSMA. Following closely behind, China has many cities with 5G access (over 356) and growing adoption rates (estimated at 36.3%). With an adoption rate of 36.6%, the United States lags behind South Korea and China but holds the record for the most cities with 5G availability.
Cloud computing complements edge computing by providing edge devices with centralized management, orchestration, and analytics capabilities. This hybrid approach enables businesses to leverage the cloud's scalability and flexibility while harnessing the low latency and real-time processing capabilities of edge computing.
There is a growing demand for cloud-based edge computing platforms, 5G-enabled services, and IoT solutions that seamlessly integrate with cloud infrastructure. Additionally, cloud providers can offer edge-to-cloud connectivity solutions and edge-based AI/ML algorithms for real-time analysis of data generated by Internet-connected devices.
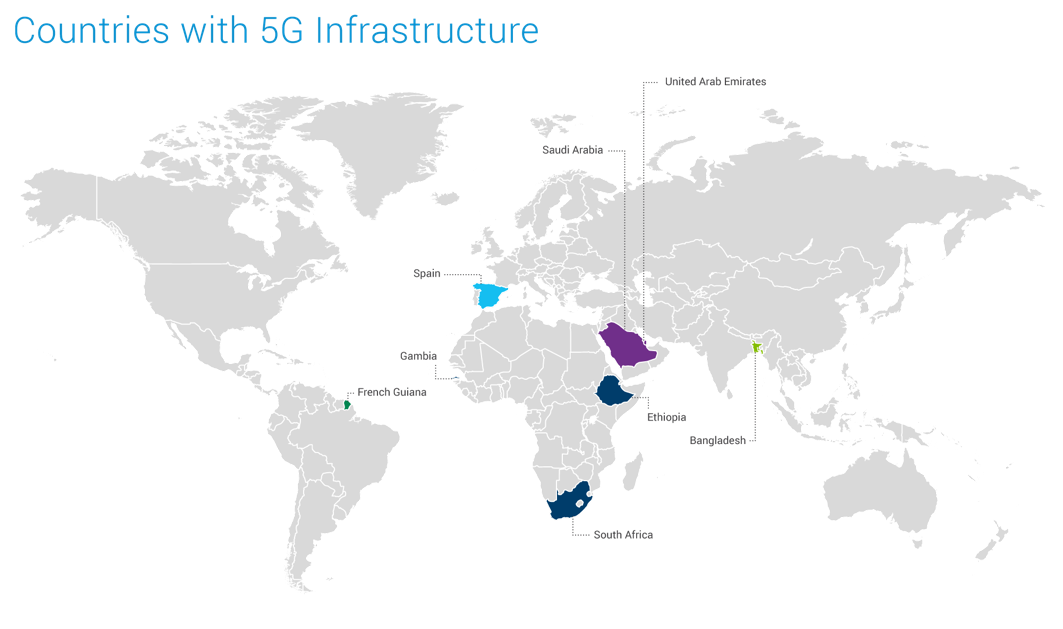
LIST OF COUNTRIES THAT DEPLOYED 5G INFRASTRUCTURE POST-DECEMBER 2022
|
Region |
Country |
Operator(s) |
Deployment Type |
Deployment Year |
|
Africa & Latin America |
Ethiopia |
Safaricom Ethiopia |
5G |
Aug 2023 |
|
Gambia |
QCell |
5G |
Jun 2023 |
|
|
French Guiana |
Orange Caraibe, SFR Caraibe |
5G |
2023 |
|
|
South Africa |
Telkom South Africa |
5G |
2023 |
|
|
Asia |
Bangladesh |
Teletalk |
5G |
Dec 2023 |
|
Europe |
Spain |
Orange, Telefónica |
5G (Standalone) |
2023 |
|
Middle East |
Saudi Arabia |
Zain |
5G (Standalone) |
Mar 2023 |
|
United Arab Emirates |
E& |
5G (Standalone) |
Feb 2023 |
Data sourced from Secondary Research
Adjacencies
The advancements in AI are driving growth adjacencies, or areas connected or newly connected to these new developments. For example, the dramatic rise in AI adoption has reshaped the Cloud Computing Market. The surge in AI adoption, initiated by significant developments like OpenAI’s ChatGPT, has impacted cloud computing significantly. This technology swiftly found its way onto Azure®, and others like Google have followed suit by introducing their own AI technologies.
"Adjacencies" in the cloud computing market context refer to related or complementary markets and technologies that intersect with cloud computing, creating opportunities for expansion, diversification, and the development of integrated solutions. Exploring adjacencies allows cloud computing providers to broaden their product offerings, increase market reach, and better meet customers' evolving needs.
- Market Expansion: Adjacencies enable cloud computing providers to enter new markets or verticals closely related to their core offerings. For example, a cloud provider specializing in Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) may expand into Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) or Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) offerings, leveraging their existing infrastructure and expertise to offer integrated solutions.
- For example, a cloud provider specializing in Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) may expand into Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) or Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) offerings, leveraging their existing infrastructure and expertise to offer integrated solutions. A prime example is Amazon Web Services (AWS™), known for IaaS, which has expanded into PaaS and SaaS offerings. They provide services like Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) for IaaS, Amazon Elastic Beanstalk for PaaS (application deployment), and Salesforce on AWS™ (SaaS) - a collaboration with a leading CRM software provider.
- Diversification: Adjacencies offer opportunities for diversification by branching out into areas that complement cloud computing, such as cybersecurity, data analytics, artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things (IoT), and digital marketing. By diversifying their product portfolio, cloud providers can reduce risk, capture new revenue streams, and differentiate themselves in a competitive market.
- Microsoft Azure® is another example. Like AWS™, Azure® offers a range of IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS solutions. They partner with companies like Adobe to provide integrated solutions combining cloud computing with adjacent technologies like digital marketing software.
- Integrated Solutions: Adjacencies allow cloud providers to develop integrated solutions that address customers' end-to-end needs. For example, a cloud provider may partner with cybersecurity vendors to offer cloud-based security solutions seamlessly integrating with their cloud platforms. Similarly, partnerships with data analytics or AI/ML companies can result in integrated offerings that enable customers to derive insights and value from their data.
- For example, a cloud provider may partner with cybersecurity vendors to offer cloud-based security solutions seamlessly integrating with their cloud platforms. Similarly, partnerships with data analytics or AI/ML companies can result in integrated offerings that enable customers to derive insights and value from their data. Google Cloud Platform™ (GCP) demonstrates this approach. They offer IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS solutions, strongly focusing on AI and Machine Learning (ML) as an adjacent technology. Their Vertex AI platform allows developers to build and deploy AI/ML models directly on GCP's infrastructure.
- Customer Value: By leveraging adjacencies, cloud providers can enhance customers' value propositions by offering comprehensive solutions that address multiple aspects of their business needs. Integrated solutions that combine cloud computing with adjacent technologies can streamline operations, improve efficiency, and drive innovation for customers across various industries and sectors.
- Competitive Advantage: Exploring adjacencies allows cloud providers to stay ahead of competitors by offering unique and differentiated offerings. By identifying emerging trends, customer pain points, and market opportunities in adjacent markets, cloud providers can develop innovative solutions that set them apart from the competition and solidify their position as industry leaders.
Overall, adjacencies play a crucial role in the growth and evolution of the Cloud Computing Market by enabling providers to expand their offerings, diversify their revenue streams, deliver integrated solutions, create value for customers, and maintain a competitive edge in a rapidly changing landscape.
Challenges to Growth
The primary challenges to growth in the Cloud Computing Market include intense competition and the complexities of forming strategic partnerships, heightened concerns regarding security, environmental considerations, and sustainability, and navigating regulatory impacts and compliance requirements.
Competition and the Need for Partnership
In the cloud service industry, the race to offer the best AI models has intensified competition, leading providers like Google Cloud Platform™ Open (GCPO) and Amazon Web Services (AWS™) to adopt new strategies. They now offer third-party models, signaling a shift from their previous focus on proprietary offerings. This change reflects the evolving market dynamics, where customers increasingly seek partnerships to co-create solutions rather than simply selecting from predefined offerings.
