By clicking the “I Accept” button, or by accessing, participating, or submitting any information, or using the Jabil Global Intelligence Portal or any of its associated software, you warrant that you are duly authorized to accept the Global Intelligence Portal Terms and Conditions on behalf of your Company, intending to be legally bound hereby, and your company shall be bound by the terms and provisions of the Global Intelligence Portal Terms and Conditions, accessible under the following link Portal T&Cs.
Global Mechanicals Intelligence
Global Mechanicals Intelligence
Cables
MARKET DYNAMICS
CABLE MARKET ESTIMATES:
- According to the latest update by Fortune Business Insights in January 2025, the global power cable market size was valued at USD 168.28 billion in 2019 and is projected to reach USD 425.47 billion by 2032, exhibiting a CAGR of 7.84% during the forecast period of 2020-2032.
- According to Global Market Insights, published in February 2025, control and communication cables are witnessing a substantial rise in demand owing to the increasing automation across industries. Industries are integrating robotics, IoT, and other digital technologies across their processes to reduce operational time and increase productivity.
- According to Global Market Insights published in February 2025, the signal and control cables held an approximately 13% share of the low voltage wire and cable market in 2024 due to the growing deployment of intelligent building systems, including HVAC, wiring, and lights across residential and commercial buildings. Builders are integrating automation and IoT across the building's essential units, which in turn is fueling product penetration.
PROCESS OVERVIEW
HARNESS CABLES
Preparation: For better connection, individual wires are cut to the required lengths, stripped of insulation at the ends, and sometimes tinned (coated with solder). Connectors and terminals are selected based on the harness's application.
Assembly: Wires are laid on a jig or harness board according to the design specifications. They are bundled together using tapes, ties, or conduits. Connectors and terminals are attached to the ends of the wires using crimping or soldering techniques.
Quality Control: The assembled harness is tested for continuity, correct wiring, and proper connection. Visual inspections are also performed.
Finishing: The harness may be covered with protective sleeving or braiding for abrasion resistance and durability. Labels or tags might be added for identification. The finished harness is then packaged for shipping.
MOLDED CABLES
Preparation: Cables are cut to length and stripped. Connectors or contacts are attached, often by crimping or soldering. The Mould tooling, which will shape the over-molding, is prepared and clamped together.
Molding: The prepared cable assembly is placed inside the mold cavity. Molten plastic material (the over-molding compound) is injected into the mold, surrounding the connectors and cable ends.
Curing/Cooling: The Mould is held at a specific temperature and pressure for a set time to allow the plastic to cure and solidify. Then, the mold is cooled.
Ejection & Finishing: The molded cable assembly is ejected from the tool. Excess plastic (flash) may be trimmed. The finished cable is inspected and tested.
RF-COAXIAL CABLES
Conductor Production: The inner conductor, typically copper or copper-clad steel, is drawn into a thin wire or strands.
Insulation Extrusion: A dielectric material (like polyethylene or foam polyethylene) is extruded over the inner conductor to provide insulation.
Shielding Application: A metallic shield, often made of braided copper or aluminum foil, is applied over the insulation to protect against electromagnetic interference.
Jacket Extrusion: A protective outer jacket, usually made of PVC or polyethylene, is extruded over the shielding.
Testing & Quality Control: The cable undergoes rigorous testing for electrical characteristics (impedance, attenuation, etc.) and physical properties.
Finishing & Packaging: The cable is cut to specified lengths, connectors may be attached, and the finished cable is packaged.
LVDS
Conductor Preparation: Fine gauge copper wires are stranded or solid, depending on the cable's flexibility requirements. These are often coated with a thin layer of insulation.
Cable Construction: The insulated conductors are twisted into pairs, often shielded or unshielded, to minimize electromagnetic interference (EMI). A drain wire may be included for grounding. The twisted pairs are then bundled together.
Jacket Extrusion: A protective outer jacket, typically made of PVC or similar material, is extruded over the bundled conductors.
Connector Attachment: Precisely designed connectors, often with very fine pitch, are attached to the ends of the cable. This may involve soldering, crimping, or other specialized termination methods.
Testing & Quality Control: Finished cables are rigorously tested for signal integrity, impedance, and other electrical characteristics to meet LVDS (Low Voltage Differential Signaling) standards.
Packaging: Cables are packaged for shipping and distribution. Due to the sensitive nature of LVDS cables, packaging is often designed to protect them from damage.
HIGH-SPEED CABLES
Conductor Preparation: Very thin-gauge copper or other conductive materials are used, often in stranded or micro-coaxial configurations. Insulation is applied frequently using specialized materials with low dielectric loss.
Cable Construction: Conductors are arranged in specific geometries (e.g., shielded twisted pairs, coaxial) to minimize signal loss and crosstalk at high frequencies. Shielding is crucial to protect against EMI.
Jacket Extrusion: A high-performance jacket material, often chosen for its flexibility, durability, and temperature resistance, is extruded over the cable core.
Connector Attachment: Precision connectors, designed for high-speed signal transmission, are attached using specialized techniques. This often involves precise soldering, crimping, or press-fit methods.
Testing & Quality Control: Rigorous testing is performed to verify signal integrity, impedance, return loss, and other critical high-frequency characteristics.
Packaging: Cables are carefully packaged to protect them during shipping and handling, especially given their sensitivity to damage.
FCC-RIBBON
Base Film Preparation: A thin, flexible, insulating film (typically polyester or polyimide) is prepared, which forms the base of the FCC.
Conductor Deposition: Conductive traces (usually copper) are deposited onto the base film using various techniques, including screen printing, etching, or sputtering. The traces are patterned to create the desired circuitry.
Coverlay Application: Another layer of insulating film (the coverlay) is applied over the conductive traces, exposing contact areas. This protects the traces and provides additional insulation. An adhesive may be used to bond the coverlay.
Cutting & Slitting: The FCC is cut or slit into individual circuits or to the final required dimensions.
Connector Attachment (Optional): Connectors or contacts may be attached to the exposed contact areas using soldering, crimping, or other methods, depending on the application.
Testing & Inspection: FCCs are inspected and tested for electrical continuity, insulation resistance, and other parameters to ensure quality and performance.
Packaging: FCCs are packaged for shipping and often rolled or placed in protective packaging to prevent damage.
POWER CORD
Conductor Preparation: Copper or other conductive wires are drawn and stranded to the required gauge and flexibility. Insulation is applied to each conductor.
Cable Construction: The insulated conductors are bundled together, often with a filler material for shape and stability. A protective outer jacket is extruded over the bundled conductors.
Plug/Connector Attachment: Plugs and connectors are attached to the ends of the cable. This typically involves stripping the cable ends, inserting the wires into the plug/connector, and securing them with screws, crimping, or Moulding.
Strain Relief: A strain relief mechanism is incorporated at the plug/connector interface to prevent stress on the wires. This can be part of the plug/connector design or added separately.
Testing & Inspection: Power cords are tested for electrical continuity, insulation resistance, and proper grounding. They are also visually inspected for defects.
Packaging: Power cords are packaged for sale and distribution.