Strategic collaborations, characterized by aligned goals and rapid market delivery, are becoming crucial for success. The traditional RFP process is proving less effective as customer needs become more complex and unique. Businesses must identify the right partners to scale infrastructure, develop advanced technologies, and enable customers. The coming year will be critical in determining how these partnerships evolve and who emerges as leaders in this rapidly changing landscape.
The accelerated pace of technological advancement necessitates swift action, often leading to acquisitions as companies strive to stay competitive. This trend is typical in times of significant technological shifts, where partnerships and acquisitions complement internal capabilities.
Identifying the right partners is crucial. From a design and technology enablement perspective, finding partners who can help scale infrastructure quickly and efficiently is essential. These partners might be the same or different, depending on their specific needs. Collaborating effectively within the ecosystem is vital to achieving mutual success.
Significant activity is pushing the limits of current technologies, highlighting the critical need for new capabilities and supply chains. Enabling these advancements is a considerable challenge. Companies increasingly require strategic partners to develop complex equipment, leading to rising market tensions. The coming year will be pivotal in determining how these issues are resolved.
Given the rapid pace of technological evolution, acquisition activity is highly likely. As building internal capabilities takes time, acquisitions become necessary to stay competitive. This trend is typical during significant technological shifts in the market, where partnerships are crucial to complement strengths. For instance, enabling liquid cooling may require swift action, and alliances or acquisitions may become imperative if a company cannot achieve this organically.
Another crucial aspect is customer enablement. Customers often identify bottlenecks or problems and seek trusted partners to help solve them within the ecosystem. Finding the right partners to work with is critical and core to their business success.
Security
The increasing number of Internet-connected devices also poses challenges related to security and compliance. Malware that encrypts access to the target enterprise's files and data is known as ransomware. The hackers/cybercriminals then demand that the business pay a ransom—essentially an excessive amount in legal parlance—to access their files. This malware could severely threaten the business if it infiltrates the organization's cloud storage. A ransomware assault could prevent the company from accessing critical company data, potentially leading to the complete cessation of the company's business activities.
Cloud computing providers must ensure robust security measures to protect sensitive data transmitted and stored in the cloud. Some keyways include data encryptions, access controls, network security, security monitoring and incident response, compliance, and certifications.
Additionally, the proliferation of Internet-connected devices makes compliance requirements related to data privacy and regulatory standards more complex, requiring cloud providers to implement stringent compliance measures.
These challenges require cloud computing companies to address security and compliance concerns proactively. However, verifying that a cloud service provider complies with applicable lAWS™ and regulations can present challenges.
Environmental Concerns
Energy
The growth of cloud computing leads to increased energy consumption. The energy consumed by data centers contributes to carbon emissions and environmental degradation, raising concerns about cloud computing's carbon footprint and its contribution to climate change.
Integral to cloud services, data centers demand significant energy power servers, networking equipment, cooling systems, and infrastructure maintenance, contributing to overall energy usage. As the demand for cloud services grows, so does the energy consumption of data centers.
The high-power demand for data centers arises from several factors:
- Server Infrastructure: Data centers with thousands of operational servers require significant amounts of electricity to operate efficiently.
- Cooling Systems: Cooling systems for data centers consume considerable power to regulate temperatures and ensure server reliability.
- Networking Equipment: Switches, routers, and other networking devices increase power demand.
- Redundancy and Backup Systems: While essential for reliability, these redundant systems including power supplies and backups add to the overall power consumption.
- Expansion and Scalability: Increasing demand for cloud services leads to higher power demands to support additional servers and equipment.
- 24/7 Operation: Data centers operate around the clock to provide continuous service to users worldwide. The constant operation requires a steady electricity supply, contributing to the overall power demand.
The cloud and storage market outlook is one of continued growth, tempered by the need to address energy consumption challenges. The sector is expected to invest heavily in energy-efficient technologies and sustainable practices to manage increasing power demands. Strategic partnerships and acquisitions will likely significantly accelerate these advancements, ensuring the market can sustain its growth trajectory while meeting environmental and operational efficiency goals.
Water
Data centers have been established worldwide to support the growing cloud computing infrastructure. These facilities house millions of servers and are equipped with essential resources such as power, cooling, and internet connectivity.
While most market intelligence research firms focus on data centers' energy consumption, more must be done to analyze their water usage. Data centers directly consume water for cooling purposes, with some drawing as much as 57% of their water from potable sources. Additionally, they indirectly impact water resources through the water requirements of non-renewable electricity generation.
Although the water consumption of data centers in the United States —approximately 450 million gallons (1.7 billion liters) per day — is relatively minor compared to the nation's total water usage of 320 billion (1,218 billion liters), there remains a transparency issue. Less than a third of data center operators currently measure their water consumption, highlighting a need for increased transparency and accountability.
Water availability and quality are crucial for industry and agriculture, and they are a growing global concern. OECD projections suggest that water demand will increase by 55% between 2000 and 2050 due to growth from manufacturing (+400%), thermal power generation (+140%), and domestic use (+130%). The cloud computing sector is another sector that contributes to that demand.
Use Case Analysis
List of Some of the top use cases for Cloud & Storage in prominent industries
|
Industry |
User (Company 1) |
Solution Provider (Company 2) |
Description |
|
Automotive |
Volkswagen |
AWS™ |
Storage and processing of data from connected vehicles for real-time analytics and predictive maintenance. |
|
Defense |
U.S. Department of Defense |
Microsoft Azure® Government |
Storage and processing of classified information, ensuring secure collaboration and data sharing. |
|
Aviation |
Boeing |
Google Cloud Platform™ |
Storage and processing of data from aircraft sensors and systems for predictive maintenance and flight optimization. |
|
Marine |
Maersk |
IBM Cloud™ |
Storage and analysis of data from vessels for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. |
|
Space |
SpaceX |
AWS™ |
Storage and processing of data from rockets and satellites for mission planning, telemetry analysis, and ground control operations. |
|
Healthcare |
Mayo Clinic |
Google Cloud Platform™ |
Storage and analysis of patient medical records, genomic data, and research data for personalized medicine development. |
|
Pharmaceutical |
Pfizer |
AWS™ |
Storage and processing of data from clinical trials, drug discovery research, and manufacturing operations. |
|
Food & Beverages |
Coca-Cola |
Azure® |
Storage and analysis of data from supply chain, manufacturing processes, and consumer preferences. |
|
Industrial |
Siemens |
AWS™ |
Storage and processing of data from industrial sensors, machines, and production lines for predictive maintenance and manufacturing optimization. |
Data sourced from Secondary Analysis
Government Initiatives
LATEST GOVERNMENT INITIATIVES THAT PROMOTE CLOUD & STORAGE INFRASTRUCTURE
|
Initiative Name |
Country |
Launch Year |
Initiative Description |
|
Cloud Smart Strategy |
USA |
2019 |
Aims to accelerate cloud adoption in federal agencies, improve cybersecurity, and enhance service delivery. |
|
Digital Government Blueprint |
Canada |
2018 (updated |
Outlines the government's plan to modernize services and improve digital infrastructure, including cloud adoption. The latest updates emphasize hybrid cloud strategies and data sovereignty. |
|
National Digital Strategy |
Ireland |
2020 |
Sets out the government's vision for a digital Ireland, with a focus on cloud infrastructure and data sharing. |
|
GovTech Catalyst Programme |
Singapore |
2019 (ongoing) |
Supports the development of innovative tech solutions for the public sector, including cloud-based services. |
|
National Cloud Strategy |
France |
2021 |
Aims to strengthen France's cloud industry and promote cloud adoption in the public sector. |
|
Cloud de Confiança |
Portugal |
2021 |
Creates a framework for secure and reliable cloud services for public administration and critical infrastructure. |
|
Cloud Strategy |
Germany |
2020 |
Defines the principles and guidelines for cloud adoption in federal agencies, with a focus on data sovereignty and security. |
Data sourced from Secondary Analysis
Cloud & Storage Market
Technology Evolution
In this new digital era, companies are aiming to become agile with the integration of new technologies. This is mainly accomplished by moving to a cloud environment. Being in the cloud entails obtaining embedded connections and intelligence, enabling the interoperability of smart operations, and developing a solid foundation for digital services linked to the cloud.
Corporate Digital & AI Transformation Reshaping Business Paradigms
Cloud computing gives digital transformation an extra dimension, from simply adopting new technology to completely rebuilding processes, tools, and experiences in a remote, virtual environment. Cloud computing boosts security, enhances user experience, and protects documents from deterioration. Because of this, businesses are now incorporating cloud computing into their ecosystem, fueling the growth of the Cloud Computing Market.
In contrast to the outdated on-premises server model that relies on human operations, cloud computing offers enormous opportunities for automation. The cloud simplifies the Platform-as-a-Service model, Infrastructure-as-Code techniques, automatic backups, version control provisioning for workflows, and security control administration through user access.
Cloud computing has emerged as a game-changer for businesses looking to develop Supply Chain Management (SCM) swiftly and successfully. For instance, as part of a multi-year partnership started in June 2022, Google Cloud and Connecticut-based XPO Logistics will work together to enhance the movement of commodities throughout supply chains. XPO will utilize Google Cloud's data analytics, machine learning, and artificial intelligence (AI) capabilities to build quicker, more effective supply chains with improved visibility.
Since the introduction of the technology, many banking and fintech organizations have gradually migrated to the cloud. Data generation and consumption are expanding quickly in the financial sector. The solution increases openness while granting consumers more control over auditing procedures and data. It offers a more scalable method of categorizing data. Also, healthcare-related functions, including telehealth and virtual care, medication adherence, drug anti-theft, counterfeiting measures, resource inefficiency, personal data privacy, and the uniformity of medical records, have much to gain from integrating cloud computing and healthcare.
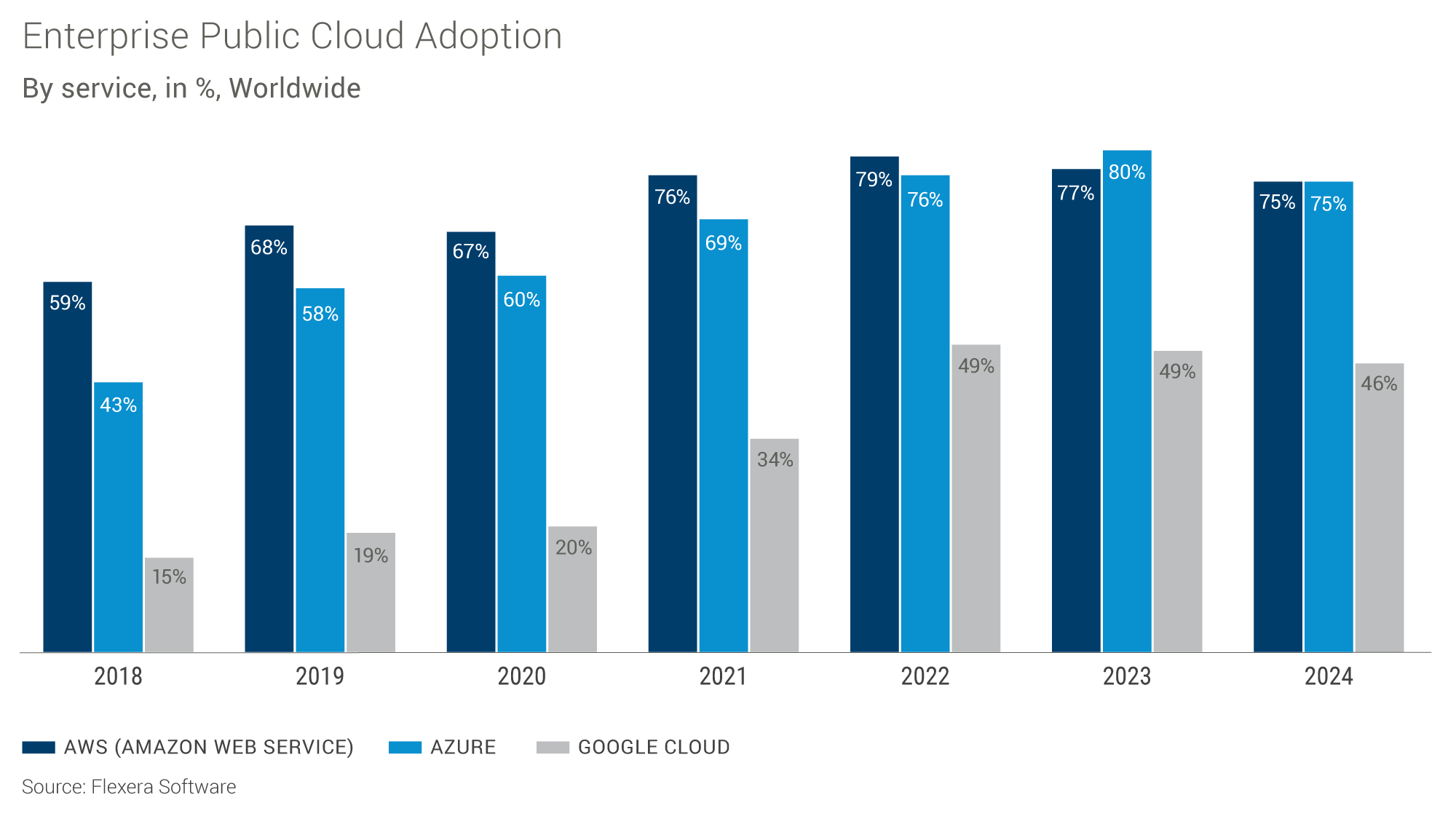
Data sourced from Flexera Software
According to an article published by McKinsey & Company in May 2024, generative AI is poised to add as much as $4.4 trillion in economic value from a combination of specific use cases, such as creating personalized content for marketing campaigns or transforming maintenance workflows by interpreting telemetry to more diffuse uses—such as assisting with code creation, debugging, and optimization —that increase productivity.
Edge Computing
Edge computing with 5G creates tremendous opportunities in every industry. It brings computation and data storage closer to where data is generated, enabling better data control, reduced costs, faster insights and actions, and continuous operations. Analysts believe that by 2025, 75% of enterprise data will be processed at the edge, compared to only 10% today.
Edge computing is a new technology that allows data to be processed at the edge of a network rather than in its center. It is a distributed computing architecture where each device can process tasks independently and send only relevant information to other devices for further processing.
This distributed model means that edge computing can reduce network latency by allowing actionable data from sources like sensors and other IoT devices to be analyzed much closer than would otherwise be possible with cloud-based systems.
In supply chain management applications, edge computing enables greater efficiency by eliminating extra steps needed when data travels back and forth between different centralized servers before it can be acted upon.
With places like warehouses close to shipping facilities and distribution centers, this technology allows them to act upon information as soon as they receive it. This will minimize delays caused by transferring data between locations via secure channels or over wireless networks, which may not operate at optimal speeds due to congestion issues.
Billions of internet-connected devices, from smartphones and computers to security cameras and machine sensors, collectively generate immense volumes of data. Much of this data is transmitted over the Internet to cloud-based applications. These applications are hosted on expansive, centralized data centers and platforms managed by a few organizations, driving the backbone of cloud computing infrastructure. The problem is that as the number of connection points explodes to 150 billion devices, generating 175 zettabytes of data by 2025, sending all that data to faraway clouds for processing will become increasingly inefficient and expensive. Moreover, this model may need more time to deliver the real-time data and response times demanded by newer applications. Consequently, more organizations are considering a hybrid cloud model that augments existing cloud strategies with edge computing.
Edge computing distributes the cloud’s scalable and elastic computing capabilities closer to where devices generate and consume data. These locations can be as varied as an enterprise’s on-premises server, a communication service provider’s central office or cell tower, a hyperscaler’s regional data center, an end-user device, or any point.
Since data doesn’t have to travel as far, edge computing can help reduce network resources, cut transit costs, improve reliability, reduce latency, and, perhaps most importantly, enhance enterprise control over data and applications. For example, edge computing can help organizations meet increasingly stringent data sovereignty, privacy, and security requirements by keeping sensitive data on-premises. Moreover, when edge computing is combined with advanced connectivity options—especially 5G—it can deliver flexible, near real-time response times for data-heavy, artificial intelligence-driven, time-sensitive, or mission-critical applications. The combination of low latency, advanced connectivity, and enhanced data control makes many IoT use cases, such as the video analytics and computer vision used in security and quality control, immersive mixed reality training, autonomous vehicles, and precision robotics, much more feasible.