RECENT DEVELOPMENTS
|
Date |
Cable Manufacturer |
End User (Company 2) |
Deal Type |
Description |
Deal Value |
|
Jan-25 |
NKT (Denmark) |
- |
Business Expansion |
To support the growing demand for medium-voltage power cables in Europe, NKT’s sites in Velke Meziříčí, Czech Republic, and Falun, Sweden, have finalized their respective investment plans on schedule and budget. The new production lines are operational, enhancing capacity and capabilities to increase output. The investments across the three sites are estimated to amount to approximately EUR 100 million, which will add 20-110 kV production capacity and capabilities and further progress layout optimizations of the factories. |
$ 103.8 Mn (€ 100 Mn) |
|
Nov-24 |
Prysmian Group (Italy) |
RTE (France) |
Contract |
Prysmian has been awarded significant batches of a three-year agreement for the supply of High Voltage and Extra High Voltage underground cables from RTE, the Transmission System Operator in France and a key player within Europe’s power system, with the most extended High and Ultra High Voltage transmission infrastructure. The award confirms Prysmian’s leadership position in the segment and underlines the long-term partnership between RTE and Prysmian. |
- |
|
Nov-24 |
NKT (Denmark) |
RTE (France) |
Contract |
NKT will deliver high-voltage power cable solutions to RTE to enable their long-term strategy to renew, adapt and develop France’s electricity grid. As one of Europe’s largest exporters of electricity, the upgrade of France’s grid is essential for the power supply of the continent. RTE, France’s Transmission System Operator (TSO), has awarded NKT the extension of two framework agreements for the supply of high-voltage power cables solutions from 2026 to 2028. The framework agreements are for onshore power cables, accessories, and installation at voltage levels 90 kV, 225 kV and 400 kV. |
- |
|
Sep-24 |
NKT (Denmark) |
Nexel (South Korea) |
Agreement |
NKT signs framework agreement with Nexel to supply low- and medium-voltage cables for grid upgrade projects |
- |
|
Sep-24 |
Nexans (France) |
SSEN Transmission (UK) |
Contract |
Nexans has signed the contract for the Orkney Link by SSEN Transmission |
- |
|
Jul-24 |
Prysmian Group (Italy) |
European Investment Bank (Luxembourg) |
Finance Contract |
The European Investment Bank (EIB) and Prysmian, the world leader in the power and telecom cables sector, have signed a new, €450 million finance contract to facilitate European electricity transmission and distribution. |
$491 Million (€450 Million) |
|
Jun-24 |
Sumitomo Electric (Japan) |
Südkabel (Germany) |
Acquisition |
Sumitomo Electric announces the acquisition of majority shareholding in Südkabel, a renowned German high-voltage cable manufacturer, and the expansion of its production capacity in Mannheim, Germany, to locally manufacture the highest end 525 kV HVDC cables. |
- |
|
Jun-24 |
Sumitomo Electric (Japan) |
Amprion (Germany) |
Contract |
German TSO Amprion has awarded a cabling contract and signed a Preferred Supplier Agreement (PSA) with Japanese cable manufacturer Sumitomo Electric to the tune of more than €3 billion ($3.2 billion). The agreement sees secured cable supply capacities for sections of the Korridor B and Rhein-Main-Link, to be built up in Germany. |
$3.2 Billion (€3 Billion) |
|
Jun-24 |
Nexans (France) |
La Triveneta Cavi (Italy) |
Acquisition |
Nexans, a leader in the global energy transition, announces the completion of its acquisition of La Triveneta Cavi, one of the European leaders in medium—and low-voltage cables. The acquisition is a significant leap forward in Nexans’ strategy to become a pure electrification player. |
- |
|
Apr-24 |
Prysmian Group (Italy) |
Encore Wire (US) |
Merger |
Prysmian announced that it has entered into a definitive merger agreement under which it will acquire Encore Wire (NASDAQ: WIRE) for $290.00 per share in cash (the “Transaction”). The Transaction represents a premium of approximately 20% to the 30-day volume-weighted average share price (VWAP) as of Friday, April 12, 2024, and approximately 29% to the 90-day VWAP as of the same date. |
$290 per share |
|
Apr-24 |
Prysmian Group (Italy) |
Aurubis (Germany) |
Contract |
Prysmian and Aurubis have entered a long-term contract for the supply of copper wire rod. According to the agreement, Aurubis will provide a significant and incremental year-over-year volume of copper wire rod. |
- |
|
Apr-24 |
Amphenol Corporation (US) |
- |
Product Development & Launch |
Amphenol TPC Wire & Cable, a leading supplier of high-performance wire, cable, connectors, and assemblies for harsh industrial environments, proudly announces the launch of its latest innovation: ATPC Medium Voltage Cables. |
- |
Source: Press releases & company websites
DEMAND/SUPPLY OVERVIEW
DEMAND COMMENTARY
- The global demand for Artificial Intelligence (AI) and high-performance computing (HPC) will continue to rise, with International Data Corporation (IDC) expecting the rise to grow by over 15% in 2025. Major application markets, ranging from cloud data centers to specific industry segments, are also expected to undergo upgrades, heralding a new boom for the semiconductor industry.