The rise of edge computing could positively impact the Cloud Computing Market by driving the adoption of hybrid models, improving efficiency, and opening new growth opportunities.
- Hybrid Models: More organizations are considering a hybrid cloud model that augments existing cloud strategies with edge computing. This approach distributes the cloud’s scalable and elastic computing capabilities closer to where devices generate and consume data.
- Cost and Efficiency: Businesses leveraging a hybrid approach of edge and cloud computing see up to a 35% reduction in latency and a 20% cost saving on data management. Edge computing is crucial for real-time data processing and IoT efficiency, reducing latency and bandwidth use.
- Market Growth: The enterprise market for edge computing is predicted to grow significantly this year. According to the International Data Corporation (IDC), worldwide spending on edge computing is expected to reach USD 232 billion in 2024, an increase of 15.4% over 2023. This includes combined enterprise and service provider spending across hardware, software, professional services, and provisioned services for edge solutions. Most of this growth will likely come from expenditures on hardware initially but will migrate toward software and services as the market matures.
- Data Management: Edge computing minimizes the need to constantly transmit vast amounts of data to the cloud, reducing bandwidth costs and alleviating the load on cloud resources. This can enhance response times and reduce latency. There are several companies here, including:
- Snowflake: The company is one of the leaders in cloud-based data warehousing, offering solutions well-suited for edge data management. Their focus on scalability and ease of use makes them a popular choice for handling large datasets at the edge.
- Amazon Web Services (AWS™): AWS™ offers a suite of services for edge computing, including AWS™ Snowball Edge and AWS™ Greengrass. Snowball Edge is a ruggedized device that can collect and process data offline at the edge before securely transferring it to the AWS™ cloud for further analysis. Greengrass is an IoT platform that allows you to run local compute workloads, machine learning models, and Lambda functions at the edge.
- Microsoft Azure®: Like AWS™, Microsoft Azure® offers Azure® Stack Edge for edge computing scenarios. This solution provides local data processing and storage capabilities at the edge while allowing seamless integration with the broader Azure® cloud platform.
- Google Cloud Platform™ (GCP): Google Cloud offers Cloud Spanner, a globally distributed relational database that can be deployed at the edge. This allows consistent data management across distributed locations, even when dealing with offline scenarios.
- Dell Technologies: Dell offers a range of hardware solutions specifically designed for edge computing environments, including ruggedized servers and gateways. These solutions can be paired with software from various vendors to create a complete edge data management platform.
- HPE (Hewlett Packard Enterprise): Like Dell, HPE provides hardware solutions like edge servers and microservers designed explicitly for edge computing deployments. They also offer software like HPE Edgeline, which helps manage and orchestrate edge resources.
Public Cloud Hyperscalers
Hyperscalers will likely be vital in standardizing, simplifying, and commercializing enterprise edge computing solutions. They leverage their platforms, ecosystems, and marketplaces to deliver easy-to-consume, right-sized, yet scalable, and affordable solutions. Hyperscalers are treating edge computing as an extension of their existing cloud business, regionalizing and scaling their massive global cloud infrastructures into smaller formats that can enable customers to process workloads closer to or in their facilities.
As part of this effort, many are partnering with Cloud or Communications Service Providers (CSPs), content delivery networks, cell tower owners, and others with highly distributed network facilities to co-locate these scaled-down edge cloud platforms close to potential clients. Some hyperscalers are shrinking their cloud platforms even further to deliver turnkey edge computing platforms that enterprise customers can deploy on their hardware infrastructure in their environments. To pursue this market, they partner with specialized system integrators and others to extend their sales channels into specific industry verticals.
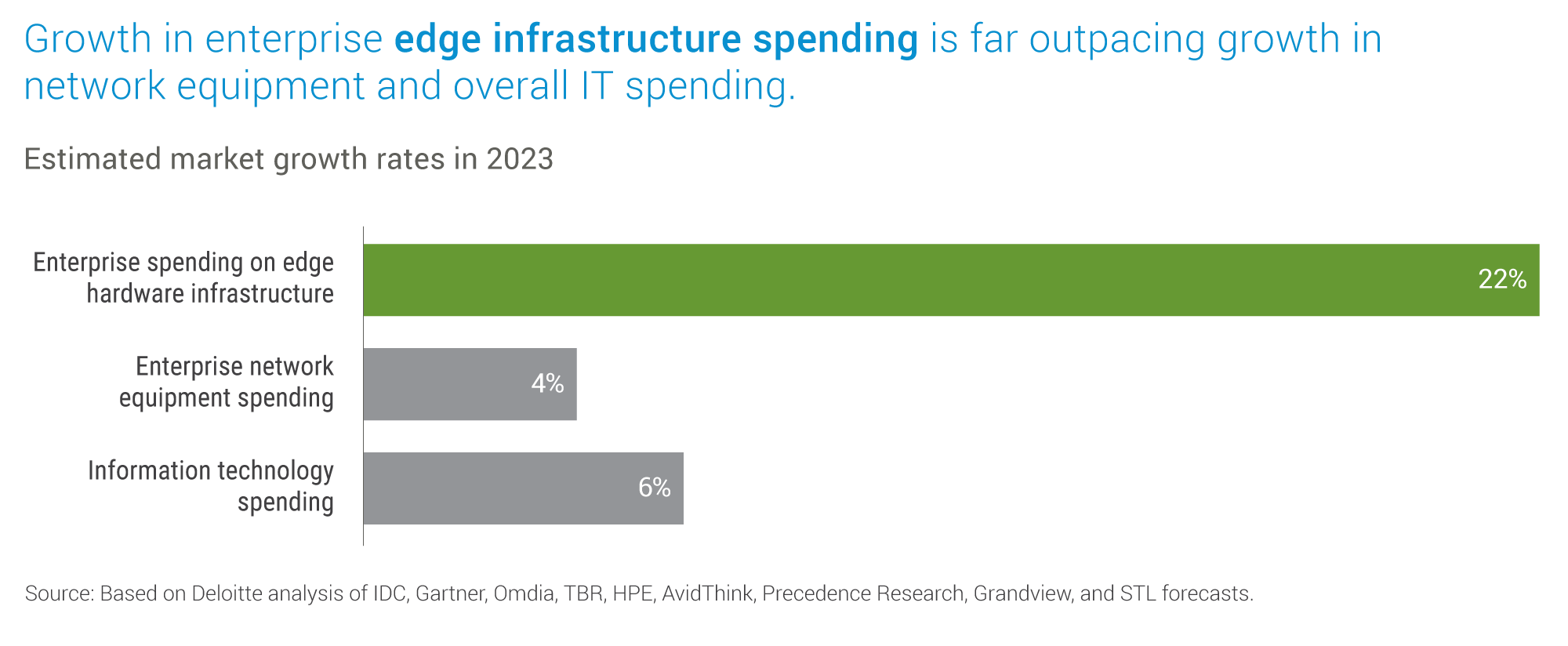 Data sourced from Deloitte
Data sourced from Deloitte
Communication Service Providers (CSPs)
CSPs are well-equipped to offer packaged edge computing solutions in edge computing, while Cisco and NetApp are hardware and data management companies, respectively.
Besides providing the connectivity between the hyperscaler’s centralized cloud and the enterprise’s on-premises data centers, servers, or devices, many believe they can also profit from offering edge computing solutions with secure and reliable connectivity to enable real-time applications. These CSPs are taking measured steps toward developing their edge computing infrastructures, platforms (often in conjunction with a hyperscaler), and services, collectively known as multi-access edge computing (MEC). As part of an MEC offering, CSPs can use their 5G networks to deliver a wide range of à la carte or fully managed connectivity, compute, storage, and security edge services, or even develop their own B2B and B2C applications tailored to an enterprise’s needs.
Many CSPs have well-established relationships, credibility, and trust with enterprise customers on which to build their MEC business. However, many still need to develop their strategy, value proposition, business and operating models, partnerships, and customer-centric sales capabilities to effectively offer and deliver these services.
Major Telecom Operators: These are the big players in the mobile network space, also known as Mobile Network Operators (MNOs). Examples include Verizon, AT&T, T-Mobile, China Mobile, Vodafone, Orange, and Deutsche Telekom.
These operators are actively building their 5G networks, which are crucial for enabling real-time applications at the edge. They are also developing MEC (Multi-access Edge Computing) platforms in collaboration with hyperscalers (large cloud providers like Google, Amazon, and Microsoft) to offer edge computing services to enterprises.
Edge Cloud Management Platforms
Because edge computing has numerous deployment options, each involving a different slate of vendors and applications, an abstraction layer—an edge-cloud management platform—can be used to reduce the complexity of They are administrating these disparate, heterogeneous environments. These management platforms increasingly seek to provide a standard operating system with centralized tools, KPIs, and dashboards, making it easier for operators, enterprises, and developers to tailor performance and security policies in diverse, hybrid environments. The programmable platforms use application programming interfaces (APIs) to control the underlying physical network infrastructure. Because these APIs are increasingly becoming standardized, open-source, and thus vendor-agnostic, their use promotes greater interoperability among the mix-and-match components from different vendors. They can also increasingly blur the distinction between infrastructure and applications as network functions and capabilities are increasingly implemented through code rather than infrastructure.
Edge Computing Takeaways
While the market for edge computing products and services is potentially huge, providers may have to wait a while for customers to catch up. Many enterprises and other organizations are rethinking their cloud, data center, and networking strategies to take advantage of new edge computing capabilities best. In doing so, they evaluate where it is best to place workloads in a hybrid cloud/edge model and how they can secure and access data in a data center at the core, cloud, and edge.
Inevitably, enterprises will likely solve these issues and increase their edge-computing investments. As they do, the various providers’ success in capturing share may depend not on an “us versus them” mentality but rather on working together to realize the market’s potential. Telcos, hyperscalers, equipment vendors, and platform providers may often serve the same customers, each providing a different value proposition. Natural synergies will frequently arise in consequence—for instance, many cross-industry partnerships are forming to offer enterprises a wide range of integrated computing and networking solutions to support turnkey computer vision, virtual and augmented reality, machine learning, and other data-intensive or connected-device applications. For this reason, it’s safe to say that the edge computing business will likely rely on partnerships and ecosystems and not on end-to-end solution providers in every case.
Serverless Computing
Serverless computing is revolutionizing the way applications are built and deployed in the cloud. By abstracting away server management, it empowers developers to focus solely on writing code, accelerating development cycles and reducing operational overhead. With automatic scaling, serverless architectures dynamically adapt to fluctuating workloads, ensuring optimal performance and cost efficiency. This pay-as-you-go model eliminates the need to provision and maintain idle server capacity, resulting in significant cost savings. As a result, serverless computing is democratizing access to scalable and efficient infrastructure, enabling businesses of all sizes to build and deploy complex applications with ease.
Moreover, serverless computing is not just about cost reduction; it's also about agility. The ability to quickly deploy and update code without worrying about infrastructure management allows businesses to respond rapidly to changing market demands. This agility is crucial in today's fast-paced digital landscape, where companies need to constantly innovate and adapt to stay ahead of the competition. By simplifying infrastructure management and accelerating development cycles, serverless computing is empowering businesses to focus on what they do best: creating value for their customers.
However, serverless computing is not without its challenges. The stateless nature of serverless functions can make it difficult to manage the application state, and cold starts can introduce latency. Additionally, debugging and monitoring serverless applications can be complex. Despite these challenges, the benefits of serverless computing are undeniable. As the technology continues to mature, we can expect to see even more innovative use cases emerge, further solidifying its position as a key component of the cloud infrastructure landscape.
Quantum Computing as a Service (QCaaS)
Quantum Computing as a Service (QCaaS) is democratizing access to quantum computing resources, traditionally limited to specialized research institutions and large corporations. By leveraging cloud infrastructure, QCaaS providers offer access to quantum processors and simulators through a pay-as-you-go model, eliminating the need for significant upfront investments in hardware and expertise. This accessibility empowers researchers, developers, and businesses of all sizes to explore the potential of quantum computing and accelerate innovation in various fields.
The impact of QCaaS extends beyond mere accessibility. It serves as a catalyst for innovation, enabling the development of new quantum algorithms and applications in diverse areas such as drug discovery, materials science, optimization problems, and financial modeling. By harnessing the unique properties of quantum mechanics, such as superposition and entanglement, QCaaS users can tackle complex problems that are intractable for classical computers, potentially leading to groundbreaking breakthroughs and transformative solutions.
Moreover, QCaaS plays a crucial role in building the quantum ecosystem. It fosters collaboration between researchers, developers, and industry experts, facilitating the exchange of knowledge and accelerating the pace of quantum technology development. As more users gain access to quantum resources through QCaaS, we can expect to see a surge in quantum applications and wider adoption of this revolutionary technology. However, challenges remain, including the need for more powerful and stable quantum hardware, standardized development tools, and education initiatives to bridge the skills gap. Nevertheless, QCaaS represents a significant step towards unlocking the full potential of quantum computing and shaping the future of technological innovation.
Cloud-based Digital Twins
Cloud-based digital twins are revolutionizing how industries operate, maintain assets, and develop new products. By creating virtual replicas of physical objects, processes, or systems in the cloud, digital twins enable real-time monitoring, simulation, and analysis, providing valuable insights for decision-making and optimization. This technology is transforming industries like manufacturing, healthcare, energy, and transportation, enabling unprecedented levels of efficiency, productivity, and innovation.
In manufacturing, digital twins are used to simulate and optimize production processes, predict equipment failures, and improve product quality. In healthcare, digital twins of patients can help personalize treatments, monitor disease progression, and predict patient outcomes. In the energy sector, digital twins of power grids can optimize energy distribution, anticipate disruptions, and enhance overall system resilience. These are just a few examples of how cloud-based digital twins are bridging the physical and virtual worlds, creating new possibilities for innovation and problem-solving.
The power of cloud-based digital twins lies in their ability to combine real-time data with advanced analytics and simulation capabilities. By collecting and processing vast amounts of data from sensors, devices, and other sources, digital twins can create a comprehensive and dynamic representation of the physical world. This allows organizations to gain deeper insights into their operations, identify inefficiencies, and make data-driven decisions to improve performance and reduce costs. As cloud computing continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more sophisticated and powerful digital twins emerge, further transforming industries and shaping the future of technology.
Blockchain as a Service (BaaS)
Blockchain as a Service (BaaS) is revolutionizing how businesses leverage blockchain technology without the complexities of building and managing their infrastructure. BaaS providers offer cloud-based platforms that handle the underlying blockchain infrastructure, allowing companies to focus on developing and deploying decentralized applications (DApps) quickly and cost-effectively. This accessibility is driving broader adoption of blockchain across various industries, from finance and supply chain management to healthcare and government services.
The core value proposition of BaaS lies in its ability to enhance trust, transparency, and security. Blockchain's decentralized nature ensures that data is distributed across multiple nodes, making it tamper-proof and resistant to hacking. This immutability is crucial for applications where trust and transparency are paramount, such as supply chain tracking, identity management, and voting systems. BaaS further simplifies the process by providing pre-built templates, smart contract libraries, and developer tools, enabling organizations to rapidly prototype and deploy blockchain applications without extensive technical expertise.
Moreover, BaaS promotes interoperability between different blockchain networks, facilitating seamless data exchange and collaboration. This interoperability is essential for building a truly decentralized ecosystem where different blockchains can interact and exchange value. As BaaS continues to mature, we can expect to see even more innovative use cases emerge, driving the adoption of blockchain technology and transforming the way businesses operate and interact. By providing a secure, transparent, and efficient platform for building and deploying decentralized applications, BaaS is unlocking the full potential of blockchain and ushering in a new era of trust and collaboration in the digital age.
Cloud & Storage Market
Competitive Landscape
The Cloud Computing Market is a dynamic landscape, with three significant providers at the forefront. However, it is highly fragmented, with a multitude of players, including SaaS companies, consistently pushing the boundaries. These companies are not only advancing but also collaborating and expanding their presence in developing regions to fortify their positions. Notable instances of this dynamic environment include Oracle's establishment of a new Oracle Interconnect for the Microsoft Azure® site in Johannesburg, South Africa, and Google Cloud's introduction of enhancements in its infrastructure and productivity solutions.