- In tandem with AI, cloud computing investments, particularly in hyperscale data centers, are expected to drive demand for cutting-edge semiconductor solutions. Chip manufacturers' competition is likely to intensify, spurring innovation in new energy-efficient designs, thus fuelling the need for more high-capacity memory systems, faster processing speeds, and the high data throughput required by AI applications.
- The semiconductor supply chain will generate new growth opportunities, spanning design, manufacturing, testing, and advanced packaging.
SUPPLY ANALYSIS
- Major cable suppliers report 70% to 85% manufacturing capacity utilization.
- Suppliers serving the AI, Telecommunication, and semiconductor sectors operate at 80% to 90% utilization.
- The book-to-bill ratio for major suppliers shows signs of demand recovery (between 1.0 to 1.2).
COPPER SUPPLY AND FUTURE OUTLOOK:
- The rapid acopper-intensive technologies such as urbanization, electrification, and the global push for decarbonization will drive high future demand. Wood Mackenzie's forecast shows that there will be an above-average 2.0% annual growth in global consumption between 2024 and 2034. Based on BHP's forecast, that could increase by up to 9% by 2050.
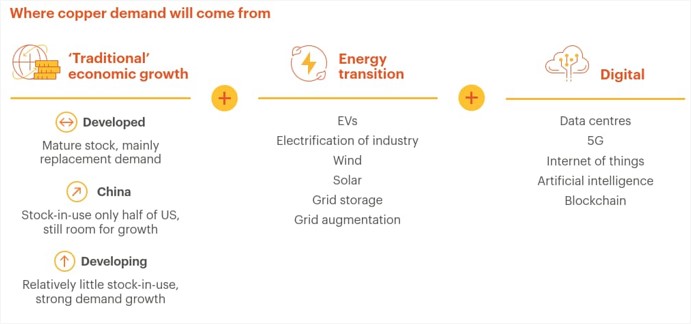
- Based on BHP analysis, recycled copper is expected to be an essential source of supply to meet the considerable copper demand growth over the next 30 years, as the most significant industry challenge today is to increase the mine supply volume substantially in less than half the time needed to build these mines, due to the global consumption growth. Another challenge is that mines already mature and likely need additional capital investment to replace or upgrade aging infrastructure or processing facilities.
PRICING SITUATION
- Copper prices have generally been rising in 2025, with a recent surge surpassing the USD 9,800 price.
- A mix of trade policy changes by the US government, geopolitical concerns, supply chain issues, and growing demand influence this price surge.
- Global trade tensions continue to affect copper prices. The ongoing trade war between the US and China has led to tariffs on various goods, including copper. Additionally, China has restricted exports of rare earth metals, which are vital for industries relying on copper, such as electronics and renewable energy. These export controls have intensified worries about potential shortages of copper, thereby driving further copper price increases.
- In the short term, copper prices are expected to face upward pressure due to strong demand, potential supply disruptions, and higher tariffs that may be implemented.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- The global demand for Artificial Intelligence (AI) and high-performance computing (HPC) is anticipated to increase by over 15% in 2025, according to the International Data Corporation (IDC). This growth in AI is expected to be reinforced by investments in cloud computing, especially in hyperscale data centres, which will further boost the need for advanced semiconductor solutions.
- The rapid adoption of copper-intensive technologies driven by urbanization, electrification, and a global push for decarbonization is projected to create significant future demand for copper. Recycled copper is expected to be crucial in meeting demand over the next 30 years.
- Copper prices have recently increased due to changes in US trade policy, global political instability, supply chain disruptions, and increased demand. International trade tensions also play a role in influencing copper prices.
- Short-term copper prices will likely rise due to robust demand, possible supply issues, and the potential implementation of increased tariffs.
- Long-term copper demand will likely be fuelled by growth in emerging technologies and infrastructure, like renewable energy and AI. However, the development of new copper mines is slow and expensive. This gap between consistently rising demand and limited supply growth will be a key factor pushing copper prices higher.
Back to Top