The Cloud Computing Market is largely shaped by a handful of key players. Amazon Web Services, Inc., Google LLC, Microsoft Corporation, Alibaba Cloud, and Salesforce, Inc. are the industry giants that dominate the market. These players not only hold significant market shares but also drive innovation in the sector, setting the pace for the cloud services landscape.
Leading Players in the Market
The leading players in the Cloud Computing Market, often recognized for their substantial growth and dominance, include prominent companies like NVIDIA, Meta Platforms, Microsoft, Amazon, and Alphabet. Five of these critical players reported significant gains in the first quarter of 2024, surpassing market expectations with robust growth.
As of the beginning of 2024, the Cloud Computing Market is primarily dominated by five key players:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS™): Holding a substantial 31% market share in the global cloud infrastructure market, AWS™ remains a frontrunner.
- Microsoft Azure®: As a primary competitor to AWS™, Microsoft Azure® has steadily grown its market share to reach an all-time high of 24% in Q4 2023.
- Google Cloud Platform™ (GCP): Securing the third position, Google Cloud holds an 11% market share.
- Alibaba Cloud: Recognized as one of the top cloud service providers, Alibaba Cloud contributes significantly to the market.
- IBM Cloud™: IBM Cloud™ is one of the leading cloud computing companies, further enriching the competitive landscape.
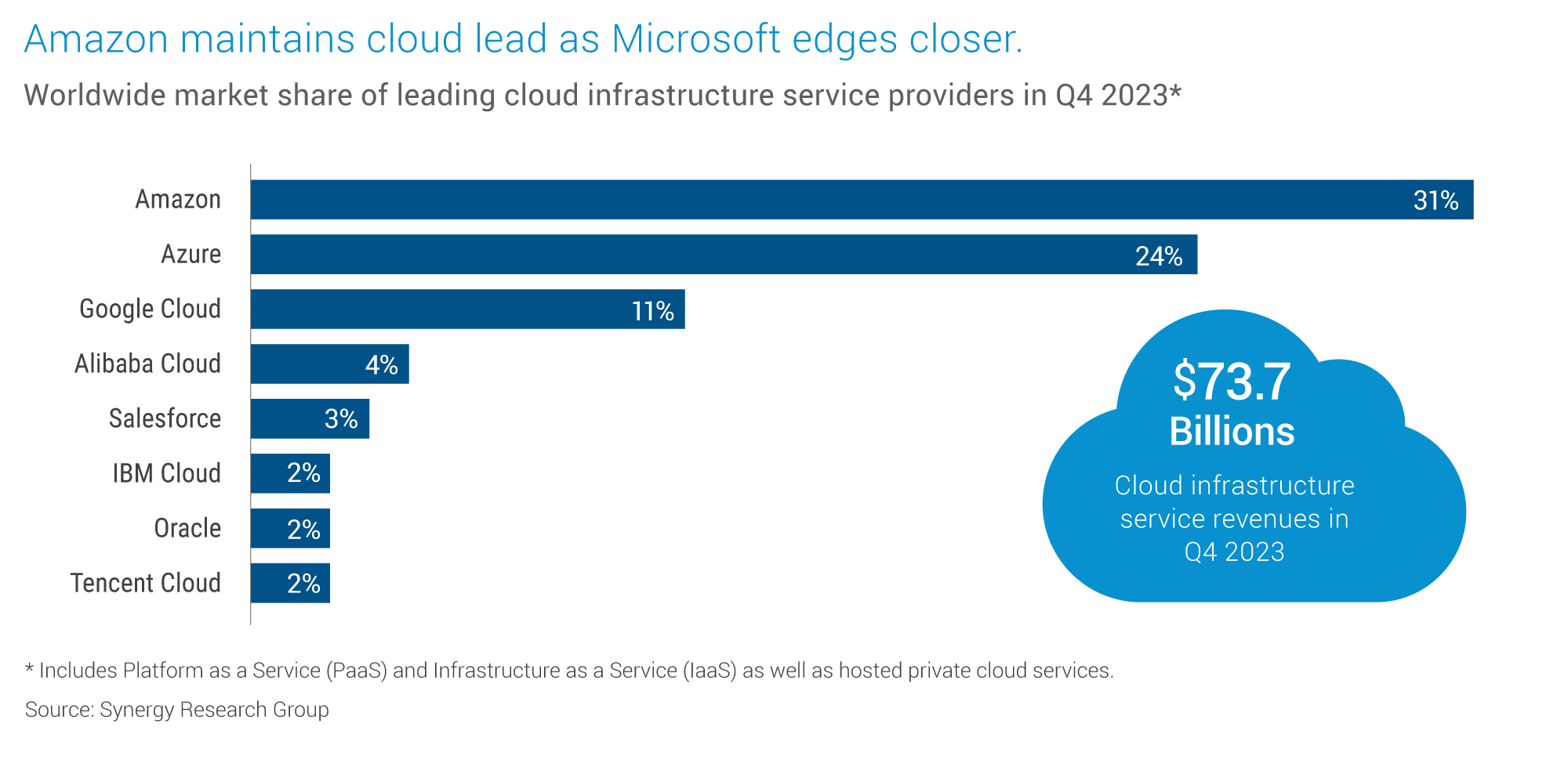
Data sourced from Synergy Research Group
Cloud & Storage Market
Supply Chain
Navigating Disruptions: Challenges and Innovations in the Cloud Storage and Data Center Supply Chain
The cloud storage industry is experiencing a perfect storm. A confluence of supply chain disruptions impacts critical aspects like cost structure, capacity availability, and innovation potential. The Supply Chain section outlines the key challenges and explores strategies to ensure continued industry growth and resilience.
The leading players in the Cloud Computing Market, often recognized for their substantial growth and dominance, include prominent companies like NVIDIA, Meta Platforms, Microsoft, Amazon, and Alphabet.
Five of these critical players reported significant gains in the first quarter of 2024, surpassing market expectations with robust growth. For example, in the first quarter of 2024, NVIDIA reported a 30% increase in revenue, driven by strong demand for its AI-driven cloud solutions. Similarly, Meta Platforms saw a 25% rise in its cloud services revenue due to the expansion of its virtual reality infrastructure. Microsoft reported a 20% growth in Azure® services, while Amazon's AWS™ division achieved a 22% increase in revenue. Alphabet's Google Cloud also posted a 19% growth, surpassing market expectations and demonstrating robust performance.
Capacity Concerns and Diversification Strategies
Despite recent expansion efforts, a potential capacity shortage looms, particularly in smaller markets with limited infrastructure. To ensure their storage needs are met, customers may need to consider a multi-pronged approach:
- Vertical Integration: Some large cloud providers may invest in building their chip manufacturing facilities or forging closer partnerships with chipmakers to secure a more reliable supply.
- Geographical Diversification: Customers can store data across multiple cloud providers' geographically distributed data centers. This mitigates capacity constraints in a single region and reduces latency for geographically dispersed users.
Network Infrastructure Challenges and Security Considerations
Supply chain disruptions impacting network equipment like routers, switches, and fiber optic cables can limit a cloud provider's ability to expand its network or reach new geographic regions. These challenges can also hinder the achievement of low-latency data transfer with geographically distributed data centers. Furthermore, reliable security equipment supply chains are essential for robust data protection and user privacy.
Cloud providers are exploring alternative solutions such as:
- Software-defined networking (SDN): This technology allows for more efficient network management and virtualization of network resources, potentially reducing reliance on specific hardware components.
- Investing in Open-Source Hardware: Standardized, open-source hardware designs can offer more flexibility and potentially shorter lead times than proprietary equipment.
The Global Chip Shortage's Impact
The ongoing global chip shortage could affect cloud provider scalability, potentially impacting customer service provisioning timelines. Additionally, it may result in:
- Increased cloud storage costs passed on to customers.
- Delays in the availability of new, more efficient storage solutions that leverage the latest chip technology.
- Cloud providers prioritize existing customers due to limited chip resources, potentially impacting new customer onboarding.
Rare Earth Minerals: A Geopolitical Consideration
China's dominance in the mining and processing rare earth minerals (REMs), essential components for cloud data center equipment, creates a potential geopolitical vulnerability for cloud providers. The lack of readily available substitutes for REMs and potential environmental regulations impacting their extraction can further disrupt supply and drive costs.
To mitigate this risk, cloud providers are exploring alternative approaches:
- Rare Earth Recycling: Research is underway to develop efficient REM recycling processes to reduce dependence on virgin materials.
- Researching Alternative Materials: Scientists are actively investigating alternative materials that could replace REMs in specific applications.
Impact on Cloud Storage and the Path Forward
Supply chain issues and REM concerns can lead to higher material costs, potentially impacting cloud storage pricing. To mitigate these challenges and ensure the continued growth and sustainability of the cloud storage market, cloud providers are exploring REM recycling initiatives and researching alternative materials. They are also likely to invest in vertical integration for chip manufacturing and collaborate more closely with suppliers to improve supply chain transparency and resilience.
Building Resilience: The China+1 Strategy
The "China+1" strategy, increasingly adopted by global OEMs, is a response to diversify manufacturing and reduce dependency on China due to various risks, including geopolitical tensions, supply chain disruptions, and rising labor costs. This strategy pushes component suppliers in the semiconductor, passive components, PCBs, and mechanical parts sectors to explore investment opportunities outside of China, notably in regions like South Asia and Mexico. This approach isn't about abandoning China entirely but building resilience through diversification.
To achieve this, businesses are actively seeking new locations to diversify their cloud operations. Cost-effectiveness, geopolitical stability, robust infrastructure, a skilled workforce, and stringent data privacy regulations are key factors in selecting a suitable "plus one" location. Additionally, government support in the form of tax breaks and incentives for the cloud sector can make a region even more appealing.
Countries like Vietnam and India are emerging as strong contenders in this space. Their combination of favorable factors makes them attractive alternatives for businesses looking to diversify their supply chains and mitigate risks associated with over-reliance on China.
By strategically choosing a new partner, businesses can maintain agility and create a more robust supply chain. They can continue to leverage China's strengths in manufacturing and technology while safeguarding against potential disruptions. The "China+1" strategy is a deliberate step towards a more secure and adaptable future for cloud operations.
Near-Shoring
Near-shoring to Mexico presents a unique opportunity for US companies seeking a geographically close and economically advantageous partner.
Mexico's proximity to the US offers significant advantages. Transportation costs plummet compared to offshoring to Asia, and logistics become simpler. The United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA) further incentivizes near-shoring by reducing tariffs and streamlining customs procedures.
Additionally, Mexico possesses a growing pool of skilled labor within its manufacturing sectors. This readily available talent pool helps US companies acquire the necessary personnel to fulfill their operational needs. This strategic partnership fosters a mutually beneficial scenario. US companies enjoy reduced production costs and a more robust and resilient supply chain, with minimized vulnerability to disruptions. Additionally
Also, closer geographical proximity potentially enhances security measures through more streamlined oversight of production processes. For Mexico, this collaboration attracts significant foreign investment, stimulates economic growth, and fosters job creation. The knowledge and technology transfer that occurs through this collaborative effort further strengthens Mexico's industrial capabilities. Finally, increased trade volumes often lead to infrastructure investments, improving transportation and communication networks across Mexico. Of course, there are challenges to address. Mexico's infrastructure, while improving, might not be entirely on par with the US, potentially adding logistical hurdles. Ensuring a skilled workforce that meets US company needs requires continuous investment in education and training programs. Additionally, implementing environmentally sustainable practices across the border is crucial.
Despite these challenges, the potential benefits of a strengthened North American manufacturing base through near-shoring are significant. This would pave the way for a more secure and prosperous future for both the US and Mexico.
Beyond Cost Considerations
While rising labor costs in China are a factor, the "plus one" location should also offer a competitive overall business environment, including:
- Favorable Exchange Rates: A stable or appreciating currency relative to the dollar can help offset potential cost increases in other areas.
- Strong Intellectual Property (IP) Protections: Robust legal frameworks are essential to protect cloud providers' and clients' intellectual property.
Subscription-Based Cloud Access: Flexible and scalable cloud access models, such as pay-as-you-go pricing, can be desirable to businesses seeking to optimize their cloud expenditures. Companies can avoid significant upfront investments and tailor cloud usage to their needs, improving cost efficiency. The “plus one” location can cater to businesses of various sizes and budgets by offering subscription-based cloud access, fostering a thriving cloud ecosystem.
Cloud & Storage Market
Jabil Insights
The cloud market is witnessing a clear shift in customer behavior. Cost optimization remains paramount, with the adoption of ARM servers offering a compelling alternative for running specific workloads. Enterprises are increasingly moving away from traditional hardware ownership and embracing the flexibility and scalability of "as-a-service" (aaS) models. This trend has significant implications for supply chain strategies and fleet management practices, requiring cloud providers to adapt their approach to optimize utilization and capacity planning.
On the other hand, cash-strapped small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) are finding the cloud to be a game-changer. Cloud services eliminate the need for expensive on-premises IT infrastructure and its associated overhead, making them a more attractive and cost-effective solution. This trend will likely accelerate, leading to a decline in traditional server sales to SMBs within the next five years. Cloud providers who cater specifically to the needs of SMBs through tailored pricing models and user-friendly interfaces are well-positioned to capitalize on this growing market segment.
Key Takeaways
Sustainability: A Growing Imperative
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) concerns are no longer on the periphery; they are becoming central to business strategy. The cloud industry embraces circular economy practices within data centers, focusing on extending the equipment's life cycle. This includes the use of refurbished hardware, which can not only reduce costs but also contribute to a company's ESG initiatives. Additionally, designing servers with modularity and reusability in mind can allow components to be repurposed and offered as separate product lines, further minimizing environmental impact.
Looking ahead, we expect a rise in the adoption of ESG-focused industry clouds and risk management software. These purpose-built cloud solutions will empower businesses to track their ESG metrics, collaborate with ecosystem partners, and demonstrate accountability in their sustainability efforts.
The Rise of AI/ML and the Evolving Role of Hyperscalers
The relentless march of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning (AI/ML) shows no signs of slowing. This has significant implications for the cloud market, as AI/ML workloads require immense processing power and efficient data movement. Silicon photonics, a technology that utilizes light instead of electricity for data transmission, is anticipated to play a critical role in enabling faster data processing and supporting the growth of AI/ML applications.
The dominance of hyperscalers like Amazon Web Services (AWS™), Microsoft Azure®, and Google Cloud Platform™ (GCP) is expected to continue, potentially mirroring the pre-1982 telecom market where a few dominant players controlled a significant share. This consolidation presents challenges for smaller players who must differentiate by offering unique value propositions and specializing in specific market niches.
Security: A Constant Vigilance
Cybersecurity remains a top concern for businesses migrating to the cloud. Data breaches and cyber-attacks are a constant threat, and cloud providers must prioritize robust security measures to earn and maintain customer trust. Hyperscalers are heavily invested in security, offering a range of features and services such as data encryption, network security, identity and access management, and compliance certifications. Additionally, independent cloud security providers offer a robust ecosystem of solutions, giving companies a choice when building their cloud security posture.
Government Incentives
Government incentives can be a tool for shaping the Cloud and Storage Market by boosting adoption and directing innovation. For businesses, grants like the US Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) program can make cloud storage more accessible, especially for cost-conscious small-to-medium-sized companies. Similarly, tax breaks offered by Singapore for migrating to cloud solutions or subsidies in developing countries can significantly reduce the initial investment barrier.
Governments can also accelerate research and development (R&D) by allocating funds like the European Union's Horizon 2020 program or forming public-private partnerships to drive advancements in secure and scalable cloud storage solutions.
Specific areas within the market can also be incentivized. Germany's "Cloud Computing Security Label Scheme" provides a framework and financial rewards for cloud providers meeting rigorous security standards, attracting businesses with data privacy concerns. Likewise, data residency requirements in countries like India can incentivize the development of local cloud storage solutions that comply with these regulations.
Emerging technologies can be fostered as well. Tax credits offered in the US for businesses investing in cloud-based AI solutions or innovation grants provided by China for cloud storage optimized for Big Data analytics are examples of how governments can encourage the integration of these technologies with cloud storage.
The impact extends beyond individual businesses. Government-funded training programs for cloud professionals can create a larger talent pool, leading to a more competitive market where providers offer better services at lower prices. Additionally, government investment in data center infrastructure and broadband networks can improve cloud accessibility and performance for businesses nationwide.
Jabil Spend Analysis
Jabil Spend on the Cloud Sector by Category (2020 vs. 2023)
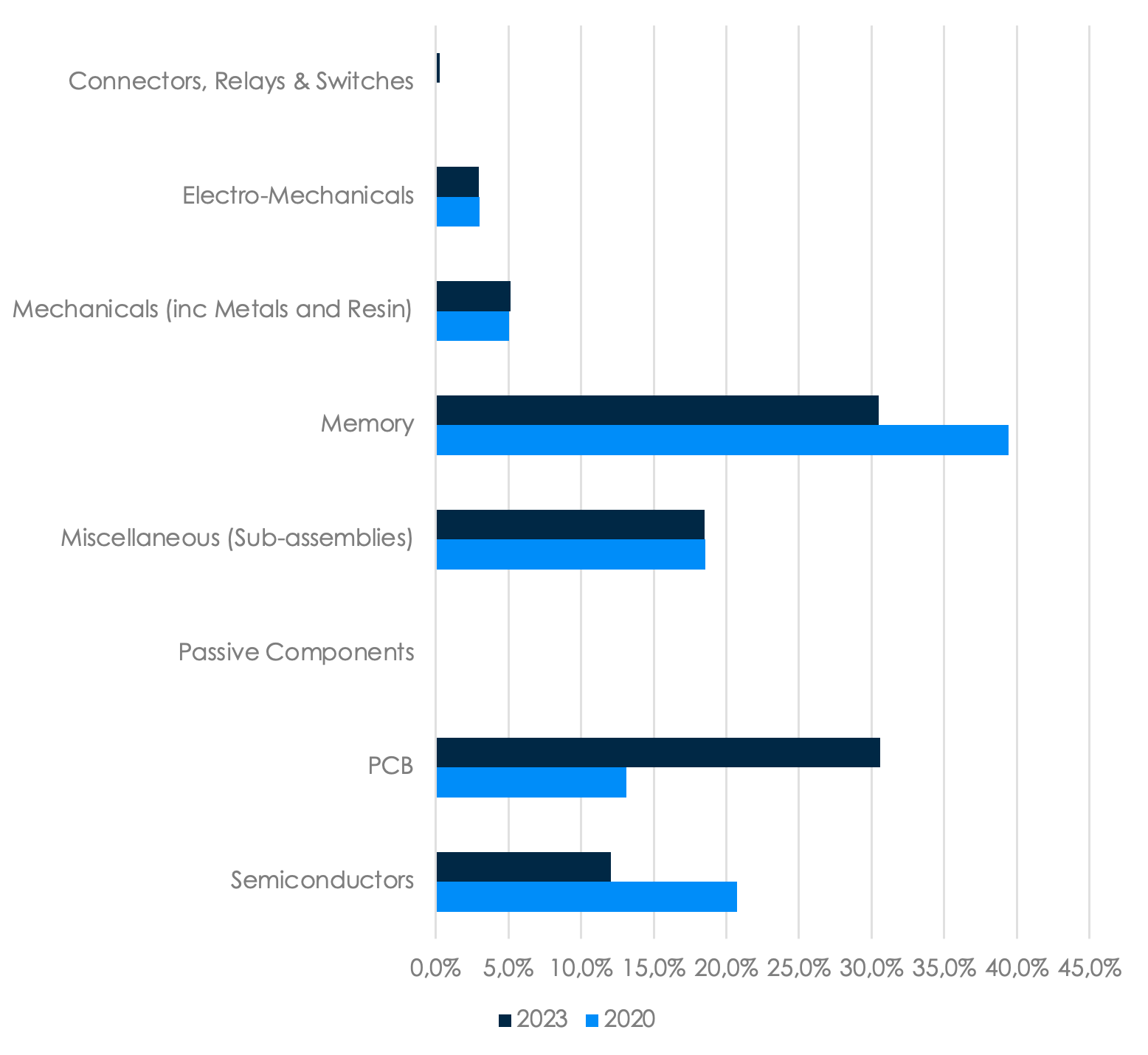
Data based on Jabil's historical spending data for the Cloud Customer Segment
Jabil Spend on Categories YoY (%)
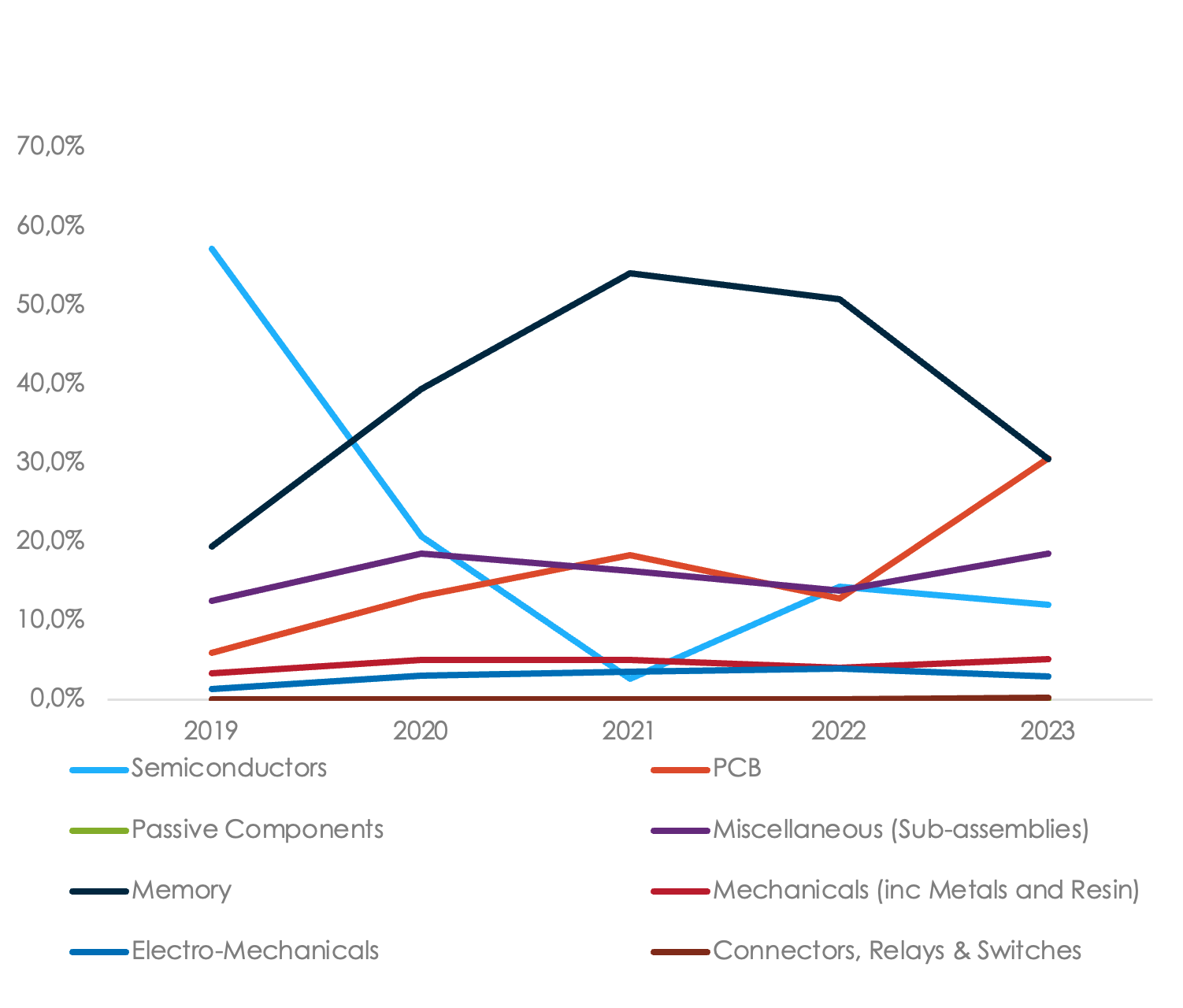
Data based on Jabil's historical spending data for the Cloud Customer Segment
Back to Top
